Dear Editor,
Nocardia species are uncommon pathogens that affect immunosuppressed patients; although cerebral nocardiosis is a rare condition, it is associated with significant morbidity and mortality [1]. Because Nocardia species exhibit different antibiotic susceptibilities, accurate species identification is important for prognoses. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of Nocardia asiatica brain abscesses reported in a systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patient.
A 51-yr old man visited our emergency department on May 2016 complaining of left leg weakness, dysarthria, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and uncontrolled fever lasting three days. His past medical history consisted of SLE (diagnosed in August 2002) treated intermittently with steroid and platelet transfusion because of severe thrombocytopenia. In addition, in April 2015, he was diagnosed as having diabetes; however, no medical treatment had been undertaken. His last admission to hospital, due to severe thrombocytopenia (6×109/L), was two months prior to this presentation. He was subsequently treated with danazol (400 mg twice daily), hydroxychloroquine (200 mg twice daily), methotrexate (15 mg/week), and prednisolone (15 mg/day).
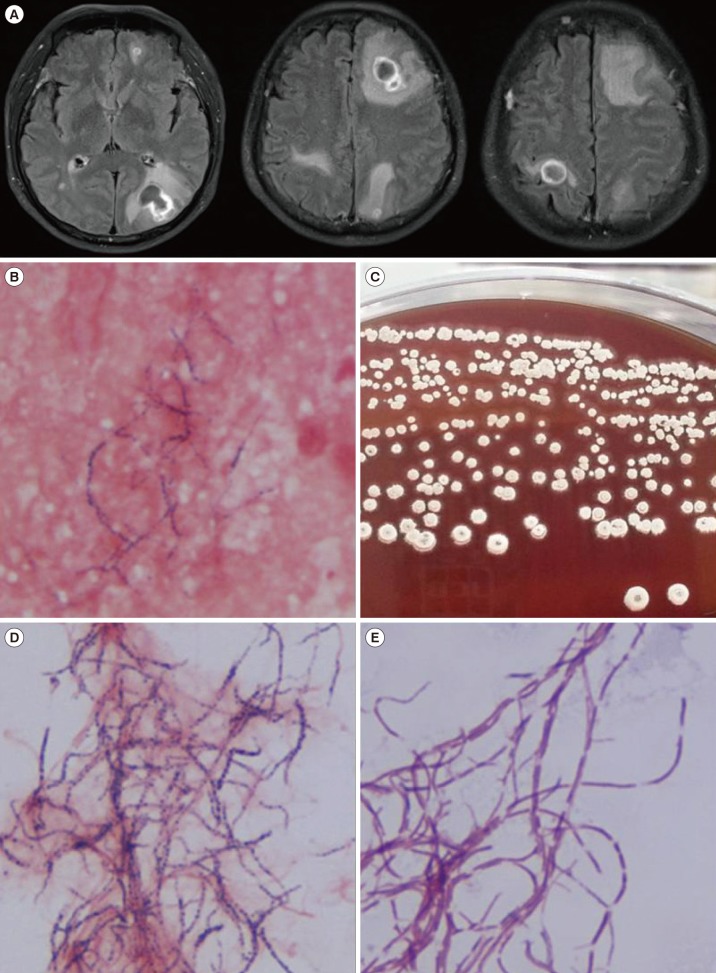
At presentation, the patient's temperature was 39.1℃, and blood tests indicated a white blood cell count of 11.03×109/L with a differential count of 76.2% neutrophils. Serum C-reactive protein (71.9 mg/L) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (28 mm/hr) were elevated. Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed multiple contrast-enhanced lesions in both cerebral and cerebellar hemispheres (Fig. 1A). A subsequent brain abscess aspiration removed 5 mL of a yellowish aspirate; Gram staining of the aspirate revealed gram-positive filamentous branched bacilli, and specimen culturing on blood agar plates for 48 hr at 37℃ under aerobic conditions yielded white, rough, and dry colonies, which also presented gram-positive filamentous branched bacilli and were modified acid fast bacilli stain-positive (Fig. 1B-E). 16S rRNA gene sequencing was performed for isolate identification according to the CLSI guidelines with primer pair forward 4F and reverse 801R [2]. The isolate 16S rRNA sequence (671 bp; GenBank accession number KY417120) showed 100% homology with N. asiatica (KC333452.1) and N. abscessus (GU471235.1). Alternative gene targets, such as the secA1 gene, are necessary for accurate species discrimination in the Nocardia asteroides group, because several N. asiatica, N. abscessus, N. asteroides, and N. arthritidis strains share ≥99.6% identity [2]. Thus, gene amplification and additional sequencing of secA1 were performed with primer pair forward F47 and reverse ConR. The results (497; KY417121) showed 99.4% (494/497) and 94.2% (468/497) similarity with N. asiatica (JQ773453.1) and N. abscessus (GU179083.1), respectively. The organism was finally identified as N. asiatica. Following treatment with trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX, 480 mg/day) and ceftriaxone (4 g/day) for one month, clinical conditions and brain MRI findings improved. Due to severe thrombocytopenia and the elevation of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine transaminase level, he was not taken the sufficient antibiotic treatment. Eventually he visited emergency room due to brain multifocal hemorrhage with septic emboli and aggravation of pulmonary aspergillosis. At ten months of follow up, the patient died during treatment.
Fig. 1. Brain infection from Nocardia asiatica. (A) Brain magnetic resonance images; multiple peripheral enhancing lesions with diffusion restriction in bilateral cerebral and cerebellar hemispheres, suggestive of abscess, (B) microscopic morphology of filamentous, branching, gram-positive bacilli in abscess aspirates, (C) colony morphology on a blood agar plate, (D) Gram stain of a cultured colony and (E) modified acid fast bacilli stain of a cultured colony.
Nocardia infection in SLE has been reported to have a high mortality rate (35%), which more than doubles (75%) when the CNS is involved [3]. Nocardial brain abscesses can be misdiagnosed as malignant brain tumors [4] and can mimic the presentations of underlying disorder flare-ups in SLE patients [5]. Therefore, the possibility of Nocardia infection should be considered during the differential diagnosis of a cerebral lesion to ensure early diagnosis and treatment.
Several cases of N. asiatica infections have been reported in the literature; however, only four have involved brain abscess (Table 1) [6,7,8,9]. TMP-SMX is active against most Nocardia species; however, susceptibility is Nocardia species-dependent; N. otitidiscaviarum is commonly resistant to TMP-SMX, while N. nova and N. farcinica are occasionally resistant [1]. Therefore, identification to the species level is required to determine appropriate treatment. Furthermore, species formerly included in the N. asteroides complex are now considered distinct species. Importantly, our case demonstrates that secA1 sequence analysis provides better resolution to the species level in N. asteroides than 16S rRNA sequence analysis [2].
Table 1. Summary of brain abscess cases due to Nocardia asiatica.
| Year reported | Sex/Age | Predisposing factor | Primary focus | Dissemination | Treatment | Outcome (follow-up period) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Underlying disease | Medication | ||||||
| 2008 [6] | M/73 | No | No | Brain | (−) | Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim, minocycline | Alive (24 months) |
| 2009 [7] | M/40s | Guillain–Barré syndrome | No | Brain | (-) | Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim, imipenem, cilastatin, minocycline | Alive (12 months) |
| 2012 [8] | M/49 | Myasthenia Gravis, Malignant thymoma | Prednisone | Mediastinum | (+) | Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim, amikacin, imipenem | Alive (5 months) |
| 2016 [9] | M/65 | Autoimmune hemolytic anemia | Prednisolone | Lung | (+) | Ceftriaxone, sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim | Alive (5 months) |
| Present case | M/51 | Systemic Lupus Erythematosus | Prednisolone | Brain | (−) | Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim, ceftriaxone, minocycline, amoxicillin/clavulanic acid | Expire (10 months) |
Here, we present the first case of multiple brain abscesses caused by N. asiatica in an SLE patient. The possibility of Nocardia infection should be considered in SLE patients, and early and accurate identification of Nocardia species is essential for successful treatment. And the administration of prolonged oral antimicrobial treatment after primary infection is also necessary for good prognosis.
Footnotes
Authors' Disclosures of Potential Conflicts of Interest: No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
References
- 1.Wilson JW. Nocardiosis: updates and clinical overview. Mayo Clin Proc. 2012;87:403–407. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2011.11.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Interpretive criteria for identification of bacteria and fungi by DNA target sequencing. Approved guideline. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; 2008. CLSI document MM18-A. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mc-Nab P, Fuentealba C, Ballesteros F, Pacheco D, Alvarez M, Dabanch J, et al. Nocardia asteroides infection in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rev Med Chil. 2000;128:526–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Yamada SM, Nakai E, Toyonaga S, Nakabayashi H, Park KC, Shimizu K. A rapidly enlarging Nocardial brain abscess mimicking malignant glioma. J Nippon Med Sch. 2005;72:308–311. doi: 10.1272/jnms.72.308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cheng HM, Huang DF, Leu HB. Disseminated nocardiosis with initial manifestation mimicking disease flare-up of systemic lupus erythematosus in an SLE patient. Am J Med. 2005;118:1297–1298. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2005.03.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wakui D, Ito H, Ikeda R, Yoshida Y, Furuya Y, Tanaka K, et al. A complicated case of Nocardia brain abscess for differential diagnosis. No Shinkei Geka. 2008;36:1011–1016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ryu A, Kawahara R, Mori K, Tamura M, Nakano K, Yoshioka A, et al. A case of brain abscess caused by Nocardia asiatica. J Jpn Soc Clin Microbiol. 2009;19:163–170. [Google Scholar]
- 8.El-Herte RI, Kanj SS, Araj GF, Chami H, Gharzuddine W. First report of Nocardia asiatica presenting as an anterior mediastinal mass in a patient with myasthenia gravis: a case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Infect Dis. 2012;2012:325767. doi: 10.1155/2012/325767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Uneda A, Suzuki K, Okubo S, Hirashita K, Yunoki M, Yoshino K. Brain abscess caused by Nocardia asiatica. Surg Neurol Int. 2016;7:74. doi: 10.4103/2152-7806.186509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]