Figure 4. In-silico docking studies of LRP6 with PAR2.
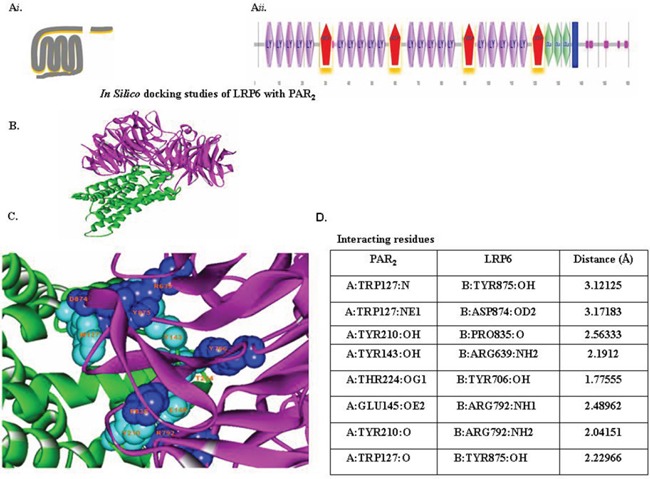
(Ai) Schematic presentation of PAR2. (Aii) Schematic presentation of LRP6. The domains present in LRP6 were predicted by Bioinformatics Tool SMART (Simple Modular Architecture Research Tool), an online resource (http://smart.embl.de/) that allows identification and annotation of genetically mobile domains and analysis of domain architecture. LRP6, a member of LDLR family, consists of four EGF domains and three LDL repeats (LDLR). (B) Protein-protein docking study. Interaction between LRP6 (magenta) with PAR2 (green) were determined with the ZDOCK protein–protein docking server, based on a Fourier transform method to search all possible binding modes for the applied proteins. Finally, most probable predictions were ranked on the basis on geometry, hydrophobicity, and electrostatic complementarity of the molecular surface using ZDOCK. (C) Determination of interacting residues (e.g., LRP6 with PAR2). The interacting residues are shown in CPK (Corey-Pauling-Koltun), a ball-shaped interacting amino acid residue, with cyan CPK for PAR2 and blue CPK for LRP6. (D) List of PAR2 and LRP6 interacting residues.
