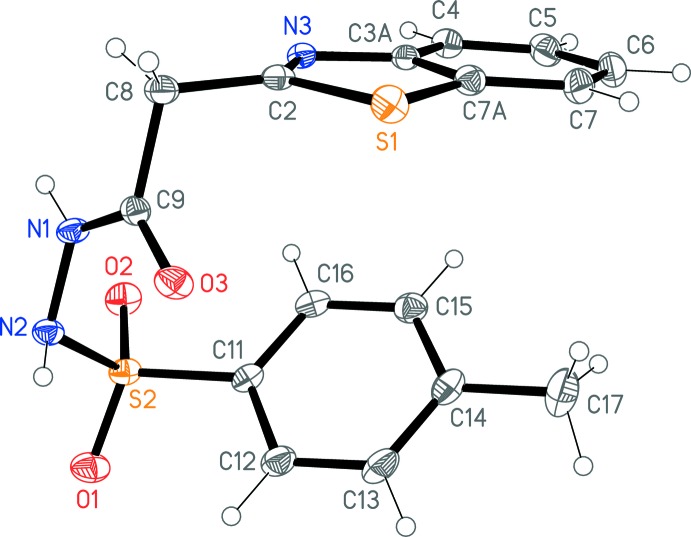
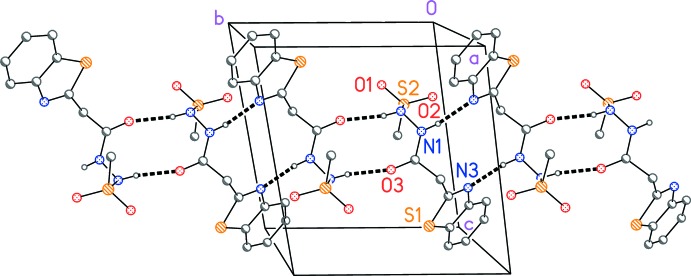
In the title compound, the hydrazide N atom bonded to the C=O group is planar, whereas that bonded to the SO2 group is pyramidally coordinated. The interplanar angle between the ring systems is 40.71 (3)°. In the crystal, molecules are connected by N—H⋯O=C and N—H⋯Nthiazole hydrogen bonds, forming ribbons parallel to the b axis.
Keywords: crystal structure, benzothiazole, hydrazide
Abstract
In the title compound, C16H15N3O3S2, the hydrazide N atom bonded to the C=O group is planar, whereas that bonded to the SO2 group is pyramidally coordinated. The interplanar angle between the ring systems is 40.71 (3)°. Molecules are connected into ribbons parallel to the b axis by two classical hydrogen bonds N—H⋯O=C and N—H⋯Nthiazole.
Chemical context
Benzothiazoles are versatile heterocyclic compounds with potential pharmaceutical applications (Elgemeie & Aal, 1986 ▸). Various benzothiazoles have been used as anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and analgesic agents and as laser dyes (Elgemeie, 1989 ▸). This has led to an increasing interest in benzothiazole derivatives in the area of drug design and discovery (Elgemeie et al., 2000 ▸). As a part of our research work on new syntheses of benzothiazoles as chemotherapeutic agents (Elgemeie et al., 2017 ▸), we have previously reported the synthesis of 2-arylbenzothiazoles that later found applications as anticancer agents and are presently in clinical use for various diseases (Elgemeie & Elghandour, 1990 ▸). We report here the new compound N′-(2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)acetyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonohydrazide (1), which was prepared by the reaction of 2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)acetohydrazide with p-toluenesulfonyl chloride in the presence of pyridine at room temperature. The structure of (1) was determined on the basis of its spectroscopic data and elemental analysis (see Experimental). In order to establish the structure of the product unambiguously, its crystal structure was determined.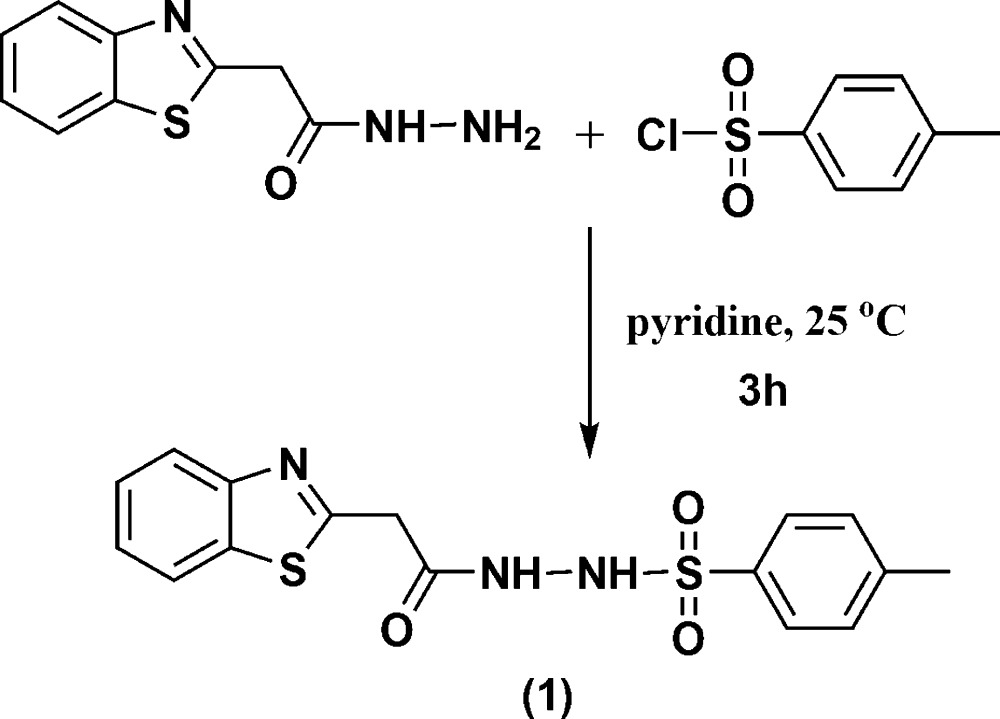
Structural commentary
The X-ray analysis confirms the exclusive presence of the form (1) in the solid state (Fig. 1 ▸). The molecular dimensions may be regarded as normal (Table 1 ▸); the torsion angles defining the conformation of the chain connecting the ring systems are also given in this Table. The bond lengths C2—S1 and C2—N3 in the heterocycle correspond well with the average values of 1.750 (15) and 1.200 (14) Å found in the Cambridge Structural Database (Version 5.38; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) for 375 examples of this ring system (unsubstituted benzo ring, carbon-substituted at C2). Nitrogen N1 displays a planar geometry, whereas N2 is pyramidal [they lie 0.014 (7) and 0.337 (8) Å, respectively, outside the plane of their substituents]. Hydrogen atom H01 is antiperiplanar to O3 and H02 to O2 across the N1—C9 and N2—S2 bonds, respectively. The interplanar angle between the ring systems is 40.71 (3)°.
Figure 1.
The structure of compound (1) in the crystal, with displacement ellipsoids at the 50% probability level.
Table 1. Selected geometric parameters (Å, °).
| S1—C2 | 1.7373 (11) | N1—N2 | 1.4069 (12) |
| C2—N3 | 1.2972 (14) | ||
| C7A—S1—C2 | 89.39 (5) | N1—N2—S2 | 112.94 (7) |
| C9—N1—N2 | 121.14 (9) | ||
| S1—C2—C8—C9 | −80.57 (10) | N2—S2—C11—C12 | 77.16 (9) |
| C2—C8—C9—N1 | −109.79 (10) | H01—N1—N2—H02 | −146.7 (17) |
| C8—C9—N1—N2 | 176.74 (9) | O3—C9—N1—H01 | 175.5 (13) |
| C9—N1—N2—S2 | −96.08 (10) | H02—N2—S2—O2 | 179.1 (12) |
| N1—N2—S2—C11 | 62.53 (8) |
Supramolecular features
Molecules are connected by two pairs of classical hydrogen bonds across inversion centres, to form ribbons parallel to the b axis (Table 2 ▸, Fig. 2 ▸). A C—H⋯O interaction connects the molecules by c-axis translation (not shown in the Figure), forming layers parallel to (100).
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H01⋯N3i | 0.866 (16) | 2.013 (16) | 2.8717 (13) | 171.0 (15) |
| N2—H02⋯O3ii | 0.845 (17) | 2.029 (17) | 2.8553 (12) | 165.7 (16) |
| C6—H6⋯O2iii | 0.95 | 2.54 | 3.4142 (15) | 154 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 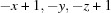 ; (ii)
; (ii) 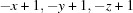 ; (iii)
; (iii) 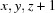 .
.
Figure 2.
Packing diagram of compound (1), viewed perpendicular to the bc plane. Hydrogen bonds are drawn as thick dashed lines. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonds have been omitted for clarity.
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Database (Version 5.38; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) for the substructure Ar—SO2—NH—NH—C(=O)—C gave six hits: EYOZIB, KUKYOG, XOVFEV, XOZDOG, YOTKAU and ZIVVUX.
Synthesis and crystallization
A solution of p-toluenesulfonyl chloride (1.90 g, 0.015 mol) in pyridine (10 ml) was added gradually to a stirred solution of 2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)acetohydrazide (2.07 g, 0.01 mol) in pyridine (10 ml) at 273 K. The reaction mixture was then stirred at room temperature for 3 h (TLC control). After the reaction was completed, the mixture was poured into ice-water with continuous stirring and neutralized with 1 N HCl solution to pH 7. The precipitate thus formed was filtered off, washed with water and recrystallized from ethanol to give colourless crystals (yield 85%; m.p. = 458 K). IR (KBr, cm−1): ν 3427 (NH), 3164 (Ar CH), 2929, 2858 (CH3, CH2), 1692 (C=O); 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d 6): δ 2.26 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.95 (s, 2H, CH2), 7.15 (d, J = 8 Hz, 2H, SO2C6H4), 7.44 (t, J = 8 Hz, 1H, benzothiazole H), 7.52 (t, J = 8 Hz, 1H, benzothiazole H), 7.62 (d, J = 8 Hz, 2H, SO2C6H4), 7.96 (d, J = 8 Hz, 1H, benzothiazole H), 8.07 (d, J = 8 Hz, 1H, benzothiazole H), 9.95 (s, 1H, NH), 10.52 (s, 1H, NH).
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. NH hydrogen atoms were refined freely. The methyl hydrogen atoms were not well defined and so were refined as a hexagon of half-occupied sites with C—H = 0.98 Å (AFIX 127). Other hydrogen atoms were included using a riding model starting from calculated positions (C—Haromatic = 0.95, C—Hmethylene 0.99 Å) with U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C).
Table 3. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C16H15N3O3S2 |
| M r | 361.43 |
| Crystal system, space group | Triclinic, P
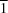
|
| Temperature (K) | 100 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 8.3436 (4), 9.7591 (5), 10.8815 (6) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 97.905 (4), 98.142 (4), 101.576 (4) |
| V (Å3) | 846.59 (8) |
| Z | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.33 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.5 × 0.4 × 0.2 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur Eos |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, 2015 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.952, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 45592, 5040, 4503 |
| R int | 0.032 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.726 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.031, 0.079, 1.05 |
| No. of reflections | 5040 |
| No. of parameters | 226 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.41, −0.42 |
Despite the slightly larger ellipsoid of the benzothiazol sulfur atom S1, there is no evidence for significant mixing (disorder) of the sites N3/S1.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017008738/hg5489sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017008738/hg5489Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017008738/hg5489Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1555516
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C16H15N3O3S2 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 361.43 | F(000) = 376 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.418 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.3436 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 13640 reflections |
| b = 9.7591 (5) Å | θ = 2.6–30.8° |
| c = 10.8815 (6) Å | µ = 0.33 mm−1 |
| α = 97.905 (4)° | T = 100 K |
| β = 98.142 (4)° | Tablet, colourless |
| γ = 101.576 (4)° | 0.5 × 0.4 × 0.2 mm |
| V = 846.59 (8) Å3 |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur Eos diffractometer | 5040 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed X-ray tube | 4503 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.032 |
| Detector resolution: 16.1419 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 31.1°, θmin = 2.5° |
| ω–scan | h = −12→11 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, 2015) | k = −14→14 |
| Tmin = 0.952, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −15→15 |
| 45592 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.031 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.079 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0354P)2 + 0.355P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 5040 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.008 |
| 226 parameters | Δρmax = 0.41 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.42 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. Least-squares planes (x,y,z in crystal coordinates) and deviations from them (* indicates atom used to define plane) 6.2088 (0.0012) x - 6.2111 (0.0022) y + 4.5043 (0.0028) z = 5.8783 (0.0023) * -0.0257 (0.0005) S1 * -0.0152 (0.0007) C2 * 0.0114 (0.0007) N3 * 0.0250 (0.0009) C3A * -0.0026 (0.0008) C4 * -0.0272 (0.0009) C5 * -0.0057 (0.0009) C6 * 0.0176 (0.0009) C7 * 0.0223 (0.0009) C7A Rms deviation of fitted atoms = 0.0190 7.8014 (0.0014) x - 0.3099 (0.0046) y + 1.6293 (0.0049) z = 2.0216 (0.0030) Angle to previous plane (with approximate esd) = 40.71 ( 0.03 ) * 0.0051 (0.0008) C11 * -0.0053 (0.0008) C12 * -0.0012 (0.0008) C13 * 0.0080 (0.0008) C14 * -0.0083 (0.0008) C15 * 0.0018 (0.0008) C16 Rms deviation of fitted atoms = 0.0057=========================================================== Least-squares planes (x,y,z in crystal coordinates) and deviations from them (* indicates atom used to define plane) 6.5691 (0.0357) x + 3.5739 (0.0897) y - 5.4501 (0.0327) z = 1.7544 (0.0236) * 0.0000 (0.0001) C9 * 0.0000 (0.0000) H01 * 0.0000 (0.0000) N2 -0.0139 (0.0071) N1 Rms deviation of fitted atoms = 0.0000 - 2.5491 (0.0143) x + 2.7622 (0.0942) y + 9.8695 (0.0419) z = 3.6614 (0.0102) Angle to previous plane (with approximate esd) = 66.25 ( 0.42 ) * 0.0000 (0.0000) S2 * 0.0000 (0.0000) H02 * 0.0000 (0.0000) N1 -0.3372 (0.0082) N2 Rms deviation of fitted atoms = 0.0000 |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| S1 | 0.57619 (4) | 0.26397 (3) | 0.86910 (3) | 0.01947 (7) | |
| C2 | 0.56817 (13) | 0.15226 (11) | 0.72845 (10) | 0.01492 (19) | |
| N3 | 0.46391 (11) | 0.03031 (9) | 0.70990 (9) | 0.01448 (17) | |
| C3A | 0.38014 (13) | 0.01774 (11) | 0.81106 (10) | 0.01466 (19) | |
| C4 | 0.25456 (14) | −0.09823 (12) | 0.81811 (11) | 0.0185 (2) | |
| H4 | 0.2221 | −0.1782 | 0.7522 | 0.022* | |
| C5 | 0.17867 (14) | −0.09401 (13) | 0.92308 (12) | 0.0223 (2) | |
| H5 | 0.0920 | −0.1714 | 0.9287 | 0.027* | |
| C6 | 0.22767 (15) | 0.02293 (14) | 1.02157 (11) | 0.0238 (2) | |
| H6 | 0.1749 | 0.0225 | 1.0934 | 0.029* | |
| C7 | 0.35125 (15) | 0.13868 (13) | 1.01602 (11) | 0.0223 (2) | |
| H7 | 0.3840 | 0.2178 | 1.0827 | 0.027* | |
| C7A | 0.42644 (13) | 0.13542 (12) | 0.90892 (10) | 0.0170 (2) | |
| C8 | 0.66708 (13) | 0.20010 (12) | 0.63115 (11) | 0.0172 (2) | |
| H8A | 0.6814 | 0.1169 | 0.5740 | 0.021* | |
| H8B | 0.7784 | 0.2573 | 0.6723 | 0.021* | |
| C9 | 0.57197 (12) | 0.28914 (11) | 0.55711 (10) | 0.01401 (19) | |
| N1 | 0.50433 (11) | 0.22734 (9) | 0.43761 (9) | 0.01544 (17) | |
| H01 | 0.519 (2) | 0.1475 (18) | 0.4007 (15) | 0.027 (4)* | |
| N2 | 0.40574 (11) | 0.29335 (10) | 0.35950 (9) | 0.01529 (17) | |
| H02 | 0.434 (2) | 0.3829 (18) | 0.3759 (15) | 0.029 (4)* | |
| O1 | 0.12667 (11) | 0.31786 (9) | 0.27597 (8) | 0.02335 (18) | |
| S2 | 0.20281 (3) | 0.23646 (3) | 0.35718 (2) | 0.01622 (7) | |
| O2 | 0.16863 (11) | 0.08446 (8) | 0.32664 (8) | 0.02168 (17) | |
| O3 | 0.55748 (10) | 0.40588 (8) | 0.60522 (8) | 0.01870 (16) | |
| C11 | 0.16430 (13) | 0.28095 (11) | 0.51069 (11) | 0.0163 (2) | |
| C12 | 0.15942 (14) | 0.42100 (12) | 0.55429 (12) | 0.0203 (2) | |
| H12 | 0.1721 | 0.4901 | 0.5007 | 0.024* | |
| C13 | 0.13587 (15) | 0.45785 (12) | 0.67661 (12) | 0.0233 (2) | |
| H13 | 0.1329 | 0.5532 | 0.7069 | 0.028* | |
| C14 | 0.11639 (14) | 0.35757 (13) | 0.75641 (11) | 0.0208 (2) | |
| C15 | 0.11840 (13) | 0.21746 (12) | 0.71012 (11) | 0.0196 (2) | |
| H15 | 0.1023 | 0.1477 | 0.7628 | 0.023* | |
| C16 | 0.14367 (13) | 0.17876 (11) | 0.58797 (11) | 0.0176 (2) | |
| H16 | 0.1468 | 0.0835 | 0.5575 | 0.021* | |
| C17 | 0.09014 (19) | 0.39948 (16) | 0.88922 (13) | 0.0327 (3) | |
| H17A | 0.0428 | 0.4838 | 0.8946 | 0.049* | 0.50 |
| H17B | 0.1969 | 0.4207 | 0.9468 | 0.049* | 0.50 |
| H17C | 0.0137 | 0.3212 | 0.9127 | 0.049* | 0.50 |
| H17D | 0.1261 | 0.3334 | 0.9415 | 0.049* | 0.50 |
| H17E | −0.0280 | 0.3964 | 0.8893 | 0.049* | 0.50 |
| H17F | 0.1552 | 0.4960 | 0.9233 | 0.049* | 0.50 |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.02314 (14) | 0.01447 (12) | 0.01758 (14) | 0.00166 (10) | 0.00006 (10) | −0.00091 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0156 (4) | 0.0138 (4) | 0.0160 (5) | 0.0062 (4) | 0.0003 (4) | 0.0028 (4) |
| N3 | 0.0162 (4) | 0.0134 (4) | 0.0152 (4) | 0.0061 (3) | 0.0028 (3) | 0.0029 (3) |
| C3A | 0.0154 (4) | 0.0149 (4) | 0.0144 (5) | 0.0061 (4) | 0.0009 (4) | 0.0027 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0177 (5) | 0.0180 (5) | 0.0193 (5) | 0.0038 (4) | 0.0019 (4) | 0.0039 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0174 (5) | 0.0285 (6) | 0.0225 (6) | 0.0043 (4) | 0.0042 (4) | 0.0101 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0215 (5) | 0.0366 (7) | 0.0168 (5) | 0.0109 (5) | 0.0054 (4) | 0.0074 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0249 (6) | 0.0279 (6) | 0.0144 (5) | 0.0104 (5) | 0.0017 (4) | 0.0003 (4) |
| C7A | 0.0178 (5) | 0.0173 (5) | 0.0155 (5) | 0.0053 (4) | 0.0003 (4) | 0.0016 (4) |
| C8 | 0.0150 (5) | 0.0175 (5) | 0.0207 (5) | 0.0054 (4) | 0.0028 (4) | 0.0064 (4) |
| C9 | 0.0130 (4) | 0.0125 (4) | 0.0169 (5) | 0.0018 (3) | 0.0033 (4) | 0.0043 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0184 (4) | 0.0119 (4) | 0.0170 (4) | 0.0071 (3) | 0.0025 (3) | 0.0012 (3) |
| N2 | 0.0186 (4) | 0.0122 (4) | 0.0155 (4) | 0.0053 (3) | 0.0018 (3) | 0.0020 (3) |
| O1 | 0.0244 (4) | 0.0237 (4) | 0.0210 (4) | 0.0090 (3) | −0.0038 (3) | 0.0031 (3) |
| S2 | 0.01722 (12) | 0.01375 (12) | 0.01595 (13) | 0.00428 (9) | −0.00088 (9) | −0.00068 (9) |
| O2 | 0.0247 (4) | 0.0139 (4) | 0.0223 (4) | 0.0018 (3) | 0.0004 (3) | −0.0036 (3) |
| O3 | 0.0264 (4) | 0.0110 (3) | 0.0175 (4) | 0.0041 (3) | 0.0012 (3) | 0.0010 (3) |
| C11 | 0.0134 (4) | 0.0156 (5) | 0.0194 (5) | 0.0047 (4) | 0.0020 (4) | −0.0002 (4) |
| C12 | 0.0219 (5) | 0.0151 (5) | 0.0258 (6) | 0.0065 (4) | 0.0074 (4) | 0.0030 (4) |
| C13 | 0.0247 (6) | 0.0163 (5) | 0.0298 (6) | 0.0070 (4) | 0.0101 (5) | −0.0014 (4) |
| C14 | 0.0162 (5) | 0.0230 (5) | 0.0235 (6) | 0.0056 (4) | 0.0060 (4) | −0.0001 (4) |
| C15 | 0.0159 (5) | 0.0206 (5) | 0.0229 (6) | 0.0053 (4) | 0.0031 (4) | 0.0049 (4) |
| C16 | 0.0149 (5) | 0.0142 (5) | 0.0228 (5) | 0.0046 (4) | 0.0006 (4) | 0.0007 (4) |
| C17 | 0.0379 (7) | 0.0349 (7) | 0.0264 (7) | 0.0088 (6) | 0.0143 (6) | −0.0010 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C7A | 1.7310 (12) | C13—C14 | 1.3957 (18) |
| S1—C2 | 1.7373 (11) | C14—C15 | 1.3949 (16) |
| C2—N3 | 1.2972 (14) | C14—C17 | 1.5056 (17) |
| C2—C8 | 1.4996 (15) | C15—C16 | 1.3882 (16) |
| N3—C3A | 1.3914 (14) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| C3A—C4 | 1.3983 (15) | C5—H5 | 0.9500 |
| C3A—C7A | 1.4040 (15) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| C4—C5 | 1.3819 (16) | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| C5—C6 | 1.4037 (18) | C8—H8A | 0.9900 |
| C6—C7 | 1.3826 (18) | C8—H8B | 0.9900 |
| C7—C7A | 1.3992 (16) | N1—H01 | 0.866 (16) |
| C8—C9 | 1.5238 (14) | N2—H02 | 0.845 (17) |
| C9—O3 | 1.2231 (13) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C9—N1 | 1.3464 (14) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| N1—N2 | 1.4069 (12) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| N2—S2 | 1.6680 (10) | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| O1—S2 | 1.4325 (8) | C17—H17A | 0.9800 |
| S2—O2 | 1.4353 (8) | C17—H17B | 0.9800 |
| S2—C11 | 1.7580 (11) | C17—H17C | 0.9800 |
| C11—C16 | 1.3907 (16) | C17—H17D | 0.9800 |
| C11—C12 | 1.3944 (15) | C17—H17E | 0.9800 |
| C12—C13 | 1.3821 (17) | C17—H17F | 0.9800 |
| C7A—S1—C2 | 89.39 (5) | C5—C6—H6 | 119.4 |
| N3—C2—C8 | 122.61 (10) | C6—C7—H7 | 121.1 |
| N3—C2—S1 | 115.98 (8) | C7A—C7—H7 | 121.1 |
| C8—C2—S1 | 121.25 (8) | C2—C8—H8A | 110.2 |
| C2—N3—C3A | 110.63 (9) | C9—C8—H8A | 110.2 |
| N3—C3A—C4 | 124.96 (10) | C2—C8—H8B | 110.2 |
| N3—C3A—C7A | 114.86 (10) | C9—C8—H8B | 110.2 |
| C4—C3A—C7A | 120.15 (10) | H8A—C8—H8B | 108.5 |
| C5—C4—C3A | 118.54 (11) | C9—N1—H01 | 124.9 (11) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.98 (11) | N2—N1—H01 | 113.9 (11) |
| C7—C6—C5 | 121.26 (11) | N1—N2—H02 | 113.1 (11) |
| C6—C7—C7A | 117.79 (11) | S2—N2—H02 | 111.0 (11) |
| C7—C7A—C3A | 121.26 (11) | C13—C12—H12 | 120.5 |
| C7—C7A—S1 | 129.57 (9) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.5 |
| C3A—C7A—S1 | 109.14 (8) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.4 |
| C2—C8—C9 | 107.51 (8) | C14—C13—H13 | 119.4 |
| O3—C9—N1 | 123.90 (10) | C16—C15—H15 | 119.6 |
| O3—C9—C8 | 121.56 (10) | C14—C15—H15 | 119.6 |
| N1—C9—C8 | 114.53 (9) | C15—C16—H16 | 120.4 |
| C9—N1—N2 | 121.14 (9) | C11—C16—H16 | 120.4 |
| N1—N2—S2 | 112.94 (7) | C14—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| O1—S2—O2 | 120.92 (5) | C14—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| O1—S2—N2 | 103.98 (5) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| O2—S2—N2 | 106.20 (5) | C14—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| O1—S2—C11 | 109.49 (5) | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| O2—S2—C11 | 107.66 (5) | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| N2—S2—C11 | 107.89 (5) | C14—C17—H17D | 109.5 |
| C16—C11—C12 | 120.86 (10) | H17A—C17—H17D | 141.1 |
| C16—C11—S2 | 120.35 (8) | H17B—C17—H17D | 56.3 |
| C12—C11—S2 | 118.76 (9) | H17C—C17—H17D | 56.3 |
| C13—C12—C11 | 119.02 (11) | C14—C17—H17E | 109.5 |
| C12—C13—C14 | 121.22 (10) | H17A—C17—H17E | 56.3 |
| C15—C14—C13 | 118.82 (11) | H17B—C17—H17E | 141.1 |
| C15—C14—C17 | 120.67 (12) | H17C—C17—H17E | 56.3 |
| C13—C14—C17 | 120.50 (11) | H17D—C17—H17E | 109.5 |
| C16—C15—C14 | 120.77 (11) | C14—C17—H17F | 109.5 |
| C15—C16—C11 | 119.28 (10) | H17A—C17—H17F | 56.3 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.7 | H17B—C17—H17F | 56.3 |
| C3A—C4—H4 | 120.7 | H17C—C17—H17F | 141.1 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.5 | H17D—C17—H17F | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.5 | H17E—C17—H17F | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 119.4 | ||
| C7A—S1—C2—N3 | 0.45 (8) | C8—C9—N1—N2 | 176.74 (9) |
| C7A—S1—C2—C8 | 175.95 (9) | C9—N1—N2—S2 | −96.08 (10) |
| C8—C2—N3—C3A | −175.40 (9) | N1—N2—S2—O1 | 178.74 (7) |
| S1—C2—N3—C3A | 0.03 (11) | N1—N2—S2—O2 | −52.67 (8) |
| C2—N3—C3A—C4 | 177.18 (10) | N1—N2—S2—C11 | 62.53 (8) |
| C2—N3—C3A—C7A | −0.66 (13) | O1—S2—C11—C16 | 146.33 (9) |
| N3—C3A—C4—C5 | −177.98 (10) | O2—S2—C11—C16 | 13.11 (10) |
| C7A—C3A—C4—C5 | −0.24 (16) | N2—S2—C11—C16 | −101.12 (9) |
| C3A—C4—C5—C6 | −0.91 (17) | O1—S2—C11—C12 | −35.40 (10) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 1.12 (18) | O2—S2—C11—C12 | −168.61 (9) |
| C5—C6—C7—C7A | −0.15 (17) | N2—S2—C11—C12 | 77.16 (9) |
| C6—C7—C7A—C3A | −1.00 (16) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | 0.85 (17) |
| C6—C7—C7A—S1 | 176.79 (9) | S2—C11—C12—C13 | −177.42 (9) |
| N3—C3A—C7A—C7 | 179.17 (10) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.25 (18) |
| C4—C3A—C7A—C7 | 1.22 (16) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −1.00 (18) |
| N3—C3A—C7A—S1 | 0.98 (11) | C12—C13—C14—C17 | −179.74 (12) |
| C4—C3A—C7A—S1 | −176.98 (8) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 1.68 (17) |
| C2—S1—C7A—C7 | −178.77 (11) | C17—C14—C15—C16 | −179.58 (11) |
| C2—S1—C7A—C3A | −0.76 (8) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | −1.10 (16) |
| N3—C2—C8—C9 | 94.63 (11) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | −0.18 (16) |
| S1—C2—C8—C9 | −80.57 (10) | S2—C11—C16—C15 | 178.06 (8) |
| C2—C8—C9—O3 | 68.95 (13) | H01—N1—N2—H02 | −146.7 (17) |
| C2—C8—C9—N1 | −109.79 (10) | O3—C9—N1—H01 | 175.5 (13) |
| O3—C9—N1—N2 | −1.96 (16) | H02—N2—S2—O2 | 179.1 (12) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H01···N3i | 0.866 (16) | 2.013 (16) | 2.8717 (13) | 171.0 (15) |
| N2—H02···O3ii | 0.845 (17) | 2.029 (17) | 2.8553 (12) | 165.7 (16) |
| C6—H6···O2iii | 0.95 | 2.54 | 3.4142 (15) | 154 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) x, y, z+1.
References
- Elgemeie, G. H. (1989). Chem. Ind. 19, 653–654.
- Elgemeie, G. H. & Aal, F. A. (1986). Heterocycles, 24, 349–353.
- Elgemeie, G. H. & Elghandour, A. H. (1990). Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon, 48, 281–284.
- Elgemeie, G. H., Salah, A. M., Abbas, N. S., Hussein, H. A. & Mohamed, R. A. (2017). Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids, 36, 213–223. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Elgemeie, G. H., Shams, H. Z., Elkholy, Y. M. & Abbas, N. S. (2000). Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon, 165, 265–272.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Rigaku OD (2015). CrysAlis PRO. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, Yarnton, England.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Siemens (1994). XP. Siemens Analytical X–Ray Instruments, Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017008738/hg5489sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017008738/hg5489Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017008738/hg5489Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1555516
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report