Figure 3.
GABAAR Trapping at Glutamatergic Synapses upon LiGluK2 Activation Modulates GABAAR Inter-synaptic Diffusion
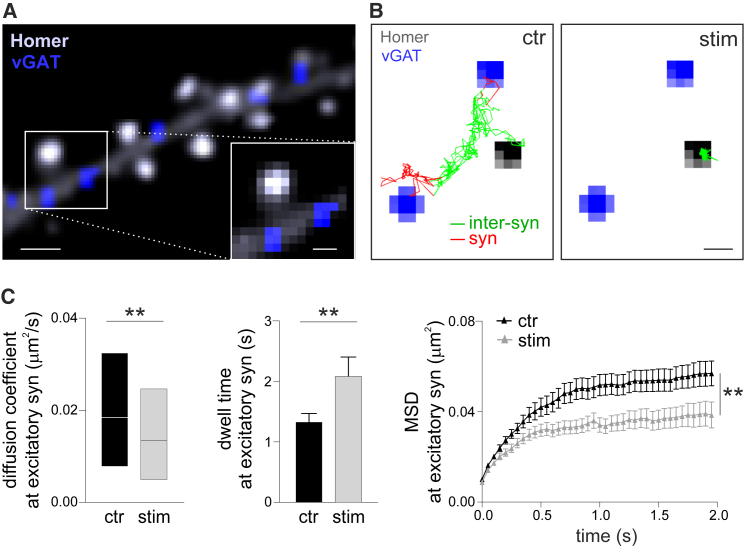
(A) Representative fluorescence image of inhibitory synapses (blue) and excitatory synapses (white). Scale bar, 1 μm. Inset: magnification of the framed area. Scale bar, 500 nm.
(B) Reconstructed inter-synaptic HA-GABAAR trajectories in the control (left) and upon LiGluK2 activation (right). Inhibitory synapses are in blue and excitatory synapses in gray. Inhibitory synaptic and inter-synaptic trajectories are represented in red and green, respectively. Scale bar, 500 nm.
(C) Left: Diffusion coefficient of HA-GABAAR at excitatory synapses in the control (ctr) (median = 0.017 μm2s−1, IQR = 0.006–0.032 μm2s−1, n = 187) and upon LiGluK2 activation (stim) (median = 0.012 μm2s−1, IQR = 0.004–0.023 μm2s−1, n = 208), p < 0.01, Mann-Whitney U-test; 15 neurons from 3 cultures. Middle: Dwell time of HA-GABAAR at excitatory synapses. Control (ctr), 1.3 ± 0.1 s, n = 122; LiGluK2 activation (stim), 2.1 ± 0.3 s, n = 100, p < 0.01, Mann-Whitney U-test; 15 neurons from 3 cultures. Right: MSD versus time plot of HA-GABAARs at excitatory synapses (steady state: ctr = 0.056 ± 0.005 μm2, n = 79; stim = 0.039 ± 0.005 μm2, n = 90, p < 0.01, Student’s t test); 15 neurons from 3 cultures. Unless otherwise stated, data are represented as mean ± SEM. Boxplots indicate the median and IQR.