Figure 2. LRP6 is a coreceptor of PAR2.
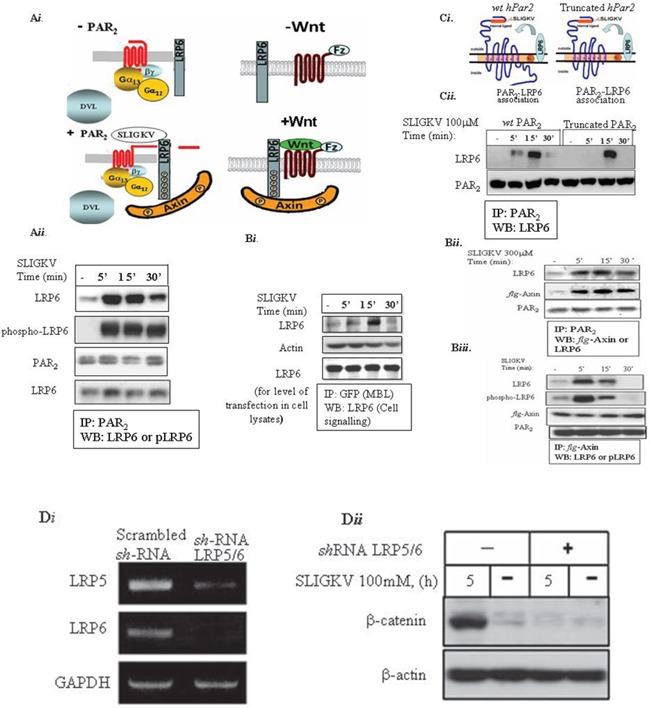
(Ai) A scheme of PAR2 and co-receptor LRP6 (Aii) HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with HA-Lrp6, wt hPar2 and flg-Axin. Following SLIGKV PAR2 activation, co-immunoprecipitation assay was carried out using anti-PAR2 abs, and LRP6 was detected following application of anti-HA (LRP6) antibodies. As early as 5 min following PAR2 activation and for up to 30 min, PAR2 and LRP6 were shown to be within the same immune complex. LRP6 phosphorylation was detected by anti-phospho-LRP6 abs. (Aiii) HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with HA-Lrp6 and YFP- hPar2. Following SLIGKV PAR2 activation, co-immunoprecipitation assay was carried out using anti-GFP abs (MBL), and LRP6 was detected following application of anti-HA (LRP6) antibodies. (Bi) Axin is present within the immune-complex of PAR2 and LRP6. Immunoprecipitation using anti-PAR2 abs shows distinct co-association with Axin as detected by anti-flg antibody application. (Bii) Axin is present in a complex with LRP6 following SLIGKV PAR2 activation. Immunoprecipitation analysis of HEK293T cells following PAR2 SLIGKV activation was carried out using anti-flg-Axin. Detection by either anti-phospho-LRP6 abs or anti-LRP6 showed a profound presence within the same immune complex of LRP6 and Axin. (Ci) A truncated form of PAR2 associates with LRP6. A scheme representing PAR2 and the coreceptor LRP6 association. (Cii) HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with Lrp6, wt hPar2, and truncated hPar2. Following SLIGKV PAR2 activation, co-immunoprecipitation was carried out using anti-PAR2 abs and LRP6 was detected by application of anti-LRP6. For 5 min following PAR2 activation and for up to 30 min, PAR2 and LRP6 were found within the same immune complex. This binding association also occurred when a truncated hPar2 was used. (Di) shRNA-LRP5/6 inhibits effectively LRP5&6 levels. Total cell RNA isolated from HEK-293T cells that were infected either with shRNA-LRP5/6 or nonspecific scrambled shRNA was isolated and RT-PCR analysis was performed using primers for LRP5, LRP6, and GAPDH (used as the internal control). shRNA-LRP5/6 effectively inhibited LRP5/6 levels. (Dii) shRNA-LRP5/6 inhibits PAR2-induced β-catenin stabilization. HEK-293T cells were transfected with flg-β-catenin and hPar2-wt following infection with shRNA-LRP5/6 viral vectors. Next, the cells were activated with SLIGKV (100μM, 5hr). Lysates were prepared and immunoblots were detected using both anti-flg (for flg-β-catenin) and anti-β-actin as a control for protein loading. The shRNA constructs significantly inhibited PAR2-induced β-catenin stabilization.
