Abstract
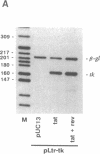
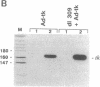
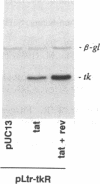
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIVs) primarily infect CD4+ T lymphocytes, leading eventually to the development of a systemic immune dysfunction termed acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). An attractive strategy to combat HIV-mediated pathogenesis would be to eliminate the initial pool of infected cells and thus prevent disease progression. We have engineered a replication-defective, conditionally cytotoxic adenovirus vector, Ad-tk, whose action is dependent on the targeted expression of the herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase gene (tk), cloned downstream of the HIV-1 long terminal repeat, in human cells expressing the HIV-1 transcriptional activator Tat. Infection of Tat-expressing human HeLa or Jurkat cells with Ad-tk resulted in high-level tk expression, which was not deleterious to the viability of these cells. However, in the presence of the antiherpetic nucleoside analog ganciclovir, Ad-tk infection resulted in a massive reduction in the viability of these Tat-expressing cell lines. As adenoviruses are natural passengers of the human lymphoid system, our results suggest adenovirus vector-based strategies for the targeted expression, under the control of cis-responsive HIV regulatory elements, of cytotoxic agents in HIV-infected cells for the therapy of HIV-mediated pathogenesis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli E., Heyman R., Hsi M., Evans R. M. Targeting of an inducible toxic phenotype in animal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7572–7576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Sharp P. A. Regulation by HIV Rev depends upon recognition of splice sites. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):789–795. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90602-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary V. K., Mizukami T., Fuerst T. R., FitzGerald D. J., Moss B., Pastan I., Berger E. A. Selective killing of HIV-infected cells by recombinant human CD4-Pseudomonas exotoxin hybrid protein. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):369–372. doi: 10.1038/335369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C., Huang E. S., Lin J. C., Mar E. C., Pagano J. S., Dutschman G. E., Grill S. P. Unique spectrum of activity of 9-[(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxy)methyl]-guanine against herpesviruses in vitro and its mode of action against herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2767–2770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Stacy T. P. Identification of sequences in the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene required for efficient processing and polyadenylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2104–2113. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Regulatory pathways governing HIV-1 replication. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90420-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion G. B., Furman P. A., Fyfe J. A., de Miranda P., Beauchamp L., Schaeffer H. J. Selectivity of action of an antiherpetic agent, 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl) guanine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5716–5720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S. The human immunodeficiency virus: infectivity and mechanisms of pathogenesis. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):617–622. doi: 10.1126/science.3277274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A. Replication and pathogenesis of the AIDS virus. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1988;1(3):217–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman R. A., Borrelli E., Lesley J., Anderson D., Richman D. D., Baird S. M., Hyman R., Evans R. M. Thymidine kinase obliteration: creation of transgenic mice with controlled immune deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2698–2702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath J., Palkonyay L., Weber J. Group C adenovirus DNA sequences in human lymphoid cells. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):189–192. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.189-192.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath J., Weber J. M. Nonpermissivity of human peripheral blood lymphocytes to adenovirus type 2 infection. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):341–345. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.341-345.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. Isolation of adenovirus type 5 host range deletion mutants defective for transformation of rat embryo cells. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):683–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor Q. S., Chinnadurai G. Method for introducing site-specific mutations into adenovirus 2 genome: construction of a small deletion mutant in VA-RNAI gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2184–2188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavery D., Fu S. M., Lufkin T., Chen-Kiang S. Productive infection of cultured human lymphoid cells by adenovirus. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1466–1472. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1466-1472.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Hauber J., Le S. Y., Maizel J. V., Cullen B. R. The HIV-1 rev trans-activator acts through a structured target sequence to activate nuclear export of unspliced viral mRNA. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):254–257. doi: 10.1038/338254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar E. C., Chiou J. F., Cheng Y. C., Huang E. S. Inhibition of cellular DNA polymerase alpha and human cytomegalovirus-induced DNA polymerase by the triphosphates of 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine and 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):776–780. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.776-780.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Fisher E. F., Caruthers M. H., Berk A. J. Resolving the functions of overlapping viral genes by site-specific mutagenesis at a mRNA splice site. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):380–384. doi: 10.1038/295380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G. J., Rice S. A., Knipe D. M., Baltimore D. Alternative mechanisms for activation of human immunodeficiency virus enhancer in T cells. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1299–1302. doi: 10.1126/science.2830675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Read E., Gallo R. C. Detection, isolation, and continuous production of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.6200935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice A. P., Mathews M. B. Trans-activation of the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat sequences, expressed in an adenovirus vector, by the adenovirus E1A 13S protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4200–4204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiki M., Inoue J., Hidaka M., Yoshida M. Two cis-acting elements responsible for posttranscriptional trans-regulation of gene expression of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7124–7128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Marciniak R. A. HIV TAR: an RNA enhancer? Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):229–230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90279-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair M. H., Furman P. A., Lubbers C. M., Elion G. B. Inhibition of cellular alpha and virally induced deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases by the triphosphate of acyclovir. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):741–745. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Till M. A., Ghetie V., Gregory T., Patzer E. J., Porter J. P., Uhr J. W., Capon D. J., Vitetta E. S. HIV-infected cells are killed by rCD4-ricin A chain. Science. 1988 Nov 25;242(4882):1166–1168. doi: 10.1126/science.2847316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zack J. A., Cann A. J., Lugo J. P., Chen I. S. HIV-1 production from infected peripheral blood T cells after HTLV-I induced mitogenic stimulation. Science. 1988 May 20;240(4855):1026–1029. doi: 10.1126/science.2835813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagury D., Bernard J., Leonard R., Cheynier R., Feldman M., Sarin P. S., Gallo R. C. Long-term cultures of HTLV-III--infected T cells: a model of cytopathology of T-cell depletion in AIDS. Science. 1986 Feb 21;231(4740):850–853. doi: 10.1126/science.2418502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]