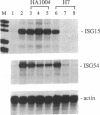
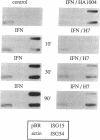
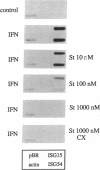
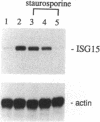
Abstract
Phospholipid/Ca2(+)-dependent protein kinase (protein kinase C; PKC) appears to be involved in the signal-transduction pathway mediated by human leukocyte interferon (IFN) in HeLa cells. IFN treatment results in a rapid increase in [3H]phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate binding to intact cells, indicating an activation of PKC. In addition, inhibitors of PKC (H7 and staurosporine) block the induction of antiviral activity by IFN against vesicular stomatitis virus. PKC inhibitors also block the accumulation of IFN-stimulated mRNAs in the cytoplasm of HeLa cells and suppress the transcriptional induction of IFN-stimulated genes. Activation of IFN-stimulated genes is mediated through a DNA response element that is necessary and sufficient for the transcriptional response to IFN. IFN treatment induces the appearance of several DNA-binding factors that specifically recognize the response element, and the appearance of these factors is suppressed by PKC inhibitors. This observation provides evidence that PKC activity is involved during IFN-stimulated signal transduction. Although activation of PKC appears to be required for the response to IFN, agonists of PKC activity alone do not turn on expression of IFN-stimulated genes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akai H., Larner A. C. Phorbol ester-mediated down-regulation of an interferon-inducible gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3252–3255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B., Peretz D., Vaiman D., Benech P., Chebath J. Enhancer-like interferon responsive sequences of the human and murine (2'-5') oligoadenylate synthetase gene promoters. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1411–1419. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02958.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale T. C., Imam A. M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Rapid activation by interferon alpha of a latent DNA-binding protein present in the cytoplasm of untreated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1203–1207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale T. C., Rosen J. M., Guille M. J., Lewin A. R., Porter A. G., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Overlapping sites for constitutive and induced DNA binding factors involved in interferon-stimulated transcription. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):831–839. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty R. W., Niedel J. E. Cytosolic calcium regulates phorbol diester binding affinity in intact phagocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4097–4100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch T., Zinn K., Maniatis T. Activation of the human beta-interferon gene requires an interferon-inducible factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):801–810. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faltynek C. R., Princler G. L., Gusella G. L., Varesio L., Radzioch D. A functional protein kinase C is required for induction of 2-5A synthetase by recombinant interferon-alpha A in Daudi cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14305–14311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner A. C., Chaudhuri A., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional induction by interferon. New protein(s) determine the extent and length of the induction. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):453–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner A. C., Jonak G., Cheng Y. S., Korant B., Knight E., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional induction of two genes in human cells by beta interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6733–6737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Biochemistry of interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:251–282. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Darnell J. E., Jr Cytoplasmic activation of ISGF3, the positive regulator of interferon-alpha-stimulated transcription, reconstituted in vitro. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1362–1371. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Reich N., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced nuclear factors that bind a shared promoter element correlate with positive and negative transcriptional control. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):383–393. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D., Larner A., Chaudhuri A., Babiss L. E., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-stimulated transcription: isolation of an inducible gene and identification of its regulatory region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8929–8933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. J., Decker T., Darnell J. E., Jr Alpha interferon and gamma interferon stimulate transcription of a single gene through different signal transduction pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5404–5411. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto M., Fujita T., Kimura Y., Maruyama M., Harada H., Sudo Y., Miyata T., Taniguchi T. Regulated expression of a gene encoding a nuclear factor, IRF-1, that specifically binds to IFN-beta gene regulatory elements. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):903–913. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91307-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer L. M., Strulovici B., Saltiel A. R. Interferon-alpha selectively activates the beta isoform of protein kinase C through phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6537–6541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine R., Decker T., Kessler D. S., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr Purification and cloning of interferon-stimulated gene factor 2 (ISGF2): ISGF2 (IRF-1) can bind to the promoters of both beta interferon- and interferon-stimulated genes but is not a primary transcriptional activator of either. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2448–2457. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. C., Chernajovsky Y., Dale T. C., Gilbert C. S., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Interferon response element of the human gene 6-16. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):85–92. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02786.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N. C., Darnell J. E., Jr Differential binding of interferon-induced factors to an oligonucleotide that mediates transcriptional activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3415–3424. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N., Evans B., Levy D., Fahey D., Knight E., Jr, Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced transcription of a gene encoding a 15-kDa protein depends on an upstream enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6394–6398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N., Pine R., Levy D., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcription of interferon-stimulated genes is induced by adenovirus particles but is suppressed by E1A gene products. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):114–119. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.114-119.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford M. N., Hannigan G. E., Williams B. R. Interferon-induced binding of nuclear factors to promoter elements of the 2-5A synthetase gene. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):751–759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02872.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nomoto H., Takahashi I., Kato Y., Morimoto M., Tomita F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari R. K., Kusari J., Kumar R., Sen G. C. Gene induction by interferons and double-stranded RNA: selective inhibition by 2-aminopurine. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4289–4294. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trilivas I., Brown J. H. Increases in intracellular Ca2+ regulate the binding of [3H]phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate to intact 1321N1 astrocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3102–3107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathelet M. G., Clauss I. M., Paillard F. C., Huez G. A. 2-Aminopurine selectively blocks the transcriptional activation of cellular genes by virus, double-stranded RNA and interferons in human cells. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Oct 1;184(3):503–509. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15043.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan C., Sehgal P. B., Tamm I. Signal transduction pathways in the induction of 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetase gene expression by interferon alpha/beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2243–2247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yap W. H., Teo T. S., Tan Y. H. An early event in the interferon-induced transmembrane signaling process. Science. 1986 Oct 17;234(4774):355–358. doi: 10.1126/science.2429366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S., Parker P. J., Ullrich A., Stabel S. Down-regulation of protein kinase C is due to an increased rate of degradation. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 15;244(3):775–779. doi: 10.1042/bj2440775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]