Abstract
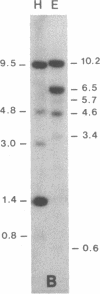
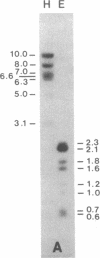
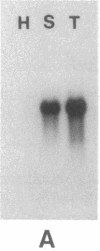
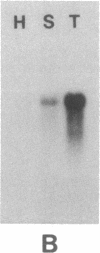
Healthy tobacco plants accumulate beta-1,3-glucanases (glucan endo-1,3-beta-glucosidase; EC 3.2.1.39) in their roots and in specific parts of the flowers. After infection with tobacco mosaic virus, acidic and basic beta-1,3-glucanases are induced in the inoculated and virus-free leaves of the plant. An analysis of cDNA clones demonstrated that at least five genes for acidic beta-1,3-glucanases are induced after tobacco mosaic virus infection. Southern blot analysis indicated that the tobacco genome contains approximately eight genes for acidic beta-1,3-glucanases and a smaller number of genes encoding basic beta-1,3-glucanases. Genes from both gene families were cloned and sequenced. The basic isozymes contain a C-terminal extension that is cleaved off during their targeting to the vacuoles. This extension is absent in the acidic isozymes, which accumulate extracellularly. Northern blot hybridization showed that genes encoding acidic and basic beta-1,3-glucanases are strongly induced after tobacco mosaic virus infection or salicylate treatment of tobacco. The cloning of these genes is a first step toward the identification of regulatory elements involved in their coordinate induction.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bulcke M. V., Bauw G., Castresana C., Van Montagu M., Vandekerckhove J. Characterization of vacuolar and extracellular beta(1,3)-glucanases of tobacco: Evidence for a strictly compartmentalized plant defense system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2673–2677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelissen B. J., Horowitz J., van Kan J. A., Goldberg R. B., Bol J. F. Structure of tobacco genes encoding pathogenesis-related proteins from the PR-1 group. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):6799–6811. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.6799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Loose M., Alliotte T., Gheysen G., Genetello C., Gielen J., Soetaert P., Van Montagu M., Inzé D. Primary structure of a hormonally regulated beta-glucanase of Nicotiana plumbaginifolia. Gene. 1988 Oct 15;70(1):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90100-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffmann S., Legrand M., Geoffroy P., Fritig B. Biological function of ;pathogenesis-related' proteins: four PR proteins of tobacco have 1,3-beta-glucanase activity. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3209–3212. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02637.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrand M., Kauffmann S., Geoffroy P., Fritig B. Biological function of pathogenesis-related proteins: Four tobacco pathogenesis-related proteins are chitinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6750–6754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linthorst H. J., van Loon L. C., van Rossum C. M., Mayer A., Bol J. F., van Roekel J. S., Meulenhoff E. J., Cornelissen B. J. Analysis of acidic and basic chitinases from tobacco and petunia and their constitutive expression in transgenic tobacco. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1990 Jul-Aug;3(4):252–258. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-3-252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan T., Ori N., Fluhr R. Pathogenesis-related proteins are developmentally regulated in tobacco flowers. Plant Cell. 1989 Sep;1(9):881–887. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.9.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauch F., Mauch-Mani B., Boller T. Antifungal Hydrolases in Pea Tissue : II. Inhibition of Fungal Growth by Combinations of Chitinase and beta-1,3-Glucanase. Plant Physiol. 1988 Nov;88(3):936–942. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.3.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Memelink J., Linthorst H. J., Schilperoort R. A., Hoge J. H. Tobacco genes encoding acidic and basic isoforms of pathogenesis-related proteins display different expression patterns. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Feb;14(2):119–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00018553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinshi H., Wenzler H., Neuhaus J. M., Felix G., Hofsteenge J., Meins F. Evidence for N- and C-terminal processing of a plant defense-related enzyme: Primary structure of tobacco prepro-beta-1,3-glucanase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5541–5545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Rhee M. D., Van Kan J. A., González-Jaén M. T., Bol J. F. Analysis of regulatory elements involved in the induction of two tobacco genes by salicylate treatment and virus infection. Plant Cell. 1990 Apr;2(4):357–366. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.4.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]