Abstract
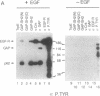
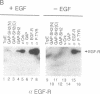
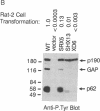
Cytoplasmic proteins that regulate signal transduction or induce cellular transformation, including cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases, p21ras GTPase-activating protein (GAP), phospholipase C gamma, and the v-crk oncoprotein, possess one or two copies of a conserved noncatalytic domain, Src homology region 2 (SH2). Here we provide direct evidence that SH2 domains can mediate the interactions of these diverse signaling proteins with a related set of phosphotyrosine ligands, including the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor. In src-transformed cells GAP forms heteromeric complexes, notably with a highly tyrosine phosphorylated 62-kDa protein (p62). The stable association between GAP and p62 can be specifically reconstituted in vitro by using a bacterial polypeptide containing only the N-terminal GAP SH2 domain. The efficient phosphorylation of p62 by the v-Src or v-Fps tyrosine kinases depends, in turn, on their SH2 domains and correlates with their transforming activity. In lysates of EGF-stimulated cells, the N-terminal GAP SH2 domain binds to both the EGF receptor and p62. Fusion proteins containing GAP or v-Crk SH2 domains complex with similar phosphotyrosine proteins from src-transformed or EGF-stimulated cells but with different efficiencies. SH2 sequences, therefore, form autonomous domains that direct signaling proteins, such as GAP, to bind specific phosphotyrosine-containing polypeptides. By promoting the formation of these complexes, SH2 domains are ideally suited to regulate the activation of intracellular signaling pathways by growth factors.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adari H., Lowy D. R., Willumsen B. M., Der C. J., McCormick F. Guanosine triphosphatase activating protein (GAP) interacts with the p21 ras effector binding domain. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):518–521. doi: 10.1126/science.2833817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calés C., Hancock J. F., Marshall C. J., Hall A. The cytoplasmic protein GAP is implicated as the target for regulation by the ras gene product. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):548–551. doi: 10.1038/332548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Hanafusa H. N-terminal deletions in Rous sarcoma virus p60src: effects on tyrosine kinase and biological activities and on recombination in tissue culture with the cellular src gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2789–2795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeClue J. E., Martin G. S. Linker insertion-deletion mutagenesis of the v-src gene: isolation of host- and temperature-dependent mutants. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):542–554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.542-554.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeClue J. E., Sadowski I., Martin G. S., Pawson T. A conserved domain regulates interactions of the v-fps protein-tyrosine kinase with the host cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9064–9068. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D. G., Mulholland J., Zhu Z. M., Botstein D. Homology of a yeast actin-binding protein to signal transduction proteins and myosin-I. Nature. 1990 Jan 18;343(6255):288–290. doi: 10.1038/343288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis C., Moran M., McCormick F., Pawson T. Phosphorylation of GAP and GAP-associated proteins by transforming and mitogenic tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):377–381. doi: 10.1038/343377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Kris R. M., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Evidence that autophosphorylation of solubilized receptors for epidermal growth factor is mediated by intermolecular cross-phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):925–929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Identification of multiple novel polypeptide substrates of the v-src, v-yes, v-fps, v-ros, and v-erb-B oncogenic tyrosine protein kinases utilizing antisera against phosphotyrosine. Oncogene. 1988 Apr;2(4):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Morrison D. K., Wong G., McCormick F., Williams L. T. PDGF beta-receptor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of GAP and association of GAP with a signaling complex. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90220-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Ellis C., Pawson T., Cooper J. A. Binding of GAP to activated PDGF receptors. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1578–1581. doi: 10.1126/science.2157284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Moran M., Sadowski I., Pawson T. The common src homology region 2 domain of cytoplasmic signaling proteins is a positive effector of v-fps tyrosine kinase function. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4131–4140. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriz R., Lin L. L., Sultzman L., Ellis C., Heldin C. H., Pawson T., Knopf J. Phospholipase C isozymes: structural and functional similarities. Ciba Found Symp. 1990;150:112–127. doi: 10.1002/9780470513927.ch8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau A. F. Phosphotyrosine-containing 120,000-dalton protein coimmunoprecipitated with pp60v-src from Rous sarcoma virus-transformed mammalian cells. Virology. 1986 May;151(1):86–99. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90106-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Zilberstein A., Franks C., Felder S., Kremer S., Ullrich A., Rhee S. G., Skorecki K., Schlessinger J. Effect of phospholipase C-gamma overexpression on PDGF-induced second messengers and mitogenesis. Science. 1990 May 4;248(4955):607–610. doi: 10.1126/science.2333512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall M. S., Hill W. S., Ng A. S., Vogel U. S., Schaber M. D., Scolnick E. M., Dixon R. A., Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B. A C-terminal domain of GAP is sufficient to stimulate ras p21 GTPase activity. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1105–1110. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03480.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hamaguchi M., Hanafusa H. A novel viral oncogene with structural similarity to phospholipase C. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):272–275. doi: 10.1038/332272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hamaguchi M., Hanafusa H. Characterization of p47gag-crk, a novel oncogene product with sequence similarity to a putative modulatory domain of protein-tyrosine kinases and phospholipase C. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):907–914. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hanafusa H. Association of the v-crk oncogene product with phosphotyrosine-containing proteins and protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2638–2642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy C. J., Bottaro D. P., Fleming T. P., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., Aaronson S. A. PDGF induction of tyrosine phosphorylation of GTPase activating protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):711–714. doi: 10.1038/342711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran M. F., Koch C. A., Sadowski I., Pawson T. Mutational analysis of a phosphotransfer motif essential for v-fps tyrosine kinase activity. Oncogene. 1988 Dec;3(6):665–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Non-catalytic domains of cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases: regulatory elements in signal transduction. Oncogene. 1988 Nov;3(5):491–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond V. W., Parsons J. T. Identification of an amino terminal domain required for the transforming activity of the Rous sarcoma virus src protein. Virology. 1987 Oct;160(2):400–410. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. B., Kanner S. B., Wang H. C., Parsons J. T. Stable association of activated pp60src with two tyrosine-phosphorylated cellular proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3951–3958. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Lee S. Y. Studies of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):546–550. doi: 10.1126/science.2541501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodaway A. R., Sternberg M. J., Bentley D. L. Similarity in membrane proteins. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):624–624. doi: 10.1038/342624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Stone J. C., Pawson T. A noncatalytic domain conserved among cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases modifies the kinase function and transforming activity of Fujinami sarcoma virus P130gag-fps. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4396–4408. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl M. L., Ferenz C. R., Kelleher K. L., Kriz R. W., Knopf J. L. Sequence similarity of phospholipase C with the non-catalytic region of src. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):269–272. doi: 10.1038/332269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., McCormick F. A cytoplasmic protein stimulates normal N-ras p21 GTPase, but does not affect oncogenic mutants. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):542–545. doi: 10.1126/science.2821624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., Wong G., Halenbeck R., Rubinfeld B., Martin G. A., Ladner M., Long C. M., Crosier W. J., Watt K., Koths K. Molecular cloning of two types of GAP complementary DNA from human placenta. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1697–1700. doi: 10.1126/science.3201259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchie H., Chang C. H., Yoshida M., Vogt P. K. A newly isolated avian sarcoma virus, ASV-1, carries the crk oncogene. Oncogene. 1989 Nov;4(11):1281–1284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verderame M. F., Kaplan J. M., Varmus H. E. A mutation in v-src that removes a single conserved residue in the SH-2 domain of pp60v-src restricts transformation in a host-dependent manner. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):338–348. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.338-348.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel U. S., Dixon R. A., Schaber M. D., Diehl R. E., Marshall M. S., Scolnick E. M., Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B. Cloning of bovine GAP and its interaction with oncogenic ras p21. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):90–93. doi: 10.1038/335090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. C., Parsons J. T. Deletions and insertions within an amino-terminal domain of pp60v-src inactivate transformation and modulate membrane stability. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):291–302. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.291-302.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]