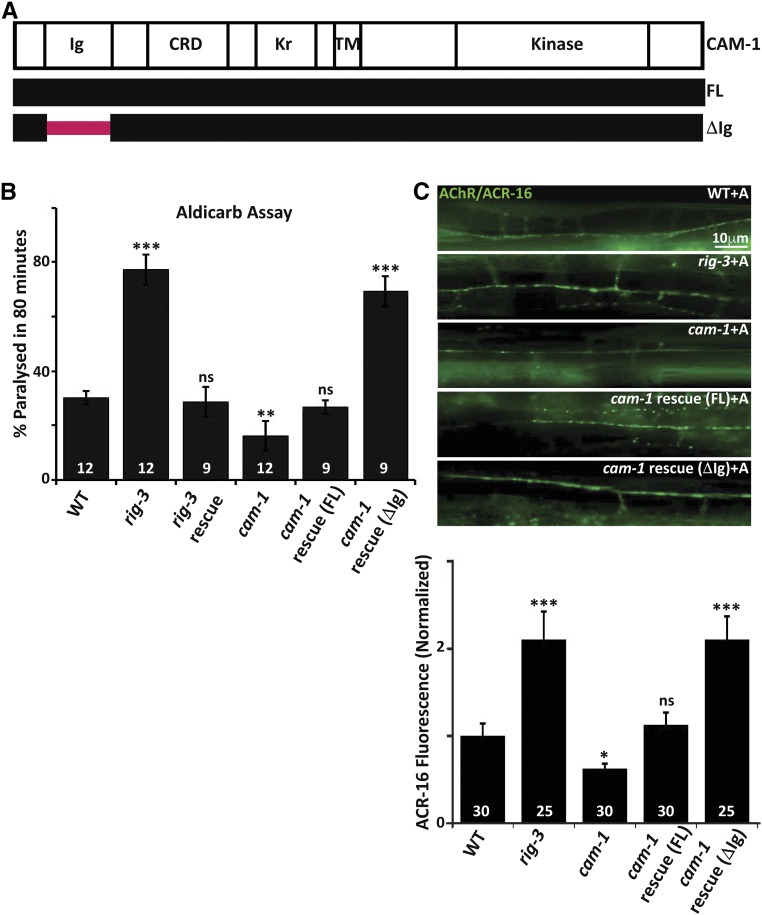
Figure 1.
RIG-3 functions through the Ig domain of CAM-1. (A) Schematic of CAM-1: the panel indicates schematic representations of CAM-1 domains for Full Length (FL) CAM-1, and the CAM-1 coding sequence lacking the Immunoglobulin domain, i.e., CAM-1(ΔIg). CRD, Cysteine Rich Domain; Kr, Kringle domain; TM, Transmembrane domain. (B) Aldicarb assays of rig-3 and cam-1 mutants and their rescue lines: this panel indicates a bar- graph showing the percentage of C. elegans paralyzed on aldicarb at the end of 80 min. In all figures, mutant and rescue lines were tested against control WT animals for significant differences. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, and *** P < 0.001. The numbers at the base of the bars for all figures showing aldicarb assays indicates number of times the assay was performed with 15–25 animals used for each trial. (C) Quantitation of AChR/ACR-16 in rig-3 and cam-1 mutants along with the CAM-1 rescue lines: the top portion of the panel shows images of AChR/ACR-16 tagged with GFP in control WT, rig-3, and cam-1 mutants, and CAM-1(FL) and CAM-1(ΔIg) rescue lines. The lower part of the panel shows quantitation of AChR/ACR-16 levels along the Ventral Nerve Cord (VNC). The numbers analyzed for each genotype are indicated. In all figures “+A” indicates “+Aldicarb,” where 1 mM aldicarb treatment was done for 80 min unless otherwise mentioned. In (B and C), the CAM-1 rescue experiments were done by expressing CAM-1 specifically in the body-wall muscle with the myo-3 promoter. In (B) and (C), RIG-3 rescue was done by expressing RIG-3 under it’s own promoter, which is expressed in cholinergic motor neurons. Error bars indicate SEM in all panels.