Abstract
Eukaryotic cells preserve genome integrity upon DNA damage by activating a signaling network that promotes DNA repair and controls cell cycle progression. One of the most severe DNA damage is the DNA double-strand break (DSB), whose 5΄ ends can be nucleolitically resected by multiple nucleases to create 3΄-ended single-stranded DNA tails that trigger DSB repair by homologous recombination. Here, we identify the Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA binding protein Npl3 as a new player in DSB resection. Npl3 is related to both the metazoan serine-arginine-rich and the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleo-proteins. NPL3 deletion impairs the generation of long ssDNA tails at the DSB ends, whereas it does not exacerbate the resection defect of exo1Δ cells. Furthermore, either the lack of Npl3 or the inactivation of its RNA-binding domains causes decrease of the exonuclease Exo1 protein levels as well as generation of unusual and extended EXO1 RNA species. These findings, together with the observation that EXO1 overexpression partially suppresses the resection defect of npl3Δ cells, indicate that Npl3 participates in DSB resection by promoting the proper biogenesis of EXO1 mRNA.
INTRODUCTION
Eukaryotic cells deal with DNA damage through a multifaceted cellular response, known as DNA damage response (DDR), which promotes DNA repair and couples it with cell cycle progression (1). DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are among the most severe lesions. DSBs can be repaired by either non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ), which directly rejoins together the two broken ends, or homologous recombination (HR) that uses intact homologous duplex DNA sequences as a template for accurate repair (2).
HR is promoted by the nucleolytic degradation of the 5΄ DSB ends (a process referred to as resection) to yield 3΄ single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) tails that invade the homologous duplex and prime reparative DNA synthesis (2). DSB resection is a two-step process that involves multiple nucleases and helicases. A protein complex, which is called MRX (Mre11–Rad50–Xrs2) in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and MRN (Mre11–Rad50–Nbs1) in mammals, initiates resection together with the Sae2/CtIP protein by catalyzing an endonucleolytic cleavage of the 5΄-terminated DNA strands. This cleavage creates a substrate for two partially overlapping pathways, which depend on the nucleases Exo1 and Dna2, respectively, and promote the generation of long ssDNA tails (reviewed in 3,4). While Exo1 is a 5΄-3΄ exonuclease capable of efficiently degrading the 5΄ end on duplex DNA, the endonuclease Dna2 requires the helicase activity of Sgs1 (orthologue of mammalian BLM) to efficiently remove small fragments from DNA ends (3,4).
DSB end degradation is tightly controlled by both positive and negative regulators, which tune the action of specific resection factors. While the cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk1 in yeast)-Clb complexes stimulate the activities of both Sae2 and Dna2, the Ku complex and Rad9 inhibit the action of Exo1 and Sgs1-Dna2, respectively (3–5). Exo1 action is also inhibited through phosphorylation by the checkpoint kinase Rad53 (6) and regulated by the ssDNA-binding complex Replication Protein A (RPA), which promotes Exo1 action in vivo, and limits Exo1-dependent degradation by increasing Exo1 turnover at DNA ends in vitro (7,8). Given the efficiency of Exo1 exonuclease (8), these multiple controls on its action can be important to prevent excessive DNA degradation that could lead to genome instability.
DSB repair is coupled with cell cycle progression by a checkpoint pathway, whose key players are the protein kinases Mec1 and Tel1, orthologs of mammalian ATR and ATM, respectively (1). While Tel1 is recruited to blunt or minimally processed DNA ends through interaction with MRX (9), Mec1 and its interactor Ddc2 (ATRIP in mammals) are activated by extended RPA-coated ssDNA that is produced by resection (10). Once activated, Mec1 and Tel1 propagate the checkpoint signal to the effector kinases Rad53 and Chk1 (Chk2 and Chk1 in mammals, respectively), whose activation requires the adaptor Rad9 (53BP1 in mammals) and leads to temporarily arrest cell cycle progression (1).
Increasing evidence suggests the existence of intimate connections between RNA metabolism, DDR and genome integrity (11). Pre-mRNA molecules are co-transcriptionally processed by the addition of both a 5΄-methylguanosine cap and a 3΄ poly(A) tail, and eventually spliced before they are exported to the cytoplasm and translated. These events are mediated by RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), most of which belong to the conserved protein families of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleo-proteins (hnRNPs) and mammalian serine-arginine-rich (SR) proteins (11). RBPs also protect mRNAs from degradation and contribute to quality control systems that recognize and target to degradation improperly processed mRNAs (12,13). In eukaryotes, mRNAs are mainly degraded either by the exosome multi-subunit complex, which includes both endo- and 3΄-5΄ exoribonuclease activities, or by the Xrn family of 5΄-3΄ exoribonucleases (13,14).
In both yeast and mammals, several RBPs participate to the DDR and the stress response. Many of these RBPs bind to nascent transcripts and prevent transcription-associated genome instability by packaging pre-mRNAs into ribonucleoprotein particles. This packaging limits the generation of DNA:RNA hybrids, which could induce replication stress and DNA damage by interfering with the progression of DNA replication forks (reviewed in 11,15). Factors involved in RNA metabolism play also more direct roles in the DDR by either recruiting DDR proteins to the site of damage or regulating the expression of repair and checkpoint genes at different levels (11). Finally, the conserved nonsense-mediated decay (NMD) pathway was recently found to limit HR in S. cerevisiae undamaged cells by controlling the transcript and protein levels of HR factors (16).
One of the most abundant S. cerevisiae RBPs is Npl3, which shares structural homologies with both SR and hnRNPs protein families, as it possesses two conserved RNA-recognition motifs (RRMs) and a serine- and arginine-rich C-terminal domain (17). Npl3 is recruited to transcribed regions through the interaction with RNA polymerase II (18,19), and participates in pre-mRNA processing and packaging as well as in mRNA export and translation (12). Npl3 accumulates at the 3΄ end of transcribed genes (20) and seems to play a role in transcription termination, although this role is somehow controversial. In fact, studies with reporter constructs indicated that Npl3 prevents both early transcription termination and recognition of polyadenylation cryptic sites by competing with polyadenylation/termination factors (18,21,22). However, recent genome-wide analyses showed significant termination defects in the absence of Npl3, suggesting that Npl3 promotes transcription termination (23).
Similar to other RBPs, Npl3 prevents transcription-associated genome instability by limiting the accumulation of DNA:RNA hybrids (20). Interestingly, several findings suggest additional Npl3 functions in the DDR. In particular, cells lacking Npl3 are highly sensitive to DSB-inducing agents (20) and to the expression of the EcoRI endonuclease (24). Furthermore, Npl3 shows negative genetic interactions with the MRX complex (25), and Npl3 inactivation increases the sensitivity of rad52 or ku mutants to genotoxic agents (20). Finally, checkpoint-dependent Npl3 phosphorylation after methyl methanesulfonate (MMS) treatment suggests that Npl3 activity may be regulated in response to DNA damage (26).
Here, we show that Npl3 promotes both checkpoint activation and the generation of long ssDNA tails at the DSB ends. These functions are at least partially linked to the regulation of Exo1 abundance through the control of EXO1 mRNA biogenesis. Altogether, our results identify a new function of Npl3 in the response to DSBs and contribute to define the role of this multifunctional RBP in preserving genome stability.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Yeast strains and media
Strain genotypes are listed in Supplementary Table S1. All the strains are derivatives of JKM139 strain, which was kindly provided by J. Haber (Brandeis University, Waltham, MA, USA). The centromeric plasmid carrying the tetO-RNH1 allele (27) and the control vector were kindly provided by A. Aguilera (University of Seville, Sevilla, Spain); the EXO1 2μ plasmid (28) and the control vector by E. Alani (Cornell University, New York, NY, USA); the control vector and the centromeric plasmids carrying the wild type NPL3 or the mutant alleles npl3-F160L, npl3-SNK (L225S, G241N, E244K), and npl3-LSNK (F160L, L225S, G241N, E244K) (29) by J. Lee-Soety (Saint Joseph's University, Philadelphia, PA, USA). Gene deletions and gene tagging were obtained by one-step PCR methods. Cells were grown in YEP medium (1% yeast extract, 2% peptone) supplemented with 2% glucose (YEPD) or 2% raffinose (YEPR). 3% galactose was added to YEPR-growing cells to induce HO expression (YEPRG). The HO-cut efficiency was evaluated after quantitative PCR (qPCR) with a primer pair that overlaps the HO cut site and gives rise a product only when the locus is uncut, and primers at the TRP3 locus as a control. The cleavage efficiency was calculated by dividing the difference between the values of the HO-specific product calculated with the ΔCt method before and two hours after galactose addition to the value of the HO-specific product before induction.
DSB resection
DSB end resection was analyzed on alkaline agarose gels by using a single-stranded RNA probe complementary to the unresected DSB strand as described in (30). This probe was obtained by in vitro transcription using Promega Riboprobe System-T7 and plasmid pML514 containing a 900-bp fragment of the MAT locus (coordinates 200 870 to 201 587 on chromosome III) as a template. Quantitative analysis of DSB resection was performed by calculating the ratio of band intensities for ssDNA to total amount of DSB products. The resection efficiency was normalized with respect to the HO cleavage efficiency by subtracting the value of the uncut band from the total amount of DSB products for each time point.
Quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR (qRT-PCR)
Total RNA was prepared with the Bio-Rad Aurum total RNA mini kit. First strand cDNA was synthetized with the Bio-Rad iScript™ cDNA Synthesis Kit. After qRT-PCR on a MiniOpticon Real-time PCR system (Bio-Rad), EXO1 RNA levels were quantified using the ΔΔCt method and normalized to ALG9 RNA levels. Primer sequences are listed in Supplementary Table S2.
Northern blot
Total RNA was resolved on a 1% agarose gel in formaldehyde gel running buffer (2.2 M formaldehyde, 20 mM MOPS pH 7.0, 8 mM sodium acetate, 1 mM EDTA pH 8.0). The gel was stained with ethidium bromide to detect 18S and 25S ribosomal RNA and then transferred on a nitrocellulose filter. A BamHI–BglII DNA fragment (1437 bp) internal to the EXO1 coding sequence (+628 to + 2065 from the ATG initiation codon) was extracted from pML546 plasmid, labeled with [α-32P]-dATP by random priming, and used as a probe. pML546 was constructed by inserting a 3109 bp XhoI–NotI blunt fragment containing the EXO1 gene from pEAm67 2μ plasmid (28) into the SalI-SmaI YEpLac195 vector (31).
5΄ rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE)
5 μg of total RNA was subjected to reverse transcription using SuperScript™ II (Invitrogen) and an EXO1 specific primer to obtain the EXO1 5΄ partial cDNA ends. After RNA degradation with RNaseH1 and poly(A) tailing of the ss-cDNA, a second DNA strand was synthetized starting from a QT (QTOTAL) primer containing both an oligo-dT sequence capable of annealing with the appended poly(A) tail and a unique sequence. The resulting cDNA was used as a template for two subsequent rounds of amplification using primers that anneal to the QT sequence and EXO1 specific primers. The PCR products were run on 1.5% agarose gels and visualized with ethidium bromide. Primer sequences are listed in Supplementary Table S2.
ChIP analysis
ChIP analysis was performed as previously described (32). Chromatin extracts from both NPL3-HA and NPL3 strains were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibodies. Input and immunoprecipitated DNA were purified and analyzed by qPCR. Data are expressed as fold enrichment at the HO-induced DSB over that at the non-cleaved ARO1 locus, after normalization of ChIP signals to the corresponding input for each time point. Fold enrichment was then normalized to the efficiency of DSB induction.
Other techniques
Flow cytometric DNA analysis was determined on a Becton-Dickinson FACScan. Rad53 was detected by using anti-Rad53 polyclonal antibodies (AB104232) from Abcam. Anti-Rfa2 and anti-Rad9 polyclonal antibodies were kindly provided by B. Stillman (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA) and N. Lowndes (University of Ireland, Galway, Ireland), respectively. Quantitative analysis of phosphorylation normalized to the cut efficiency was performed by calculating the ratio of band intensities for slowly-migrating bands to the total amount of protein, and dividing the obtained values by the cleavage efficiency evaluated by qPCR.
RESULTS
Npl3 promotes the activation of a Mec1-dependent checkpoint
The hypersensitivity of npl3 mutant cells to DSB-inducing agents (20,24) suggests that Npl3 is involved in the response to DSBs. To explore further this hypothesis, we asked whether the lack of Npl3 affects the checkpoint response to a single DSB that is generated by the HO endonuclease, whose gene is expressed from a galactose-inducible promoter in JKM139 haploid cells (33). Galactose addition to these cells induces the generation at the MAT locus of a single DSB that cannot be repaired by HR because the homologous donor loci HML and HMR are deleted (33). This HO-induced DSB triggers a Mec1-dependent checkpoint that causes a G2/M cell cycle arrest, as well as the phosphorylation of both the checkpoint effector kinase Rad53 and the Mec1 interactor Ddc2 (34–36). We analyzed cell cycle progression and phosphorylation of Rad53 and Ddc2 after the induction of a single irreparable DSB in wild type and npl3Δ cells carrying a fully functional Ddc2-HA tagged variant. The cleavage efficiency was evaluated by quantitative PCR (qPCR) at the HO cut site 2 h after galactose addition. Cells carrying the deletion of MEC1 and kept viable by the lack of the ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor Sml1 were used as a control (37).
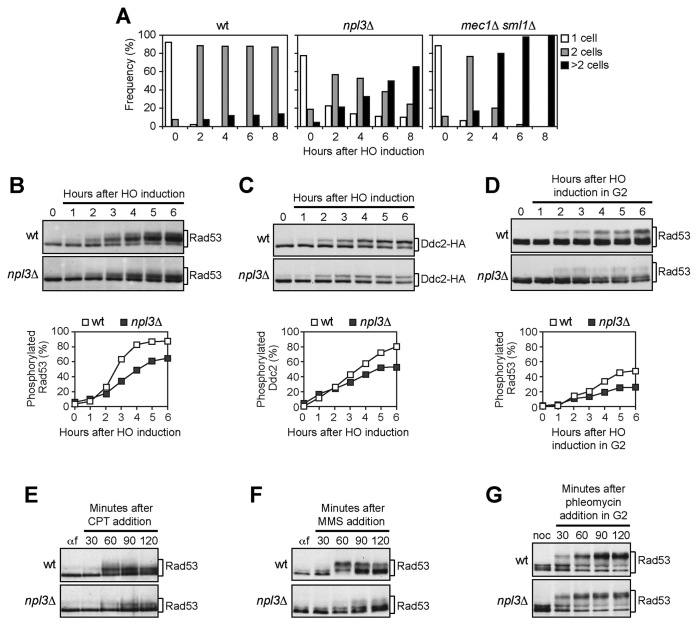
When G1-arrested cell cultures were spotted on galactose-containing plates, wild type cells arrested as large-budded cells for at least 8 hours after HO induction, while mec1Δ sml1Δ cells, which are unable to activate the checkpoint, formed microcolonies with more than two cells within 4–6 hours (Figure 1A). Although the cleavage efficiency was reduced to 82% in npl3Δ cells compared to wild type (95%), 60% of npl3Δ cells formed microcolonies 8 hours after HO induction, when >80% wild type cells were still arrested (Figure 1A), indicating that Npl3 contributes to arrest the cell cycle in response to an irreparable DSB.
Figure 1.
The lack of NPL3 impairs Mec1 signaling activity. (A) YEPR G1-arrested cell cultures of JKM139 derivative strains were plated on galactose-containing plates to induce HO expression (time zero). At the indicated time points, 200 cells for each strain were analyzed to determine the frequency of unbudded cells, large budded cells and microcolonies with more than two cells. (B and C) Exponentially growing YEPR cell cultures expressing a fully functional Ddc2-HA protein were transferred to YEPRG (time zero). Protein extracts prepared at the indicated time points were subjected to western blot with anti-Rad53 (B) or anti-HA (C) antibodies. Quantitative analysis of Rad53 and Ddc2 phosphorylation was performed by calculating the ratio of band intensities for slowly-migrating bands to total amount of protein, and dividing the obtained values by the HO cleavage efficiency. Cut efficiency was evaluated as the difference in the normalized amount of qPCR products obtained with a primer pair that amplifies only the uncut MAT locus before and 2 h after galactose addition. (D) YEPR G2-arrested cell cultures were transferred in YEPRG (time zero) in the presence of nocodazole. Protein extracts were analyzed by western blot with anti-Rad53 antibodies. Quantitative analysis of Rad53 phosphorylation was performed as in (B). (E and F) YEPD G1-arrested cell cultures were released in fresh medium containing camptothecin (CPT) (50 μM) (E) or methyl methanesulfonate (MMS) (0,02%) (F). Rad53 phosphorylation was monitored by western blot with anti-Rad53 antibodies. (G) Phleomycin (15 μg/ml) was added to YEPD G2-arrested cell cultures kept arrested in G2. Protein extracts were subjected to western blot with anti-Rad53 antibodies.
Rad53 and Ddc2 phosphorylation, which causes decreased electrophoretic mobility of the proteins, was analyzed by western blot of comparable amounts of protein extracts (Supplementary Figure S1) after galactose addition to cell cultures exponentially growing in raffinose. As the HO cleavage efficiency was reduced in npl3Δ cells compared to wild type (85% versus 97%), we also performed quantitative analyses of Rad53 and Ddc2 phosphorylation by calculating the ratio of slowly-migrating phosphorylated forms to total protein amount, and normalizing this value with respect to the efficiency of DSB formation evaluated by qPCR. Slowly-migrating Rad53 bands appeared 2–3 hours after HO induction and then became prevalent in wild type extracts (Figure 1B). Conversely, the unphosphorylated Rad53 species remained abundant until the end of the experiment in npl3Δ extracts although some slowly-migrating bands appeared 3–4 hours after HO induction (Figure 1B), indicating that Npl3 promotes the HO-induced Rad53 phosphorylation. Npl3 enhances also the phosphorylation of the Mec1-specific target Ddc2, as the amount of phosphorylated Ddc2 was lower in npl3Δ extracts than in wild type after HO induction (Figure 1C). Altogether, these results indicate that Npl3 promotes the activation of the Mec1-dependent checkpoint in response to a single irreparable DSB.
As cells lacking Npl3 showed growth defects (20), we asked whether their checkpoint defect could be ascribed to alterations in cell cycle progression. This was not the case, because Rad53 phosphorylation was defective in npl3Δ cells even when the HO cut was induced in cells arrested in G2 with nocodazole and kept in G2 throughout the experiment (Figure 1D).
To test whether Npl3 participates to checkpoint activation specifically after a single HO-induced DSB, we analyzed Rad53 phosphorylation in wild type and npl3Δ cells treated with different genotoxic agents. Cell cultures were arrested in G1 with α-factor and released in the presence of the topoisomerase poison camptothecin (CPT) or the alkylating agent MMS. As expected (38), Rad53 phosphorylation was slightly induced by CPT in wild type cells (Figure 1E). However, this phosphorylation was further reduced in npl3Δ cells (Figure 1E). Similarly, Rad53 was less phosphorylated in MMS-treated npl3Δ cells than in wild type (Figure 1F). Conversely, Rad53 was efficiently phosphorylated in both wild type and npl3Δ cells arrested in G2 and treated with the DSB-inducing drug phleomycin (Figure 1G). As checkpoint activation in all these conditions depends specifically on Mec1 (38,39), these results suggest that Npl3 is not directly required to activate Mec1 but rather to generate specific signals that activate Mec1.
Npl3 promotes the generation of ssDNA at DSBs
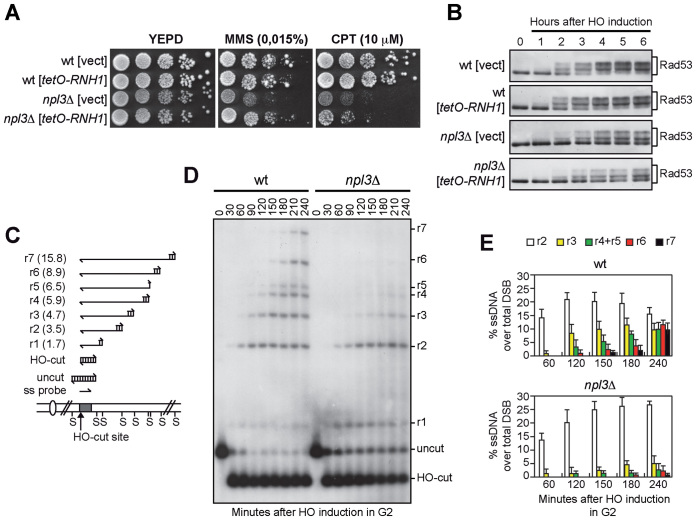
Mec1 activation requires the formation of RPA-coated ssDNA, which is generated by the 5΄-3΄ nucleolytic degradation of the DSB ends (10). In both Schizosaccharomyces pombe and human cells, RPA loading at DSB ends was found to be inhibited by the presence of DNA:RNA hybrids (40,41). As Npl3 counteracts the accumulation of DNA:RNA hybrids during transcription (20), the reduced Mec1 activation in npl3Δ cells could be due to the inability of these cells to remove DNA:RNA hybrids from the DSB ends. If this were the case, the checkpoint defect of npl3Δ cells should be alleviated by high levels of ribonuclease H1 (RNase H1), which is known to remove DNA:RNA hybrids in vivo (27). We therefore transformed wild type and npl3Δ cells carrying the HO system with a centromeric plasmid carrying the RNase H1-encoding gene (RNH1) under the control of tetO promoter, which acts as a strong promoter in the absence of tetracyclin (27). As expected (20), the tetO-RNH1 plasmid suppressed the hypersensitivity of npl3Δ cells spotted on plates with MMS (Figure 2A). However, the hypersensitivity to CPT of the same cells was only very slightly suppressed by RNase H1 overproduction (Figure 2A), which was also unable to restore the HO-induced checkpoint in cells lacking Npl3. In fact, npl3Δ cells carrying either the tetO-RNH1 plasmid or the empty vector showed similar defects in both Rad53 phosphorylation (Figure 2B) and cell cycle arrest after HO induction compared to wild type cells (Supplementary Figure S2). This finding indicates that the checkpoint defect of npl3Δ cells is not likely due to DNA:RNA hybrid accumulation.
Figure 2.
The lack of NPL3 impairs extensive resection of DSB ends. (A and B) Exponentially growing cell cultures of wild type and npl3Δ strains, both carrying a centromeric plasmid either expressing the RNH1 gene from the tetO promoter or empty (vect), were either serially diluted (1:10) before being spotted out onto YEPD plates with or without MMS or CPT (A), or transferred to YEPRG to monitor Rad53 phosphorylation by western blot (B). (C) System to detect DSB resection. Gel blots of SspI-digested genomic DNA separated on alkaline agarose gel were hybridized with a single-stranded RNA MAT probe (ss probe) that anneals to the unresected strand. 5΄-3΄ resection progressively eliminates SspI sites (S), producing larger SspI fragments (r1 through r7) detected by the probe. (D and E) Exponentially growing YEPR cell cultures were arrested in G2 with nocodazole and transferred to YEPRG (time zero) in the presence of nocodazole. (D) DSB resection as described in (C). (E) Resection products in (D) were analyzed by densitometry. The mean values are represented with error bars denoting SD (n = 5).
We then asked whether Npl3 promotes DSB processing by directly monitoring ssDNA generation at the DSB ends. Galactose was added to cell cultures arrested in G2 with nocodazole to produce the HO-induced DSB in cells that were then maintained in G2. Because ssDNA is resistant to cleavage by restriction enzymes, we measured the 5΄ strand degradation of one DSB end by following the loss of SspI restriction fragments at different time points after galactose addition by Southern blot of genomic DNA under alkaline conditions, using a single-stranded RNA probe that anneals to the unresected 3΄ strand on one side of the break (Figure 2C and D). We then evaluated the resection efficiency by calculating the ratio of band intensities for ssDNA to total amount of DNA, normalized with respect to the efficiency of DSB formation for each time point (Figure 2E). The 1.7 and 3.5 kb resection fragments (r1-r2 in Figure 2C–E) appeared with similar kinetics in both wild type and npl3Δ cells, suggesting that the lack of Npl3 does not affect initiation of DSB resection. However, the generation of resection fragments longer than 3.5 kb (r3–r7 in Figure 2C–E) was severely affected by the absence of Npl3 (Figure 2D and E), indicating that npl3Δ cells are specifically impaired in extensive resection. Thus, Npl3 is dispensable to initiate DSB resection, whereas it is required to produce long ssDNA tails.
The Npl3 RNA-binding domains are required for Npl3 functions in the DDR
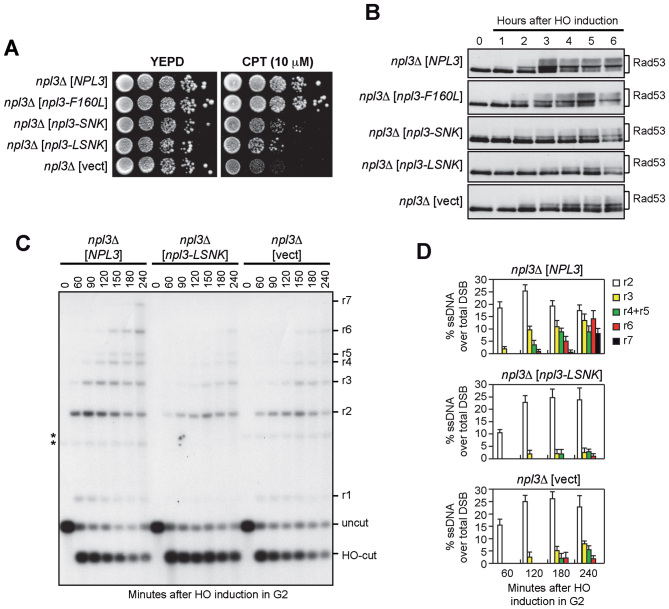
Npl3 binds RNA through the RNA recognition motifs RRM1 and RRM2 (17). We therefore investigated whether the integrity of Npl3 RRMs is required for cell survival in the presence of DNA damage and/or HO-induced checkpoint activation. We transformed npl3Δ cells with either an empty centromeric plasmid or with similar plasmids carrying wild type NPL3, the npl3-F160L allele, which inactivates RRM1, the npl3-SNK (L225S, G241N, E244K) allele, which inactivates RRM2, and the npl3-LSNK (F160L, L225S, G241N, E244K) allele, which disrupts both RRM domains (17,29). Cells expressing the npl3-F160L allele were as sensitive as wild type to CPT (Figure 3A) and phosphorylated Rad53 similarly to wild type cells after HO-induction (Figure 3B and Supplementary Figure S3). By contrast, npl3-SNK and npl3-LSNK cells were more sensitive than wild type to CPT, although their hypersensitivity was less pronounced compared to npl3Δ cells (Figure 3A). Furthermore, the HO-induced Rad53 phosphorylation was reduced in npl3-SNK and npl3-LSNK mutants, similar to npl3Δ cells (Figure 3B).
Figure 3.
The Npl3 RNA binding domains are required for checkpoint and resection. (A–D) Exponentially growing cell cultures of a npl3Δ strain transformed with an empty centromeric vector (vect) or with the same vector carrying either the wild type NPL3 gene or the indicated npl3 mutant alleles were either spotted out onto YEPD plates with or without CPT (A), or transferred to YEPRG to follow Rad53 phosphorylation by western blot (B), or arrested in G2 and transferred to YEPRG (time zero) in the presence of nocodazole to monitor DSB resection as described in Figure 2C (C). *indicates cross hybridization signals likely due to the presence of the plasmids. (D) Resection products in (C) were analyzed by densitometry. The mean values are represented with error bars denoting SD (n = 3).
We also analyzed whether the integrity of Npl3 RRM domains is required for resection by measuring ssDNA generation at the HO-induced DSB in npl3-LSNK mutant cells. Similar to the absence of Npl3, the npl3-LSNK allele impairs long-range resection. In fact, the r3–r7 resection fragments accumulated less efficiently in both npl3Δ and npl3-LSNK cells than in wild type (Figure 3C and D). These results indicate that the RRM domains are required to support Npl3 functions in the DDR, with RRM2 playing a major role, suggesting that Npl3 regulates specific RNA molecules involved in the DDR.
The lack of Npl3 reduces Exo1 levels
Npl3 might either directly participate in resection or support DSB processing by promoting the expression of resection proteins. To discriminate between these two possibilities, we first evaluated whether Npl3 is recruited to DNA ends. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and real-time qPCR were performed after generation of an HO-induced DSB in G2-arrested cells expressing a fully functional Npl3-HA variant. Similar amounts of DNA at 0.6 or 5.4 kb from the HO-cut site were recovered in immunoprecipitates from cells expressing either the Npl3-HA variant or untagged Npl3 both before and after DSB formation (Supplementary Figure S4). This suggests that Npl3 is not bound/recruited to DSB ends and thus does not directly participate in resection.
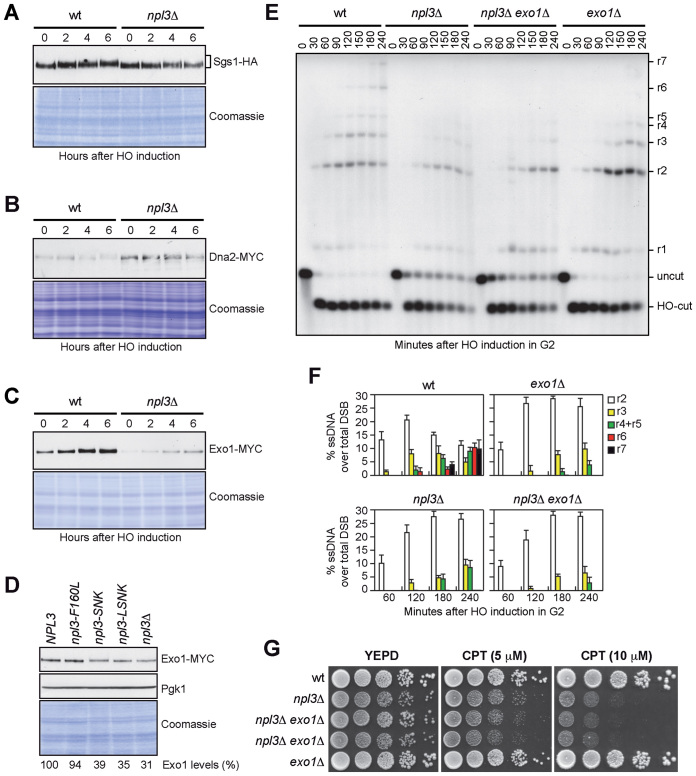
Generation of ssDNA at DSBs is promoted by several proteins, which control either initiation (Mre11, Rad50, Xrs2 and Sae2) or extension (Dna2, Sgs1 and Exo1) of resection (3,4). To assess whether Npl3 supports DSB processing by promoting the expression of resection factors, we measured the amount of the above proteins by western blot of protein extracts from wild type and npl3Δ cells expressing fully functional tagged versions of these proteins and treated with galactose to induce the HO cut. Similar amounts of Sgs1 (Figure 4A), Mre11 and Xrs2 (Supplementary Figure S5A and B) were detected in wild type and npl3Δ cells, indicating that Npl3 does not control the levels of these proteins. Consistent with the checkpoint defect of npl3Δ cells, Xrs2 and Sgs1, which are known to undergo DNA damage-induced phosphorylation (39,42), were less phosphorylated in npl3Δ cells compared to wild type (Figure 4A and Supplementary Figure S5B). The amount of Dna2 (Figure 4B), Rad50 and Sae2 (Supplementary Figure S5C and D) was higher in npl3Δ cells than in wild type. However, it is unlikely that these effects can account for the resection defect of npl3Δ cells. In fact, overexpression of neither SAE2 nor DNA2 affects ssDNA generation at DSB ends in wild type cells (43,44). Furthermore, Rad50 forms the MRX complex together with Mre11 and Xrs2, and Mre11 was found to be limiting for the recruitment of the MRX complex to DSBs (45), suggesting that high Rad50 levels should not affect DSB resection because they do not increase MRX recruitment to DSBs.
Figure 4.
NPL3 and EXO1 belong to the same resection pathway. (A–C) Exponentially growing YEPR cell cultures of strains expressing the indicated tagged proteins were transferred to YEPRG (time zero). The same amounts of protein extracts were separated on SDS-PAGE and either subjected to western blot with antibodies specific for the indicated tags or stained with Coomassie as a loading control. (D) The same amounts of protein extracts prepared from exponentially growing YEPD cultures of strains as in Figure 3, all expressing the Exo1-MYC tagged protein, were either stained with Coomassie or subjected to western blot with anti-MYC and anti-Pgk1 (loading control) antibodies. The relative intensity of the Exo1-MYC signal compared to wild type (set to 100%) was estimated after normalization to the Pgk1 band. (E and F) G2-arrested cell cultures of the indicated strains were transferred to YEPRG (time zero) in the presence of nocodazole. (E) DSB resection as described in Figure 2C. (F) Resection products in (E) were analyzed by densitometry. The mean values are represented with error bars denoting SD (n = 3). (G) Exponentially growing cell cultures of the indicated strains were spotted out onto YEPD plates with or without CPT.
Interestingly, the amount of Exo1 was strongly reduced in npl3Δ cells compared to wild type both in raffinose and after galactose addition (Figure 4C). As Exo1 levels were not affected by treatment with the proteasome inhibitor MG132 of either wild type or npl3Δ cells exponentially growing in glucose (Supplementary Figure S6), altogether these data indicate that Npl3 promotes Exo1 production independently of both the DNA damage and the carbon source.
We investigated whether the integrity of the Npl3 RRM motifs is important to regulate Exo1 levels by evaluating the amount of MYC-tagged Exo1 in cells expressing RRM1 and/or RRM2 defective Npl3 variants. The amount of Exo1, quantified using Pgk1 as a normalization control, was reduced of ∼70% in YEPD exponentially growing npl3Δ cells compared to wild type (Figure 4D). Npl3 interaction with RNA is important to regulate Exo1 levels, as we detected a similar reduction in npl3-LSNK and npl3-SNK mutant cells, although inactivation of only RRM1 did not affect Exo1 amount (Figure 4D).
NPL3 and EXO1 belong to the same epistasis group for resection
As Exo1 is required for extensive resection of DNA ends (46,47), the low Exo1 levels in npl3Δ cells could be the cause of the resection defect of these cells. If this were the case, npl3Δ and exo1Δ cells should show a similar resection defect, and the lack of Exo1 should not increase the resection defect of npl3Δ cells. When we monitored ssDNA generation at the HO-induced DSB, both exo1Δ and npl3Δ single mutant cells efficiently initiated resection, but were impaired in the generation of the r3-r7 ssDNA products, and a similar defect in long-range resection was detectable in npl3Δ exo1Δ double mutant cells (Figure 4E). Although the HO-cut is induced more efficiently in exo1Δ cells (98%) than in both npl3Δ and npl3Δ exo1Δ cells (83% and 79%, respectively), a quantitative analysis of the resection products normalized to the cleavage efficiency confirmed that the resection kinetics were similar in these three mutant strains (Figure 4F).
The lack of Exo1 exacerbates the hypersensitivity to DNA damaging agents of mutants affecting other resection pathways, such as sae2Δ or sgs1Δ (47,48). Similarly, NPL3 deletion increased the hypersensitivity to CPT of sae2Δ cells (Supplementary Figure S7A). Furthermore, the npl3Δ sgs1Δ spores obtained by tetrad dissection of a sporulated NPL3/npl3Δ SGS1/sgs1Δ diploid strain generated very small colonies (Supplementary Figure S7B), suggesting that Npl3 and Sgs1 participate in different pathways to support cell viability. Conversely, EXO1 deletion neither increased the growth defect nor the hypersensitivity to CPT of npl3Δ cells (Figure 4G), indicating that Exo1 and Npl3 belong to the same resection pathway.
Exo1 high levels partially restore resection in npl3Δ cells
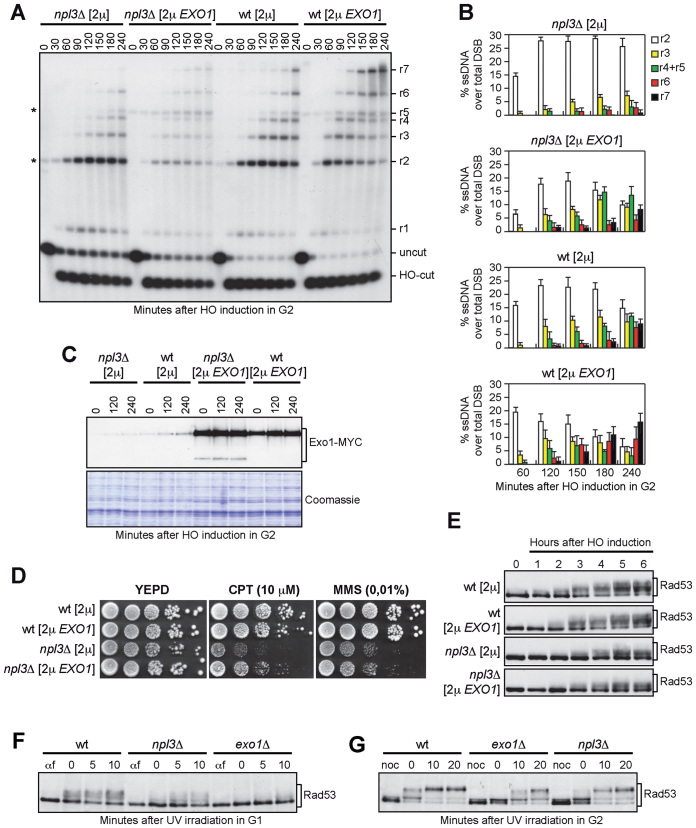
If the low Exo1 amount causes the resection defect in npl3Δ cells, increased Exo1 levels are expected to restore resection in these cells. We therefore monitored the resection kinetics in wild type and npl3Δ cells carrying a high copy number 2μ plasmid with the EXO1 gene (28). The EXO1 2μ plasmid markedly increased the amount of long resection products in npl3Δ cells compared to the empty vector (Figure 5A and B). In particular, npl3Δ cells with the empty vector were specifically impaired in the generation of resection fragments longer then 3.5 kb, while these longer ssDNA fragments appeared in npl3Δ cells carrying the EXO1 2μ plasmid. This indicates that Npl3 promotes the generation of long ssDNA tails by positively regulating Exo1 levels.
Figure 5.
EXO1 overexpression partially suppresses both the resection defect and the hypersensitivity to CPT of npl3Δ cells. (A and B) G2-arrested YEPR cell cultures of wild type and npl3Δ strains, both transformed with a 2μ plasmid either carrying the EXO1 gene or empty (2μ), were transferred to YEPRG (time zero) in the presence of nocodazole. (A) DSB resection as described in Figure 2C. *indicates cross hybridization signals that partially overlap the r2 or r5 bands, and are due to the presence of the 2μ plasmid. (B) Resection products in (A) were analyzed by densitometry. The mean values are represented with error bars denoting SD (n = 3). (C) G2-arrested cell cultures of wild type and npl3Δ strains, both expressing the Exo1-MYC tagged protein from the EXO1 locus and transformed with a 2μ plasmid either carrying the EXO1-MYC gene or empty (2μ), were transferred to YEPRG (time zero) in the presence of nocodazole. The same amounts of protein extracts were either subjected to western blot with anti-MYC antibodies or stained with Coomassie as a loading control. (D and E) Exponentially growing cell cultures of the strains described in (A and B) were either spotted out onto YEPD plates with or without CPT or MMS (D), or transferred to YEPRG (time zero) to analyze Rad53 phosphorylation by western blot with anti-Rad53 antibodies (E). (F) YEPD G1-arrested cell cultures (αf) of the indicated strains were UV irradiated (75 J/m2) (time zero) and held in G1 in the presence of α-factor. Protein extracts were subjected to western blot with anti-Rad53 antibodies. (G) YEPD G2-arrested cell cultures (noc) of the strains in (F) were UV irradiated (75 J/m2) (time zero) and held in G2 in the presence of nocodazole. Protein extracts were analyzed by western blot with anti-Rad53 antibodies.
To verify that the EXO1 2μ plasmid increased Exo1 amount in the absence of Npl3, a 2μ plasmid either empty or carrying the EXO1-MYC allele was transformed into wild type and npl3Δ cells expressing the Exo1-Myc variant from the EXO1 genomic locus. Although the Exo1 levels were increased by the EXO1-MYC 2μ plasmid in both wild type and npl3Δ cells, some fast-migrating Exo1 forms appeared specifically in npl3Δ cells (Figure 5C), suggesting that overproduced Exo1 may be unstable in the absence of Npl3. This might explain why the EXO1-MYC 2μ plasmid only partially restores resection in npl3Δ cells (Figure 5A and B).
Interestingly, the EXO1 2μ plasmid partially suppressed the hypersensitivity to CPT of npl3Δ cells (Figure 5D), indicating that the hypersensitivity of cells lacking Npl3 is at least partially due to the resection defect. Conversely, this plasmid did not suppress the hypersensitivity to MMS of npl3Δ cells (Figure 5D), nor the elevated levels of spontaneous recombination caused by the Npl3 lack (Supplementary Figure S8). To measure mitotic recombination frequency, we used strains carrying the his3-513::TRP1::his3-537 heteroallelic duplication on chromosome XV (49) and transformed with either the EXO1 2μ plasmid or the empty vector. As expected (20), NPL3 deletion increased 12.8-fold the recombination frequency at the HIS3 locus compared to wild type cells (Supplementary Figure S8). The EXO1 2μ plasmid did not reduce, but rather slightly increased the recombination frequency in both wild type and npl3Δ cells (Supplementary Figure S8), indicating that the high recombination frequency in npl3Δ cells is not due to the low amount of Exo1.
The EXO1 2μ plasmid was also unable to restore the DSB-induced checkpoint in npl3Δ cells. In fact, HO-induced npl3Δ cells carrying either the empty vector or the EXO1 2μ plasmid showed similar defective Rad53 phosphorylation compared to wild type cells (Figure 5E and Supplementary Figure S9), indicating that the checkpoint defect of npl3Δ cells cannot be ascribed only to the resection defect. This result, together with the finding that the lack of Exo1 only very slightly affects the HO-induced Rad53 phosphorylation despite the resection defect (35,50), suggests that Npl3 might control the levels of other checkpoint proteins. However, we detected similar amounts of the three RPA subunits Rfa1, Rfa2 and Rfa3 in wild type and npl3Δ cells (Supplementary Figure S10A–C). Furthermore, the abundance of the checkpoint proteins Tel1, Ddc2, Rad53, and Rad9 was unaffected by the absence of Npl3 (Supplementary Figure S10D-F). Conversely, the amount of Mec1 was slightly lower in npl3Δ cells than in wild type (Supplementary Figure S10E). However, a Mec1-dependent checkpoint is strongly activated in npl3Δ cells treated with phleomycin (Figure 1G), suggesting that the slightly reduced amount of Mec1 detected in npl3Δ cells does not likely account for the checkpoint defect of the same cells. Altogether these results indicate that Npl3 plays two functions in the DDR: it promotes DSB resection by regulating Exo1 levels and it contributes to checkpoint activation by regulating some still unknown targets.
Npl3 and Exo1 are required for checkpoint activation after UV irradiation
If the Npl3-mediated control of Exo1 protein levels is biologically relevant, we expect exo1Δ and npl3Δ cells to show some common phenotypes. Exo1 is required to activate the checkpoint after UV treatment in non-cycling cells by promoting the generation of large ssDNA gaps during nucleotide excision repair (NER) processing (51). We then asked whether npl3Δ cells fail to activate the UV-induced checkpoint in G1- and G2-arrested cells, similarly to exo1Δ cells. Wild type, npl3Δ and exo1Δ cells were arrested either in G1 with α-factor or in G2 with nocodazole, UV irradiated, and transferred in fresh medium containing α-factor or nocodazole, respectively, to maintain the cell cycle arrests, as confirmed by FACS analyses (Supplementary Figure S11). As expected (51), Rad53 hyperphosphorylated forms appeared immediately after UV irradiation in wild type cells arrested either in G1 (Figure 5F) or in G2 (Figure 5G), while they were strongly reduced in similarly treated exo1Δ cells (Figure 5F and G). Also the lack of Npl3 impaired Rad53 phosphorylation in both G1 (Figure 5F) and G2 (Figure 5G), although to a lesser extent than the absence of Exo1 (Figure 5F and G), possibly because Exo1 is not totally absent in npl3Δ cells (Figure 4C and D). Thus, similarly to Exo1, Npl3 is required for checkpoint activation after UV irradiation in G1 and in G2. As Npl3 is not required per se to activate the checkpoint, at least in G2-arrested cells (Figure 1G), these results suggest that the low Exo1 levels in npl3Δ cells are not sufficient to efficiently process the UV lesions and generate enough ssDNA to activate the checkpoint in non-cycling cells.
Abnormal EXO1 RNA species are produced in the absence of Npl3
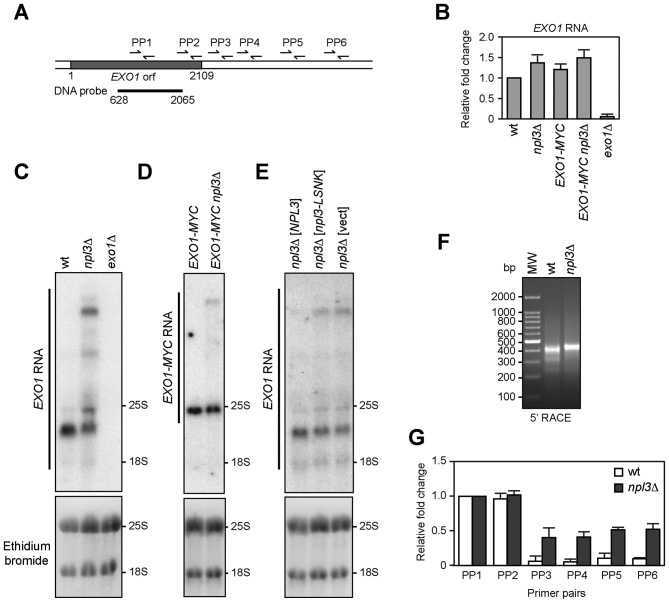
Genome-wide analyses have shown that the absence of Npl3 results in either down- or up-regulation of many protein-coding genes (20,23,52). These analyses did not show significant differences in EXO1 expression in npl3Δ versus wild type cells, suggesting that Npl3 controls the abundance of the Exo1 protein by acting at post-transcriptional level. To verify this possibility, we first employed quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR (qRT-PCR) to measure the amount of EXO1 RNA either in the presence or in the absence of Npl3. Total RNA was extracted from wild type, npl3Δ and exo1Δ cells exponentially growing in YEPD and subjected to reverse transcription followed by quantitative real-time PCR with primer pairs located either inside the EXO1 coding region (PP1 in Figure 6A) or the ALG9 control gene. The amount of EXO1 RNA was not diminished in the absence of Npl3 (Figure 6B). Rather, we found a modest increase of EXO1 RNA levels in npl3Δ cells compared to wild type (Figure 6B). The levels of the Exo1 protein (Figure 4C and D) were monitored by using a tagged version of the protein generated by inserting a 18 MYC epitopes coding sequence just before the EXO1 stop codon. Similarly to EXO1 RNA, the EXO1-MYC RNA was slightly more abundant in npl3Δ cells than in wild type (Figure 6B), indicating that neither Npl3 nor the insertion of the MYC coding sequence into the EXO1 gene affects EXO1 transcription.
Figure 6.
EXO1 RNA in the absence of Npl3. (A) Schematic representation of the EXO1 locus. Primer pairs (PP1-PP6) used for qRT-PCR are indicated by arrows. A bar indicates the 1437 bp-DNA probe internal to the EXO1 coding sequence (+628 to + 2065 from the ATG initiation codon) used for northern blot. (B) Total RNA was extracted from exponentially growing YEPD cell cultures of the indicated strains and subjected to quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR (qRT-PCR) with primer pairs located into the EXO1 (PP1 in (A)) and ALG9 coding sequences. The EXO1 RNA levels relative to wild type (set to 1.0) were calculated using ΔΔCt method after normalization to the ALG9 RNA levels for each sample. The mean values are represented with error bars denoting SD (n = 5). (C–E) Total RNA extracted from the indicated cell cultures was subjected to northern blot and hybridized with the probe as in (A). The agarose gels were stained with ethidium bromide to detect 18S and 25S rRNAs (bottom). (F) Total RNA extracted from wild type and npl3Δ cells was subjected to 5΄ RACE to visualize the EXO1 5΄ partial cDNA ends. After reverse transcription with a EXO1 specific primer and poly(A) tailing, two subsequent PCR reactions were performed with primers annealing to the appended tail and to the EXO1 coding sequence 718 and 248 bp downstream the EXO1 initiation codon. The final PCR products were separated on a 1.5% agarose gel and visualized with ethidium bromide. (G) Total RNA as in (F) was subjected to qRT-PCR with primer pairs depicted in (A), or located in the ALG9 coding sequence. The amount of products obtained with different EXO1 primer pairs was normalized to the ALG9 product using ΔΔCt method. Then, the normalized RNA levels estimated with the different primer pairs in the EXO1 locus were normalized to the RNA levels evaluated with the PP1 primer pair and set to 1.0 for each strain. The mean values are represented with error bars denoting SD (n = 4).
If Npl3 promoted EXO1 pre-mRNA processing, npl3Δ cells should accumulate aberrant RNA molecules. Thus, the same RNA extracts were analyzed by northern blot with a 1437 nt DNA probe complementary to the EXO1 coding sequence (Figure 6A). The probe was specific for the EXO1 RNA species, as no signal was detected in RNA prepared from exo1Δ cells (Figure 6C). In wild type RNA extracts this probe revealed a single band that migrated between the two ribosomal RNA (rRNA) species 25S (3392 nt) and 18S (1798 nt), as expected for the EXO1 RNA, whose length should be approximately 2400 nt, considering that the average S. cerevisiae mRNA consists of the protein coding sequence (2109 nt for EXO1) plus 260 nt of 5΄ and 3΄ untranslated sequences (53). The same probe detected at least 3 additional longer bands in the npl3Δ RNA preparation (Figure 6C), indicating that the absence of Npl3 leads to the generation of longer than normal EXO1 RNA molecules. Similarly, a single EXO1 RNA species migrating just below the 3392 nt-long 25S rRNA was detected in cells carrying the EXO1-MYC construct, while at least an additional longer band was present in RNA extracts from npl3Δ EXO1-MYC cells (Figure 6D). Furthermore, longer than normal EXO1 RNA molecules were produced also in npl3-LSNK cells, where both Npl3 RRM domains were inactivated (Figure 6E). Thus, extended EXO1 RNA species are produced in the absence of Npl3 or of its RNA-binding capacity, suggesting that Npl3 might regulate initiation, termination or processing of the EXO1 transcript.
In order to verify whether the abnormal EXO1 transcripts in npl3Δ cells are extended at the 5΄ end, we performed 5΄ rapid amplification of cDNA ends (5΄-RACE) on wild type and npl3Δ RNA extracts that were subjected to reverse transcription with an EXO1 specific primer. A poly(A) tail was added to the resulting cDNA, which was then used as a template for two subsequent PCR reactions with primers annealing to the appended tail and to the EXO1 coding sequence. A PCR with primers located at the 5΄ tail and 248 bp downstream the EXO1 initiation codon revealed a ∼400 bp abundant product and two weak smaller products in wild type extracts, while a single slightly bigger band was detected in npl3Δ (Figure 6F). Although this result suggests that Npl3 influences the use of different transcription start sites in EXO1 promoter, the small difference in length at the 5΄ of the EXO1 transcripts does not likely account for the extended RNA species observed by northern blot in npl3Δ cells (Figure 6C and E).
We then evaluated whether these transcripts were extended at the 3΄ end, as Npl3 was recently found to prevent transcriptional readthrough of both protein-coding and non-coding genes (23). We therefore performed qRT-PCR analyses with different primer pairs located either internally to the EXO1 coding sequence (PP1 and PP2), or 100, 300, 850, 1000 bp (PP3–PP6, respectively) downstream to the stop codon (Figure 6A). The RNA levels estimated with the different primer pairs were normalized with respect to the RNA levels evaluated with the PP1 primer pair, which were set to 1.0 for each strain (Figure 6G). The RNA levels estimated with the primer pair located immediately before the stop codon (PP2) were almost identical to those evaluated with the primer pair internal to the EXO1 coding sequence (PP1) in both wild type and npl3Δ extracts (Figure 6G). Strikingly, only npl3Δ extracts generated products with the primer pairs located downstream to the stop codon (PP3–PP6) (Figure 6G), although the amount of these products was lower (almost 40%) than that of the products obtained with primer pairs internal to the EXO1 coding sequence (Figure 6G). These results indicate that a substantial fraction of EXO1 RNA is not properly terminated in the absence of Npl3, thus generating RNA molecules with long 3΄ tails that extend at least 1000 bp downstream to the EXO1 stop codon.
Rrp6 controls the levels of the EXO1 RNA
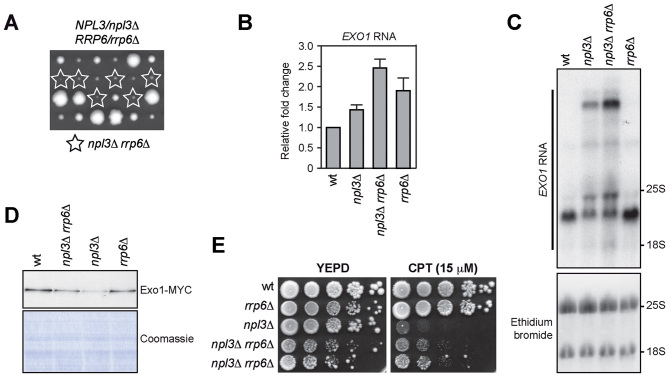
It is known that 3΄-extended RNAs might be unstable and targeted to degradation by the RNA decay systems. In particular, defects in 3΄-end processing result in nuclear retention and degradation of faulty transcripts mainly by the nuclear exosome (14). To test whether the nuclear exosome degrades the extended EXO1 RNA molecules produced in the absence of Npl3, we checked if these abnormal EXO1 RNAs further accumulate in npl3Δ cells lacking the exosome catalytic subunit Rrp6, whose lack was reported to impair viability of npl3Δ cells (54). In our genetic background, npl3Δ rrp6Δ spores generated by sporulation and tetrad dissection of a NPL3/npl3Δ RRP6/rrp6Δ diploid gave rise to very small colonies, which could be further propagated in YEPD, despite their growth defect (Figure 7A and E). We then subjected to both qRT-PCR and northern blot analysis the EXO1 RNAs derived from exponentially growing wild type, npl3Δ, rrp6Δ and npl3Δ rrp6Δ cells. Both analyses revealed higher levels of EXO1 RNA in npl3Δ rrp6Δ cells than in npl3Δ and rrp6Δ single mutants (Figure 7B and C). The intensity of the bands detected by the EXO1 probe in the northern blot, and in particular that of the slowest migrating band, was higher in npl3Δ rrp6Δ RNA extracts than in npl3Δ (Figure 7C), suggesting that Rrp6 partially removes abnormal RNA intermediates that accumulate in the absence of Npl3.
Figure 7.
Rrp6 limits the accumulation of abnormal EXO1 RNAs in the absence of Npl3. (A) Meiotic tetrads from diploid cells with the indicated genotype were dissected on YEPD plates that were incubated at 30°C for 3 days, followed by spore genotyping. (B, C) Total RNA was extracted from exponentially growing YEPD cultures of the indicated strains and subjected to both qRT-PCR as in Figure 6B and northern blot as in Figure 6C–E. (D) The same amounts of protein extracts prepared from exponentially growing cell cultures with the indicated genotypes and expressing the Exo1-MYC tagged protein were either stained with Coomassie or subjected to western blot with anti-MYC antibodies. (E) Exponentially growing cell cultures of the indicated strains were spotted out onto YEPD plates with or without CPT.
As the amount of the 2400 nt-long EXO1 RNA species was also higher in npl3Δ rrp6Δ cells compared to npl3Δ cells (Figure 7C), we asked whether the absence of Rrp6 also increased the levels of Exo1 protein in cells lacking Npl3. Indeed, the amount of the Exo1-MYC tagged variant was slightly higher in exponentially growing npl3Δ rrp6Δ cells than in npl3Δ cells (Figure 7D). This suggests that, in the presence of improperly processed transcripts, the exosome targets not only the faulty, but also some functional EXO1 RNA molecules. Interestingly, although npl3Δ rrp6Δ cells grew poorly on YEPD plates (Figure 7A and E), they formed colonies in the presence of CPT more efficiently than npl3Δ cells (Figure 7E), similarly to what we observed with the overexpression of the EXO1 gene (Figure 5D). Taken together, these results indicate that Npl3 promotes proper maturation of the EXO1 RNA, thus preventing its degradation by the nuclear exosome.
DISCUSSION
Resection of DSB ends is a two-step process, which is initiated by MRX and Sae2 that induce an endonucleolytic cleavage of the 5΄-terminated DNA strands. This cleavage promotes the access of the Exo1 and Dna2 nucleases, which allow the generation of long ssDNA tails (reviewed in (3,4)). Here, we show that the lack of the RBP Npl3 impairs the generation of long stretches of ssDNA at DSB ends and decreases the amount of the exonuclease Exo1. Furthermore, the lack of Exo1 does not exacerbate the resection defect of npl3Δ cells, while high Exo1 levels partially restore resection in these cells, indicating that Npl3 supports long-range resection by ensuring the production of a sufficient amount of Exo1.
We also found that Npl3 is required to activate a Mec1-dependent checkpoint in response to different kinds of DNA damage, but it is dispensable for checkpoint activation after phleomycin treatment in G2 (Figures 1 and 5). As Exo1 is required to generate long stretches of ssDNA (35,51,55), which are the signals that activate Mec1 at least in response to both DSBs and UV-induced DNA lesions (10,34,35,55,56), the reduced Exo1 amount in npl3Δ cells could account for the checkpoint defect of the same cells. However, EXO1 overexpression does not alleviate the checkpoint defect of npl3Δ cells experiencing a single DSB. This result, together with the finding that the lack of Exo1 causes a very mild, if any, checkpoint defect in response to a single DSB (35,50), suggests that Npl3 regulates the functions of other proteins involved in checkpoint activation besides Exo1. Although genome-wide transcription analyses showed that most checkpoint genes are not significantly downregulated in the absence of Npl3 (20), a very mild decrease of MEC1 gene expression was reported in npl3Δ cells (23), which also show a slight reduction in Mec1 protein abundance (Supplementary Figure S10E). Furthermore, npl3Δ cells show increased amounts of SAE2 mRNA (23) that correlate with increased levels of the Sae2 protein (Supplementary Figure S5D). As high Sae2 levels have been shown to counteract Mec1-dependent checkpoint activation (50), the checkpoint defect of npl3Δ cells might be due to the high Sae2 levels. Thus, we speculate that the checkpoint defect of npl3Δ cells may result both from a defect in ssDNA generation due to low Exo1 levels and from a mild deregulation of factors involved in checkpoint signaling, such as Sae2 and Mec1. These Mec1 and Sae2 misregulations are likely not sufficient to impair checkpoint activation by themselves, as the checkpoint is strongly activated in npl3Δ cells treated with phleomycin. However, they might impair Mec1 recruitment/activation in response to DNA lesions that require extensive nucleolytic processing to be detected by Mec1, such as DSBs or UV-induced DNA lesions.
The idea that Npl3 regulates other DDR factors besides Exo1 is also supported by the observation that the lack of Npl3 causes hypersensitivity to DSB-inducing agents, whereas EXO1 deletion does not (47,55). Accordingly, EXO1 overexpression partially rescues the hypersensitivity to CPT of npl3Δ cells, while it does not affect the hypersensitivity of the same cells to MMS. This result also suggests that Exo1 is important to repair the damage induced by CPT, while other defects can contribute to the hypersensitivity to MMS of npl3Δ cells. One of these defects might be the replication stress caused by the accumulation of transcription-dependent DNA:RNA hybrids in the absence of Npl3. In fact, overproduction of RNaseH1, which removes these hybrids in vivo (20,27), suppresses the hypersensitivity to MMS (Figure 2A) and reduces the high levels of spontaneous mitotic recombination caused by the lack of Npl3 (20). On the contrary, EXO1 overexpression does not reduce the recombination frequency in npl3Δ cells (Supplementary Figure S8).
How does Npl3 control the abundance of the Exo1 protein? As the low Exo1 amount in npl3Δ cells does not correlate with a decrease in total EXO1 RNA levels (Figure 6) (20,23), we exclude that Npl3 promotes EXO1 transcription. Rather, the extended EXO1 RNA species detected in the absence of Npl3 may be due to termination defects and transcription readthrough. In fact, defects in transcription termination were seen for approximately 30% of protein-coding genes in npl3Δ cells (23), and we found that a region 1000 bp downstream to the EXO1 stop codon was transcribed in npl3Δ cells but not in wild type, while we did not find a significant extension of the EXO1 RNA 5΄ end in the absence of Npl3. Furthermore, Npl3 was found to be co-transcriptionally recruited to DNA at highly transcribed genes (among which EXO1), where it distributes in a gradient that increases toward the 3΄ end of the coding region (20), and to bind both the 5΄ (23,52) and the 3΄ ends of mRNAs (52). Npl3 inactivation is also known to impair mRNA export and to cause the accumulation of transcripts in the nucleus (57). Taken together, these results suggest that, in the absence of Npl3, some EXO1 nascent transcripts are not appropriately packaged, thus possibly interfering with the transcription termination process and forming abnormal EXO1 RNA species that are not exported to the cytoplasm and/or not efficiently translated.
These abnormal EXO1 RNAs are likely degraded, at least in part, by the nuclear exosome, as the lack of Rrp6 in npl3Δ cells results in a further accumulation of extended EXO1 RNA species. Accordingly, the exosome was found to degrade transcripts that are not co-transcriptionally packaged because of mutations in the THO complex, which, similarly to Npl3, is required for pre-mRNA processing and export (58). The lack of Rrp6 slightly increases Exo1 protein levels in npl3Δ cells, suggesting that in the presence of faulty transcripts Rrp6 can sequester and/or degrade also functional RNAs. Rrp6 was found to prevent chromatin release of aberrant transcripts when co-transcriptional pre-mRNA processing fails, thus eventually providing these transcripts with additional time to complete their maturation (59,60). Furthermore, Rrp6 was recently reported to participate in mRNA nuclear retention caused by Npl3 inactivation. In fact, while npl3 temperature-sensitive mutant cells accumulate mRNAs in the nucleus at the restrictive temperature, mRNAs are partially released in the cytoplasm in npl3 rrp6 double mutant cells (61). Interestingly, Rrp6 deletion also partially suppresses the temperature sensitivity of these npl3 mutant cells, suggesting that part of the improperly packaged mRNAs produced in the absence of Npl3 may be functional, although incompetent for export (61).
Exo1 is an evolutionarily conserved processive exonuclease that can degrade several kilobases of DNA (7,8) and is implicated in a variety of DNA metabolic processes including DNA repair as well as processing of both stalled replication forks and uncapped telomeres (2,5,62–64). Exo1 action is modulated by both positive and negative regulators, which control Exo1 access to DNA and limit excessive DNA degradation (3,4,6–8). Exo1 expression is also induced during yeast meiosis to promote meiotic DSB processing and crossing over (65). In mammals, splicing of EXO1 transcripts is facilitated after DNA damage by a splicing complex that contains the DDR protein BRCA1 (66). The Npl3-mediated regulation of Exo1 amount that we show here represents another level of control of Exo1 activity that guarantees the availability of suitable amounts of Exo1 to respond to DNA damage and maintain genome integrity.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank J. Haber for yeast strains; A. Aguilera, E. Alani and J. Lee-Soety for plasmids and N. Lowndes and B. Stillman for antibodies. We are particularly grateful to M. Vai and I. Orlandi for technical advises, and to G. Lucchini for useful suggestions and critical reading of the manuscript.
Footnotes
Present address: Camilla Trovesi, Istituto Nazionale di Genetica Molecolare ‘Romeo ed Enrica Invernizzi’, 20122 Milano, Italy.
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
Supplementary Data are available at NAR Online.
FUNDING
Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC) [IG15210]; Progetti di Ricerca di Interesse Nazionale (PRIN) 2015 (to M.P.L.). Funding for open access charge: Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC) [IG15210 to M.P.L].
Conflict of interest statement. None declared.
REFERENCES
- 1. Ciccia A., Elledge S.J.. The DNA damage response: making it safe to play with knives. Mol. Cell. 2010; 40:179–204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Symington L.S., Rothstein R., Lisby M.. Mechanisms and regulation of mitotic recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 2014; 198:795–835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Daley J.M., Niu H., Miller A.S., Sung P.. Biochemical mechanism of DSB end resection and its regulation. DNA Repair (Amst.). 2015; 32:66–74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Villa M., Cassani C., Gobbini E., Bonetti D., Longhese M.P.. Coupling end resection with the checkpoint response at DNA double-strand breaks. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016; 73:3655–3663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Ferrari M., Dibitetto D., De Gregorio G., Eapen V.V., Rawal C.C., Lazzaro F., Tsabar M., Marini F., Haber J.E., Pellicioli A.. Functional interplay between the 53BP1-ortholog Rad9 and the Mre11 complex regulates resection, end-tethering and repair of a double-strand break. PLoS Genet. 2015; 11:e1004928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Morin I., Ngo H.P., Greenall A., Zubko M.K., Morrice N., Lydall D.. Checkpoint-dependent phosphorylation of Exo1 modulates the DNA damage response. EMBO J. 2008; 27:2400–2410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Cannavo E., Cejka P., Kowalczykowski S.C.. Relationship of DNA degradation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae Exonuclease 1 and its stimulation by RPA and Mre11-Rad50-Xrs2 to DNA end resection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2013; 110:E1661–E1668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Myler L.R., Gallardo I.F., Zhou Y., Gong F., Yang S.H., Wold M.S., Miller K.M., Paull T.T., Finkelstein I.J.. Single-molecule imaging reveals the mechanism of Exo1 regulation by single-stranded DNA binding proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2016; 113:E1170–E1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Nakada D., Matsumoto K., Sugimoto K.. ATM-related Tel1 associates with double-strand breaks through an Xrs2-dependent mechanism. Genes Dev. 2003; 17:1957–1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Zou L., Elledge S.J.. Sensing DNA damage through ATRIP recognition of RPA-ssDNA complexes. Science. 2003; 300:1542–1548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Wickramasinghe V.O., Venkitaraman A.R.. RNA processing and genome stability: cause and consequence. Mol. Cell. 2016; 61:496–505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Tutucci E., Stutz F.. Keeping mRNPs in check during assembly and nuclear export. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011; 12:377–384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Eberle A.B., Visa N.. Quality control of mRNP biogenesis: networking at the transcription site. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014; 32:37–46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Fox M.J., Mosley A.L.. Rrp6: Integrated roles in nuclear RNA metabolism and transcription termination. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA. 2016; 7:91–104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. García-Muse T., Aguilera A.. Transcription-replication conflicts: how they occur and how they are resolved. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016; 17:553–563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Janke R., Kong J., Braberg H., Cantin G., Yates J.R., Krogan N.J., Heyer W.D.. Nonsense-mediated decay regulates key components of homologous recombination. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016; 44:5218–5230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Deka P., Bucheli M.E., Moore C., Buratowski S., Varani G.. Structure of the yeast SR protein Npl3 and Interaction with mRNA 3΄-end processing signals. J. Mol. Biol. 2008; 375:136–150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Dermody J.L., Dreyfuss J.M., Villén J., Ogundipe B., Gygi S.P., Park P.J., Ponticelli A.S., Moore C.L., Buratowski S., Bucheli M.E.. Unphosphorylated SR-like protein Npl3 stimulates RNA polymerase II elongation. PLoS One. 2008; 3:e3273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Lei E.P., Krebber H., Silver P.A.. Messenger RNAs are recruited for nuclear export during transcription. Genes Dev. 2001; 15:1771–1782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Santos-Pereira J.M., Herrero A.B., García-Rubio M.L., Marín A., Moreno S., Aguilera A.. The Npl3 hnRNP prevents R-loop-mediated transcription-replication conflicts and genome instability. Genes Dev. 2013; 27:2445–2458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Bucheli M.E., He X., Kaplan C.D., Moore C.L., Buratowski S.. Polyadenylation site choice in yeast is affected by competition between Npl3 and polyadenylation factor CFI. RNA. 2007; 13:1756–1764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Wong C.M., Tang H.M., Kong K.Y., Wong G.W., Qiu H., Jin D.Y., Hinnebusch A.G.. Yeast arginine methyltransferase Hmt1p regulates transcription elongation and termination by methylating Npl3p. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010; 38:2217–2228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Holmes R.K., Tuck A.C., Zhu C., Dunn-Davies H.R., Kudla G., Clauder-Munster S., Granneman S., Steinmetz L.M., Guthrie C., Tollervey D.. Loss of the yeast SR protein Npl3 alters gene expression due to transcription readthrough. PLoS Genet. 2015; 11:e1005735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. McKinney J.S., Sethi S., Tripp J.D., Nguyen T.N., Sanderson B.A., Westmoreland J.W., Resnick M.A., Lewis L.K.. A multistep genomic screen identifies new genes required for repair of DNA double-strand breaks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. BMC Genomics. 2013; 14:251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Pan X., Ye P., Yuan D.S., Wang X., Bader J.S., Boeke J.D.. A DNA integrity network in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 2006; 124:1069–1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Smolka M.B., Albuquerque C.P., Chen S.H., Zhou H.. Proteome-wide identification of in vivo targets of DNA damage checkpoint kinases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2007; 104:10364–10369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Castellano-Pozo M., García-Muse T., Aguilera A.. R-loops cause replication impairment and genome instability during meiosis. EMBO Rep. 2012; 13:923–929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Sokolsky T., Alani E.. EXO1 and MSH6 are high-copy suppressors of conditional mutations in the MSH2 mismatch repair gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 2000; 155:589–599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Lee-Soety J.Y., Jones J., MacGibeny M.A., Remaly E.C., Daniels L., Ito A., Jean J., Radecki H., Spencer S.. Yeast hnRNP-related proteins contribute to the maintenance of telomeres. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012; 426:12–17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Trovesi C., Falcettoni M., Lucchini G., Clerici M., Longhese M.P.. Distinct Cdk1 requirements during single-strand annealing, noncrossover, and crossover recombination. PLoS Genet. 2011; 7:e1002263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Gietz R.D., Sugino A.. New yeast-Escherichia coli shuttle vectors constructed with in vitro mutagenized yeast genes lacking six-base pair restriction sites. Gene. 1988; 74:527–534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Viscardi V., Bonetti D., Cartagena-Lirola H., Lucchini G., Longhese M.P.. MRX-dependent DNA damage response to short telomeres. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2007; 18:3047–3058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Lee S.E., Moore J.K., Holmes A., Umezu K., Kolodner R.D., Haber J.E.. Saccharomyces Ku70, Mre11/Rad50 and RPA proteins regulate adaptation to G2/M arrest after DNA damage. Cell. 1998; 94:399–409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Pellicioli A., Lee S.E., Lucca C., Foiani M., Haber J.E.. Regulation of Saccharomyces Rad53 checkpoint kinase during adaptation from DNA damage-induced G2/M arrest. Mol. Cell. 2001; 7:293–300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Mantiero D., Clerici M., Lucchini G., Longhese M.P.. Dual role for Saccharomyces cerevisiae Tel1 in the checkpoint response to double-strand breaks. EMBO Rep. 2007; 8:380–387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Paciotti V., Clerici M., Lucchini G., Longhese M.P.. The checkpoint protein Ddc2, functionally related to S. pombe Rad26, interacts with Mec1 and is regulated by Mec1-dependent phosphorylation in budding yeast. Genes Dev. 2000; 14:2046–2059. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Zhao X., Muller E.G., Rothstein R.. A suppressor of two essential checkpoint genes identifies a novel protein that negatively affects dNTP pools. Mol. Cell. 1998; 2:329–340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Redon C., Pilch D.R., Rogakou E.P., Orr A.H., Lowndes N.F., Bonner W.M.. Yeast histone 2A serine 129 is essential for the efficient repair of checkpoint-blind DNA damage. EMBO Rep. 2003; 4:678–684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Nakada D., Shimomura T., Matsumoto K., Sugimoto K.. The ATM‐related Tel1 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae controls a checkpoint response following phleomycin treatment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003; 31:1715–1724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Ohle C., Tesorero R., Schermann G., Dobrev N., Sinning I., Fischer T.. Transient RNA-DNA hybrids are required for efficient double-strand break repair. Cell. 2016; 167:1001–1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Li L., Germain D.R., Poon H.Y., Hildebrandt M.R., Monckton E.A., McDonald D., Hendzel M.J., Godbout R.. DEAD Box 1 facilitates removal of RNA and homologous recombination at DNA double-strand breaks. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2016; 36:2794–2810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Hegnauer A.M., Hustedt N., Shimada K., Pike B.L., Vogel M., Amsler P., Rubin S.M., van Leeuwen F., Guénolé A., van Attikum H. et al. . An N-terminal acidic region of Sgs1 interacts with Rpa70 and recruits Rad53 kinase to stalled forks. EMBO J. 2012; 31:3768–3783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Clerici M., Mantiero D., Lucchini G., Longhese M.P.. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae Sae2 protein promotes resection and bridging of double strand break ends. J. Biol. Chem. 2005; 280:38631–38638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Manfrini N., Trovesi C., Wery M., Martina M., Cesena D., Descrimes M., Morillon A., d’Adda di Fagagna F., Longhese M.P.. RNA-processing proteins regulate Mec1/ATR activation by promoting generation of RPA-coated ssDNA. EMBO Rep. 2015; 16:221–231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Shima H., Suzuki M., Shinohara M.. Isolation and characterization of novel xrs2 mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 2005; 170:71–85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Mimitou E.P., Symington L.S.. Sae2, Exo1 and Sgs1 collaborate in DNA double-strand break processing. Nature. 2008; 455:770–774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Zhu Z., Chung W.H., Shim E.Y., Lee S.E., Ira G.. Sgs1 helicase and two nucleases Dna2 and Exo1 resect DNA double-strand break ends. Cell. 2008; 134:981–994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Gobbini E., Villa M., Gnugnoli M., Menin L., Clerici M., Longhese M.P.. Sae2 Function at DNA Double-Strand Breaks Is Bypassed by Dampening Tel1 or Rad53 Activity. PLoS Genet. 2015; 11:e1005685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Longhese M.P., Plevani P., Lucchini G.. Replication factor A is required in vivo for DNA replication, repair, and recombination. Mol Cell Biol. 1994; 14:7884–7890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Clerici M., Mantiero D., Lucchini G., Longhese M.P.. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae Sae2 protein negatively regulates DNA damage checkpoint signalling. EMBO Rep. 2006; 7:212–218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Giannattasio M., Follonier C., Tourrière H., Puddu F., Lazzaro F., Pasero P., Lopes M., Plevani P., Muzi-Falconi M.. Exo1 competes with repair synthesis, converts NER intermediates to long ssDNA gaps, and promotes checkpoint activation. Mol. Cell. 2010; 40:50–62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Baejen C., Torkler P., Gressel S., Essig K., Söding J., Cramer P.. Transcriptome maps of mRNP biogenesis factors define pre-mRNA recognition. Mol. Cell. 2014; 55:745–757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Hurowitz E.H., Brown P.O.. Genome-wide analysis of mRNA lengths in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genome Biol. 2003; 5:R2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Burkard K.T., Butler J.S.. A nuclear 3΄-5΄ exonuclease involved in mRNA degradation interacts with Poly(A) polymerase and the hnRNA protein Npl3p. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000; 20:604–616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Nakada D., Hirano Y., Sugimoto K.. Requirement of the Mre11 complex and exonuclease 1 for activation of the Mec1 signaling pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004; 24:10016–10025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Zierhut C., Diffley J.F.. Break dosage, cell cycle stage and DNA replication influence DNA double strand break response. EMBO J. 2008; 27:1875–1885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Lee M.S., Henry M., Silver P.A.. A protein that shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm is an important mediator of RNA export. Genes Dev. 1996; 10:1233–1246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Libri D., Dower K., Boulay J., Thomsen R., Rosbash M., Jensen T.H.. Interactions between mRNA export commitment, 3΄-end quality control, and nuclear degradation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002; 22:8254–8266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Hilleren P., McCarthy T., Rosbash M., Parker R., Jensen T.H.. Quality control of mRNA 3΄-end processing is linked to the nuclear exosome. Nature. 2001; 413:538–542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Kallehauge T.B., Robert M.C., Bertrand E., Jensen T.H.. Nuclear retention prevents premature cytoplasmic appearance of mRNA. Mol. Cell. 2012; 48:145–152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Babour A., Shen Q., Dos-Santos J., Murray S., Gay A., Challal D., Fasken M., Palancade B., Corbett A., Libri D. et al. . The Chromatin Remodeler ISW1 Is a Quality Control Factor that Surveys Nuclear mRNP Biogenesis. Cell. 2016; 167:1201–1214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Tran P.T., Erdeniz N., Dudley S., Liskay R.M.. Characterization of nuclease-dependent functions of Exo1p in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. DNA Repair (Amst). 2002; 1:895–912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Cotta-Ramusino C., Fachinetti D., Lucca C., Doksani Y., Lopes M., Sogo J., Foiani M.. Exo1 processes stalled replication forks and counteracts fork reversal in checkpoint-defective cells. Mol. Cell. 2005; 17:153–159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Maringele L., Lydall D.. EXO1-dependent single-stranded DNA at telomeres activates subsets of DNA damage and spindle checkpoint pathways in budding yeast yku70Delta mutants. Genes Dev. 2002; 16:1919–1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Tsubouchi H., Ogawa H.. Exo1 roles for repair of DNA double-strand breaks and meiotic crossing over in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2000; 11:2221–2233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Savage K.I., Gorski J.J., Barros E.M., Irwin G.W., Manti L., Powell A.J., Pellagatti A., Lukashchuk N., McCance D.J., McCluggage W.G. et al. . Identification of a BRCA1-mRNA splicing complex required for efficient DNA repair and maintenance of genomic stability. Mol. Cell. 2014; 54:445–459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.