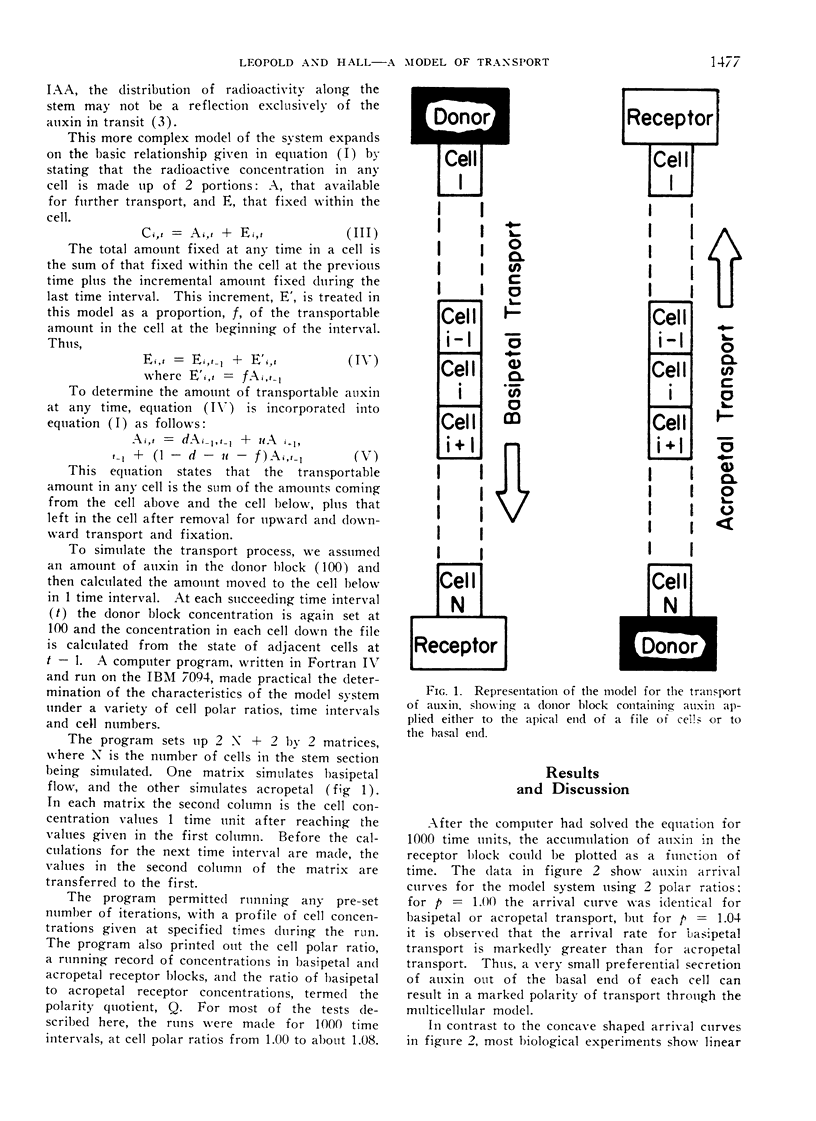
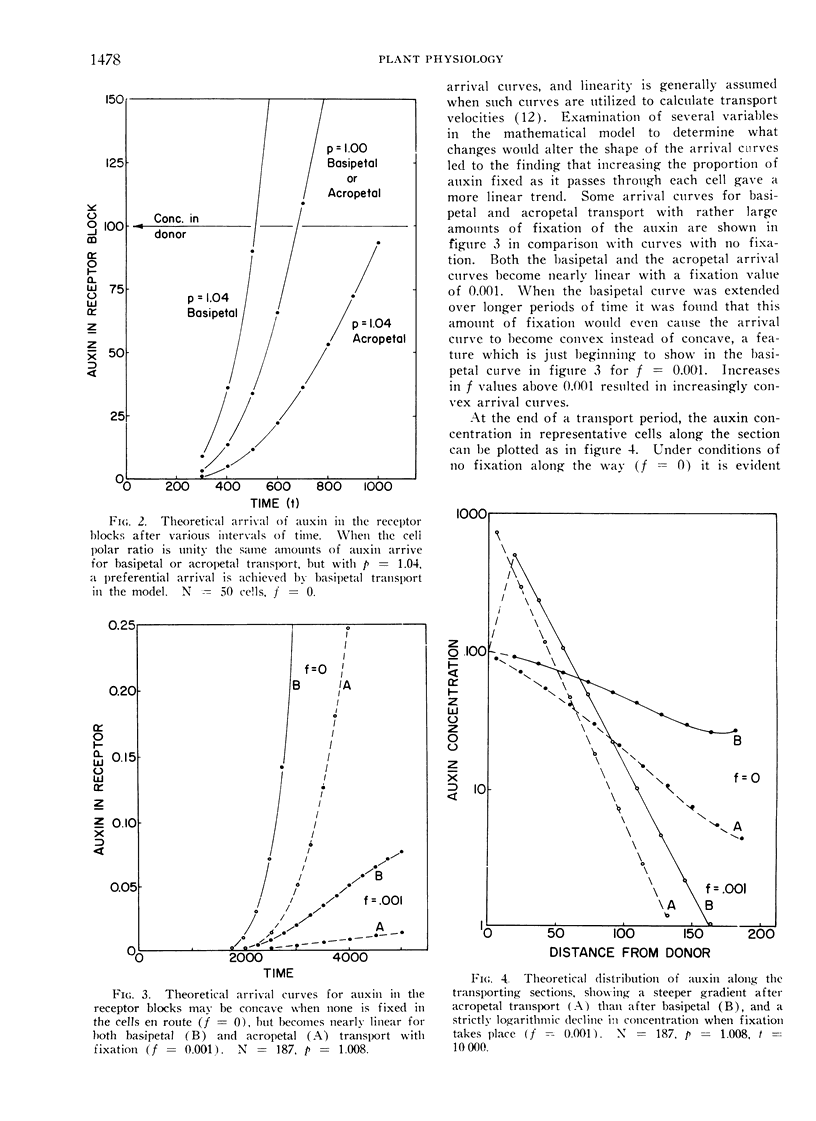
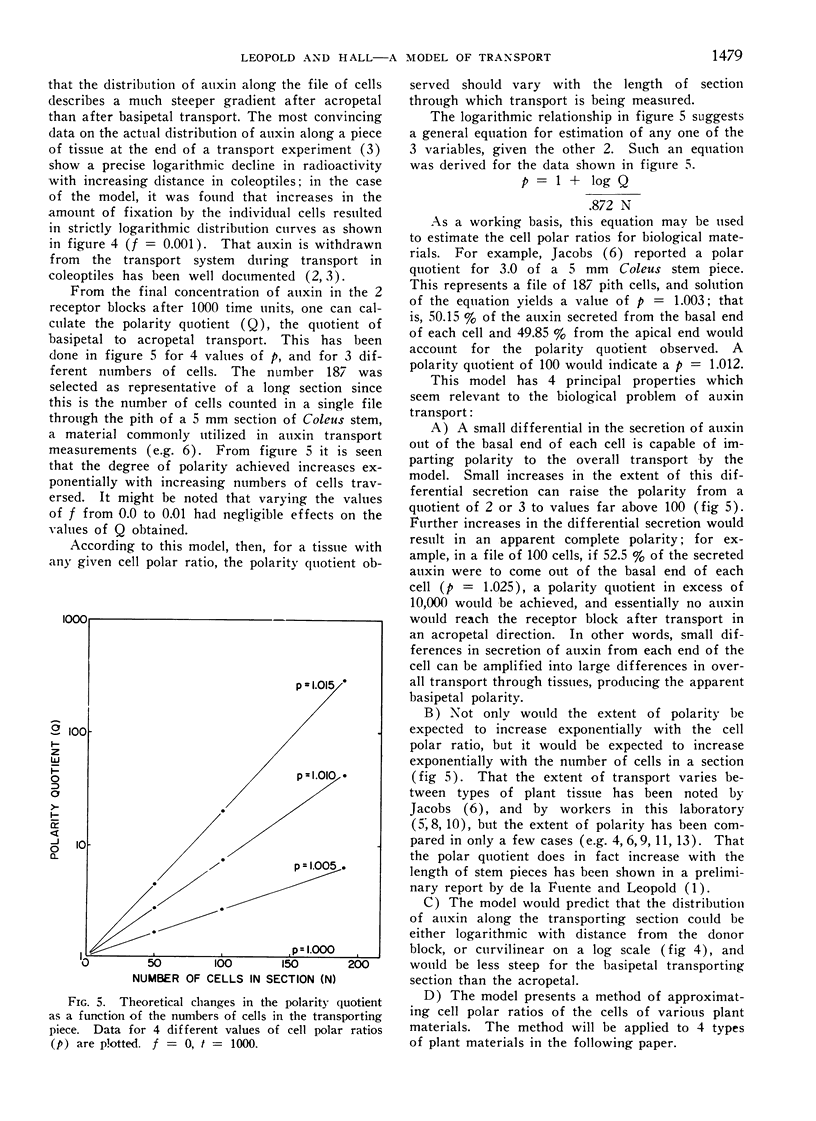
Abstract
Polar auxin transport can be simulated by a model which achieves polarity through the preferential secretion of more auxin from the lower end than from the upper end of each cell. Solution of the model using a computer provides a possible explanation of the differences between the polarity expressed by different tissues and the differences between pieces of different lengths, on the basis of small differences in the polarity of auxin secretion from individual cells. A method of estimating the polarity of individual cells is described.
Full text
PDF