Figure 1.
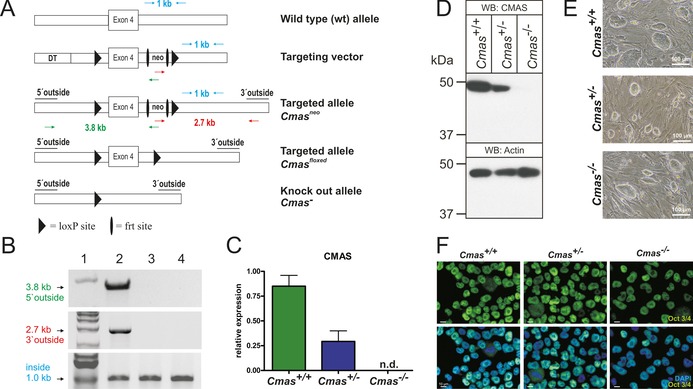
Targeting strategy and characterisation of CMAS‐deficient mESC. A) Cmas targeting strategy. Targeting vector with diphtheria toxin cassette (DT) to increase homologous recombination, frt‐flanked neomycin resistance cassette (neo), exon 4 and neo flanked by LoxP sites. Correct homologous integration of the targeting vector into ES cells was confirmed by the neo and a 5′ outside primer pair (green arrows; amplifying a 3.8 kb fragment) and by neo and a 3′ outside primer pair (red arrows; amplifying a 2.7 kb fragment). Inside primers were used as a control (light blue arrows; 1 kb fragment). Correctly targeted mESCs were used to generate mutant mice. The neo cassette was deleted by inter‐crosses with ACTFLPe mice, and exon 4 and the remaining frt site were deleted by crosses with Zp3‐cre mice, thereby resulting in the Cmas knock‐out allele. B) PCR analysis of homologous integration. A PCR product of 3.8 kb was amplified with neo‐ and 5′ outside primers (green in A), and a 2.7 kb product was amplified with neo‐ and 3′ outside primers (red in A). Both fragments occurred correctly only in the targeted Cmas neo mESC (lane 2), not in wild‐type mESC (lane 3) or in wild‐type mouse tail tissue (lane 4). A 1 kb PCR fragment from inside primers served as control for the PCR reaction (blue in A). 1 kb marker in lane 1. C) Quantitative PCR of Cmas expression from feeder‐free cultures of Cmas +/+, Cmas +/− and Cmas −/− mESCs (n=3 of one representative cell line with the respective genotype). n.d.=not detectable. D) Cell lysates of Cmas +/+, Cmas +/− and Cmas −/− mESC were separated by SDS‐PAGE, blotted and immunostained with anti‐CMAS antibody. The 48 kDa CMAS protein was detected in Cmas +/+ and Cmas +/− lysates but not in Cmas −/−. Anti‐actin staining was used as loading control. E) Morphology of Cmas +/+, Cmas +/− and Cmas −/− mESC cultured on MEFs supplemented with LIF. F) Indirect immunofluorescence staining of Oct3/4 in Cmas +/+, Cmas +/− and Cmas −/− mESC cultured feeder‐free with LIF supplementation. Representative results from one cell line per genotype are shown in D)–F).
