Abstract
Background
The aim was to investigate the clinical characteristics of lipid metabolism and the effect of apolipoprotein E (ApoE) gene polymorphism on lipid metabolism in hemodialysis patients.
Methods
The serum levels of total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDLC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDLC), ApoA1, ApoB, ApoE and lipoprotein Lp(a) were detected by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length (PCR-RFLP).
Results
The level of serum TG was significantly increased and the level of HDLC was significantly decreased in hemodialysis patients. Serum TG level was 33% higher than normal, and HDLC was 10.4% less than normal. The correlation analysis showed that TG level was significantly correlated with serum albumin level and extracorporeal circulation blood flow during dialysis. HDLC was significantly correlated with KT/V. The incidence of hypertension in hemodialysis patients was 73.6% and cardiovascular disease was 25%. The level of TG in the cardiovascular disease group was significantly higher than that in the non-cardiovascular disease group, and there was no significant difference between the hypertensive group and the non-hypertensive group. ApoE gene polymorphism test showed that the frequency of ApoE genotype ε3/3 and allele ε3 was the highest in hemodialysis patients, and the levels of TC, TG and LDLC were higher in ApoE genotype ε3/4 + ε4/4.
Conclusion
The levels of serum TG and ApoB were significantly increased in patients with hemodialysis, and HDLC and other indexes were significantly decreased. The level of TG in patients with cardiovascular complications was significantly higher than in patients without complications. TG level was significantly correlated with serum albumin level and extracorporeal circulation blood flow during dialysis. HDLC was significantly correlated with KT/V. Hemodialysis patients who had ApoE allele ε4 are prone to lipid metabolism disorders.
Keywords: Hemodialysis, Lipid, Apolipoprotein E, Gene polymorphism
Introduction
Considerable evidence has indicated that hemodialysis patients are often accompanied by lipid metabolism disorders, cardiovascular complications in patients with one of the important factors [1-5]. However, the etiology and underlying mechanism are not entirely clear. It may be related to renal dysfunction, dialysis adequacy, the type of dialysis membrane and uremia basic diseases, genetic and other factors [6-9]. Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) is an important component of very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and chylomicrons, which may play an important role in lipid metabolism [10-12]. Recently, an interesting study demonstrated that triacylglycerol (TAG) hydrolysis mediated by lipoprotein lipase in VLDL is accompanied by the release of surface material containing phospholipids, free cholesterol and ApoE and ApoCs (CII and CIII). The released molecules are accepted by HDL, and new HDL-sized ApoE-containing particles are also generated. A decrease in the number of HDL particles or abnormalities in their structure is associated with unfavourable changes in the features of VLDL remnants [11].
Its genetic polymorphism is an important genetic factor affecting lipid metabolism. As a matter of fact, approximately 14-17% variation of plasma cholesterol concentration can be associated with genetic polymorphism [13-16].
In a study reported by Echeverria et al, they performed a cross-sectional study to investigate the impact of 13 polymorphisms of nine genes affecting lipid metabolism. Polymorphisms were identified in the selected genes for their role in the development of atherogenic dyslipidemia including triglycerides and HDL [17]. At present, more and more studies on the relationship between ApoE gene polymorphism and lipid metabolism are being conducted in patients with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Dyslipidemia plays a major role determining the epidemic cardiovascular burden attributed to the metabolic syndrome. ApoE is involved on cholesterol and triglycerides metabolism regulation. If ApoE polymorphism influences lipid metabolism, it may bring on induced susceptibility to the development of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease [18-20].
However, the effect of ApoE gene polymorphism on lipid metabolism in hemodialysis patients has not been reported in China. In this study, polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length (PCR-RFLP) was used to detect the polymorphism of ApoE gene in hemodialysis patients and explore the effect of ApoE gene polymorphism on lipid metabolism in hemodialysis patients.
Materials and Methods
Research objects
Case group
A total of 112 patients with hemodialysis (58 males and 54 females) were included in this study, and the median age was 51 ± 11 years. Dialysis time was 2 - 21 years, an average of 6.1 ± 3.7 years. The primary disease was 86 cases of chronic glomerulonephritis, four cases of polycystic kidney disease, two cases of chronic pyelonephritis, two cases of chronic interstitial nephritis, two cases of systemic lupus erythematosus, and 16 cases of unknown causes. Hemodialysis was performed 12 h per week, by using arteriovenous fistula and acetate fiber membrane dialyzer. Anticoagulation with heparin sodium was applied in vitro, and blood flow was 200 - 250 mL/min. Bicarbonate dialysate was used, and dialysis fluid flow was approximately 500 mL/min. Patients did not take lipid-lowering drugs within 3 months, but those patients who had diabetes, liver dysfunction or were taking β-blockers were excluded.
Control group
A total of 372 healthy subjects (212 males and 160 females) were included, with a median age of 41 ± 8 years.
Research methods
Blood lipid detection methods
Total cholesterol (TC) and triglyceride (TG) were measured with enzymatic assay (British RANDOX Company). High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDLC) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDLC) were using direct method (Germany Bao Ling Man products). ApoA1, ApoB, ApoE, and Lp(a) were tested using immunoturbidimetry (provided by WAKO Co., Ltd, Japan).
Routine tests
Electrocardiogram, X-ray, blood tests, liver function, plasma protein, serum creatinine, urea nitrogen, and uric acid were determined before and after dialysis, and the KT/V value was calculated.
Cardiovascular check-up
The diagnosis of high blood pressure, ischemic heart disease, and cardiac insufficiency was made with reference to the related literature [9]. Cardiac enlargement was diagnosed based on the dry weight increase of greater than 50% on the chest X-ray radiograph at three times of measurement; cerebrovascular disease diagnosis was confirmed according to clinical manifestations in combination with CT examination.
ApoE gene polymorphism
By use of multi-PCR-RFLP analysis, the detailed procedures were described as follows. Primer design: the upstream sequence was 5′-AACAACTGACCCCGGTGGGG-3′, the downstream sequence was 5′-ATAA AT ATAAAATATAAATAATGGCGCTGAGGCCGCGCTC-3′, the length of the amplified product was 312 bp, and the length of the product fragment was 91, 83, 72, 61, 48, and 35 bp, respectively.
Extraction of genomic DNA
Rapid extraction and purification method of genomic DNA derived from small amounts of blood were performed according to the instructions provided by the Huashun products.
PCR
The 10 × buffer 2.5 µL, 25 mM magnesium chloride 2 µL, dNTP 200 µM, Taq DNA polymerase 1 U, primer 1 pmmol/µL, template DNA 1 µg, water added to 25 µL. PCR procedure was 95 °C pre-denaturation for 4 min into the cycle, with each cycle at 94 °C degeneration for 40 s, 60 °C refolding for 1 min, 70 °C extension for 3 min, a total of 35 cycles, the last 70 °C heat for 7 min terminate the reaction. The amplified product 5 µL was identified by 1.2% agarose gel electrophoresis.
ApoE gene polymorphism analysis
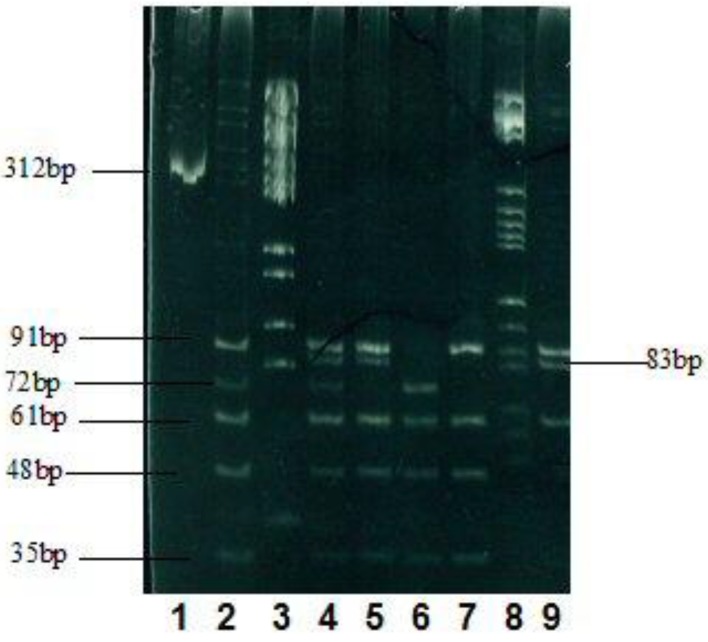
Successful product 20 µL was amplified by adding 10 × buffer 2 µL, calf serum 0.2 µL, endonuclease HhaI5u, 65 °C warm bath for 4 h, 3 µL of the digested product, 3 h of polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (voltage 150 V), and silver nitrate staining was performed to record the results by taking images (Fig. 1).
Figure 1.
Electrophoresis results of the enzyme and the cleavage products. 1: PCR product (312 bp); 2: genotype ε3/4 (91, 72, 61, and 48 bp); 3: marker; 4: ε2/4 (91, 83, 72, 61, and 48 bp) (91, 61, and 48 bp); 5: ε2/3 (91, 83, 61, and 48 bp); 6: ε4/4 (72, 61, and 48 bp); 7: ε3/3 (91, 61, and 48 bp); 8: marker; 9: ε2/2 (91, 83, and 61 bp).
Statistical analysis
The number of groups between the use of t-test or analysis of variance, composition than with the Chi-square test, correlation analysis using Spearman rank correlation analysis.
Results
General characteristics of lipid metabolism in patients with hemodialysis
The main performance of TG and ApoB levels was significantly increased, and HDLC and other indicators were significantly reduced (Table 1). According to the criteria of normal values made by our hospital laboratory, 37 cases (33%) of the patients who received hemodialysis had higher TG levels than the normal upper limit (1.7 mmol/L), and 10 cases (9.4%) had higher levels of ApoB than normal upper limit (300 mg/dL), whereas HDLC levels were found lower than the normal lower limit (0.85 mM) in 11 cases (10.4%). TC levels of all patients were in the normal range or below normal.
Table 1. Comparisons of Blood Lipid Levels Between the Control Group and the Hemodialysis Group, the Hemodialysis Patients With Hypertension and the Normal Blood Pressure Group, and the Cardiovascular Disease Group and the Non-Cardiovascular Disease Group.
| Control | Hemodialysis | Hypertension | Normal BP | CVD | No CVD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC (mM) | 4.61 ± 0.35 | 3.70 ± 0.78** | 3.78 ± 0.68 | 3.84 ± 0.92 | 3.70 ± 0.83 | 3.68 ± 0.81 |
| TG (mM) | 1.23 ± 0.82 | 1.56 ± 0.65** | 1.44 ± 0.63 | 1.56 ± 0.53 | 1.65 ± 0.71*** | 1.33 ± 0.39 |
| HDLC (mM) | 1.37 ± 0.29 | 1.03 ± 0.21** | 1.04 ± 0.22 | 1.05 ± 0.24 | 1.03 ± 0.21 | 0.98 ± 0.23 |
| LDLC (mM) | 2.42 ± 0.66 | 2.02 ± 0.61** | 2.10 ± 0.56 | 2.09 ± 0.69 | 2.02 ± 0.60 | 2.10 ± 0.70 |
| ApoA1 (g/L) | 1.20 ± 0.17 | 1.12 ± 0.23** | 1.12 ± 0.23 | 1.17 ± 0.27 | 1.11 ± 0.23 | 1.07 ± 0.23 |
| ApoB (g/L) | 0.98 ± 0.27 | 1.33 ± 0.93* | 0.93 ± 0.20 | 0.94 ± 0.18 | 0.93 ± 0.20 | 0.94 ± 0.21 |
| ApoE (mg/L) | 50 ± 9 | 45 ± 12* | 43 ± 11 | 46 ± 12 | 44 ± 11 | 43 ± 8 |
| Lp(a) (mg/L) | 333 ± 214 | 221 ± 149** | 186 ± 141 | 202 ± 116 | 217 ± 160 | 196 ± 102 |
Compared with the control group: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; compared with non-cardiovascular disease group: ***P < 0.05. CVD: cardiovascular disease.
Factors related to blood lipid levels in hemodialysis patients were analyzed by Spearman rank correlation
TG, HDLC, sex, age, height, body weight, body mass index, KT/V, serum albumin, ex vivo blood flow during hemodialysis and correlation with serum creatinine, urea nitrogen and uric acid levels before and after dialysis were recorded during the study. The results showed that TG was significantly correlated with serum albumin level and extracorporeal circulation blood flow during dialysis, and the correlation coefficients were -0.367** and -0.202*, respectively. HDLC was significantly associated with KT/V, gender (one for males and two for females), and the correlation coefficients were 0.302** and 0.364**, respectively (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01); however, the level of HDLC in male patients was significantly lower than that in females.
With high blood pressure and cardiovascular disease in patients with hemodialysis lipid metabolism
Hemodialysis patients with high blood pressure and cardiovascular disease
The incidence of hypertension was 73.6% (78/106) and cardiovascular disease was 25% (26/104), of which six cases had ischemic heart disease; heart failure was found in five cases; 21 cases were found to have cardiac enlargement, and cerebrovascular accident occurred in three cases. There was no significant difference in the level of blood lipid between hypertensive group and non-hypertensive group, and the level of TG in cardiovascular disease group was significantly higher than that in the group without cardiovascular disease (Table 1).
ApoE genotype and allele frequency
This study found that all six genotypes of ApoE, genotype ε3/3 and allele ε3 had the highest frequency, as shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Distribution of ApoE Genotype and the Allele Frequency.
| ApoE genotype distribution |
Allele frequency |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ε2/2 | ε2/3 | ε2/4 | ε3/3 | ε3/4 | ε4/4 | ε2 | ε3 | ε4 | |
| Hemodialysis group | 3 | 15 | 0 | 76 | 9 | 2 | |||
| Frequency (%) | 2.9 | 14.5 | 0 | 73.3 | 8.6 | 1.9 | 6.2 | 89.2 | 4.5 |
ApoE gene polymorphism and blood lipid levels
In order to study the pure effects of alleles ε2 and ε4 on blood lipids, ε2/4 type was removed and divided into three groups according to different genotypes: ε2/2 + ε2/3, ε3/3, and Ε3/4 + ε4/4. The results showed that the levels of TC, TG and LDLC in ApoE genotype ε3/4 + ε4/4 were significantly higher in hemodialysis group (Table 3).
Table 3. Comparison of Blood Lipid Levels in Different ApoE Genotypes in Hemodialysis Patients.
| ε2/2 + ε2/3 | ε3/3 | ε3/4 + ε4/4 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC | 3.61 ± 0.60 | 3.84 ± 0.54 | 4.33 ± 0.68 | 0.046 |
| TG | 1..33 ± 0.68 | 1.64 ± 0.52 | 2.12 ± 0.80 | 0.008 |
| HDLC | 1.08 ± 0.13 | 1.00 ± 0.19 | 1.26 ± 0.22 | 0.051 |
| LDLC | 1.87 ± 0.70 | 2.16 ± 0.68 | 2.34 ± 0.74 | 0.022 |
| ApoA1 | 1.11 ± 0.16 | 1.09 ± 0.24 | 1.39 ± 0.32 | 0.090 |
| ApoB | 0.85 ± 0.34 | 0.93 ± 0.24 | 0.92 ± 0.24 | 0.662 |
| ApoE | 49 ± 23 | 38 ± 10 | 46 ± 7 | 0.018 |
| Lp(a) | 337 ± 165 | 207 ± 144 | 266 ± 5 | 0.070 |
Discussion
In this study, TG and ApoB were significantly increased in patients with hemodialysis, while TC and HDLC were significantly decreased. TG levels were associated with serum albumin and decreased blood circulation during dialysis. The decrease of HDLC level was related to dialysis insufficiency and gender, and male patients were more significant. The mechanism of lipid metabolism disorder in hemodialysis patients is not yet clear. Elevated levels of TG and ApoB may be due to increased TG-rich lipoprotein production in chronic renal insufficiency, reduced degradation, decreased activity of liver TG and lipoprotein lipase [21, 22], and decreased serum albumin at the feedback caused by increased liver lipoprotein production. This study shows that hemodialysis extracorporal blood circulation can significantly affect the level of TG. The mechanism may be due to the increase of dialysis permeability when large volume of extracorporal blood circulation was performed, in which more lipoproteins and other large and medium molecular substances, lipoprotein lipase inhibitors and ApoC III clearance can be removed, meanwhile lipoprotein lipase activity was increased. Serum cholesterol levels were mainly due to reduction of lipoprotein synthesis in the liver and intestinal tract [22]. Decrease of HDLC levels is mainly related to inadequate dialysis and malnutrition. It has been reported that 50-70% of hemodialysis patients had increased plasma Lp(a) levels, higher than 0.3 g/L, inconsistent with the results of this article [8, 23], perhaps due to different conditions, different ways, different time to start doing hemodialysis and treatment course, and all the above factors can affect the metabolism of Lp(a) [22]; Lp(a) level was increased significantly in diabetic patients; however, it was found irrelevant to diabetes in this study. In addition, variability of Lp(a) levels is huge dependent on the size of samples. If the number of samples is quite small, it tends to have a greater impact on the observed results. It has been reported that the incidence of hypertension was as high as 50-90% in hemodialysis patients, whereas the incidence of cardiovascular disease was 30-50% [6, 8]. In our study, the incidence of hypertension in hemodialysis patients was 73.6%, and the incidence of cardiovascular disease was 25%. Interestingly, TG levels in serum were significantly associated with cardiovascular disease.
ApoE has three isomers (E2, E3, and E4), encoded by the three alleles ε2, ε3, and ε4 on chromosome 19, respectively. In vitro studies have shown that the binding capacity of E2 with its receptor is low, leading to the delay of degradation of the chylomicrons in blood and VLDL residue catabolism, the reduction of intermediate density lipoprotein to LDL conversion, the increase of intermediate density lipoprotein, and the decrease of LDL concentration. The net effect of E2 results in an increase of TG and a decrease of cholesterol, while the effect of E4 is just on the opposite [9]. But in fact, the mechanisms that ApoE involved in lipid metabolism and atherosclerosis may be very complex. Clinical and animal experimental studies have come to the inconsistent results. Dallongeville et al reported that the TG levels of alleles ε2, ε4 carriers were higher than those of E3 carriers [14]. Animal experiments show that ApoE-deficient animals can cause severe lipid metabolism disorders and atherosclerosis, which can be improved by transgenic treatment [24]. In this study, the levels of TC, TG and LDLC in the control group and hemodialysis group were increased in the order of ε2/2 + ε2/3, ε3/3, and ε3/4 + ε4/4, which was not consistent with some reported results. It is reported that the effect of ApoE genotype ε on TG level is quite different. The consensus is that the level of TG in the normal human and coronary heart disease patients is higher in the allele ε2 carriers than that in ε3 carriers. On the other hand, TG level of the allele ε4 carriers either higher or lower than that of the allele ε3 carriers was obtained in previous studies [7].
These results showed that ApoE genotype had different effects on the blood lipid level of different people. In this study, hemodialysis patients and normal people carrying allele ε4 were prone to hyperlipidemia, yet the mechanisms need to be investigated in future studies.
References
- 1.Taguchi K, Moriyama A, Kodama G, Nakayama Y, Fukami K. The coexistence of multiple myeloma-associated amyloid light-chain amyloidosis and fabry disease in a hemodialysis patient. Intern Med. 2017;56(7):841–846. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.56.7623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Silva CA, Barreto FC, Dos Reis MA, Moura Junior JA, Cruz CM. Targeted screening of fabry disease in male hemodialysis patients in Brazil highlights importance of family screening. Nephron. 2016;134(4):221–230. doi: 10.1159/000448740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Banach M, Aronow WS, Serban MC, Rysz J, Voroneanu L, Covic A. Lipids, blood pressure and kidney update 2015. Lipids Health Dis. 2015;14:167. doi: 10.1186/s12944-015-0169-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Taheri S, Baradaran A, Aliakbarian M, Mortazavi M. Level of inflammatory factors in chronic hemodialysis patients with and without cardiovascular disease. J Res Med Sci. 2017;22:47. doi: 10.4103/jrms.JRMS_282_15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Elsayed ET, Nassra RA, Naga YS. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma-coactivator 1alpha (PGC-1alpha) gene expression in chronic kidney disease patients on hemodialysis: relation to hemodialysis-related cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Int Urol Nephrol. 2017 doi: 10.1007/s11255-017-1628-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Stefoni S, Scolari MP, Cianciolo G, Mosconi G, De Sanctis LB, De Pascalis A, La Manna G. et al. Membranes, technologies and long-term results in chronic haemodialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2000;15(Suppl 2):12–15. doi: 10.1093/ndt/15.suppl_1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Roy GC, Sutradhar SR, Barua UK, Datta NC, Debnath CR, Hoque MM, Hossain AS. et al. Cardiovascular complications of chronic renal failure - an updated review. Mymensingh Med J. 2012;21(3):573–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Senti M, Romero R, Pedro-Botet J, Pelegri A, Nogues X, Rubies-Prat J. Lipoprotein abnormalities in hyperlipidemic and normolipidemic men on hemodialysis with chronic renal failure. Kidney Int. 1992;41(5):1394–1399. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Locatelli F, Bommer J, London GM, Martin-Malo A, Wanner C, Yaqoob M, Zoccali C. Cardiovascular disease determinants in chronic renal failure: clinical approach and treatment. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2001;16(3):459–468. doi: 10.1093/ndt/16.3.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chmurzynska A, Malinowska AM, Twardowska-Rajewska J, Gawecki J. Elderly women: homocysteine reduction by short-term folic acid supplementation resulting in increased glucose concentrations and affecting lipid metabolism (C677T MTHFR polymorphism) Nutrition. 2013;29(6):841–844. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2012.09.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cwiklinska A, Gliwinska A, Senderowska Z, Kortas-Stempak B, Kuchta A, Dabkowski K, Jankowski M. Impact of phosphatidylcholine liposomes on the compositional changes of VLDL during lipoprotein lipase (LPL)-mediated lipolysis. Chem Phys Lipids. 2016;195:63–70. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2015.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rideout TC, Movsesian C, Tsai YT, Iqbal A, Raslawsky A, Patel MS. Maternal Phytosterol Supplementation during Pregnancy and Lactation Modulates Lipid and Lipoprotein Response in Offspring of apoE-Deficient Mice. J Nutr. 2015;145(8):1728–1734. doi: 10.3945/jn.115.215061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Walden CC, Hegele RA. Apolipoprotein E in hyperlipidemia. Ann Intern Med. 1994;120(12):1026–1036. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-120-12-199406150-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dallongeville J, Lussier-Cacan S, Davignon J. Modulation of plasma triglyceride levels by apoE phenotype: a meta-analysis. J Lipid Res. 1992;33(4):447–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Konialis C, Spengos K, Iliopoulos P, Karapanou S, Gialafos E, Hagnefelt B, Vemmos K. et al. The APOE E4 Allele Confers increased risk of ischemic stroke among Greek carriers. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2016;25(3):471–478. doi: 10.17219/acem/38841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lahoz C, Schaefer EJ, Cupples LA, Wilson PW, Levy D, Osgood D, Parpos S. et al. Apolipoprotein E genotype and cardiovascular disease in the Framingham Heart Study. Atherosclerosis. 2001;154(3):529–537. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9150(00)00570-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Echeverria P, Guardiola M, Gonzalez M, Vallve JC, Bonjoch A, Puig J, Clotet B. et al. Association between polymorphisms in genes involved in lipid metabolism and immunological status in chronically HIV-infected patients. Antiviral Res. 2015;114:48–52. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2014.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hanh NT, Nhung BT, Dao DT, Tuyet LT, Hop LT, Binh TQ, Thuc VT. Association of apolipoprotein E polymorphism with plasma lipid disorders, independent of obesity-related traits in Vietnamese children. Lipids Health Dis. 2016;15(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0349-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Teixeira AA, Marrocos MS, Quinto BM, Dalboni MA, Rodrigues CJ, Carmona Sde M, Kuniyoshi M. et al. Diversity of apolipoprotein E genetic polymorphism significance on cardiovascular risk is determined by the presence of metabolic syndrome among hypertensive patients. Lipids Health Dis. 2014;13:174. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-13-174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Berkinbayev S, Rysuly M, Mussayev A, Blum K, Baitasova N, Mussagaliyeva A, Dzhunusbekova G. et al. Apolipoprotein Gene Polymorphisms (APOB, APOC111, APOE) in the development of coronary heart disease in ethnic groups of Kazakhstan. J Genet Syndr Gene Ther. 2014;5(2):216. doi: 10.4172/2157-7412.100021610.4172/2157-7412.1000216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Olmer M, Renucci JE, Planells R, Bouchouareb D, Purgus R. Preliminary evidence for a role of apolipoprotein E alleles in identifying haemodialysis patients at high vascular risk. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1997;12(4):691–693. doi: 10.1093/ndt/12.4.691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Klin M, Smogorzewski M, Ni Z, Zhang G, Massry SG. Abnormalities in hepatic lipase in chronic renal failure: role of excess parathyroid hormone. J Clin Invest. 1996;97(10):2167–2173. doi: 10.1172/JCI118657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Namba T, Masaki N, Matsuo Y, Sato A, Kimura T, Horii S, Yasuda R. et al. Arterial stiffness is significantly associated with left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in patients with cardiovascular disease. Int Heart J. 2016;57(6):729–735. doi: 10.1536/ihj.16-112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Shimano H, Yamada N, Katsuki M, Shimada M, Gotoda T, Harada K, Murase T. et al. Overexpression of apolipoprotein E in transgenic mice: marked reduction in plasma lipoproteins except high density lipoprotein and resistance against diet-induced hypercholesterolemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992;89(5):1750–1754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]