Abstract
The efficacy of current influenza vaccines and small molecule antiviral drugs is curtailed by the emerging of multidrug-resistant influenza viruses. As resistance to the only FDA-approved oral influenza antiviral, oseltamivir (Tamiflu), continues to rise, there is a clear need to develop the next-generation of antiviral drugs. Since more than 95% of current circulating influenza A viruses carry the S31N mutation in their M2 genes, the AM2-S31N mutant proton channel represents an attractive target for the development of broad-spectrum antivirals. In this study we report the design and synthesis of the first class of organosilanes that have potent antiviral activity against a panel of human clinical isolates of influenza A viruses, including viruses that are resistant to amantadine, oseltamivir, or both.
Keywords: Influenza A virus, AM2 proton channel, AM2-S31N inhibitor, organosilane, antiviral
Graphical Abstract
1. Introduction
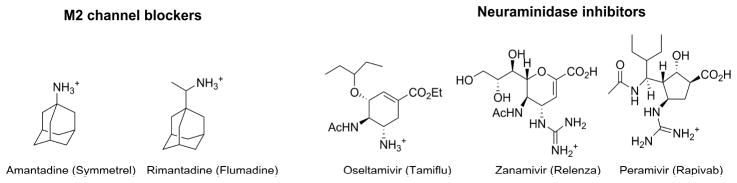
The current countermeasures in preventing and treating influenza virus infection have limited efficacy:[1] despite the existence of vaccines and antiviral drugs, influenza virus infection accounts for approximately 36,000 deaths and millions of hospitalizations in the United States during the annual influenza epidemic.[2–4] In addition, influenza pandemics caused by emerging or re-emerging influenza viruses have more catastrophic impact as demonstrated by the 1918 Spanish influenza and the recent 2009 swine influenza.[5, 6] Influenza vaccine remains the mainstay in prophylaxis of influenza virus infection.[7] However, it has to be reformulated each year to match the antigens of influenza viruses in the coming influenza season. As the manufacturing of influenza vaccines takes at least six months, influenza viruses might continue to mutate during this period, resulting in vaccine mismatch.[8–10] Moreover, influenza vaccines have little to no efficacy in young children, the elderly, and immunocompromised persons.[11] In addition to vaccines, there are two classes of anti-influenza drugs approved for the prevention and treatment of influenza virus infection (Fig. 1): M2 inhibitors, e.g., amantadine and rimantadine, that inhibit virus uncoating, and neuraminidase inhibitors, e.g., oseltamivir, zanamivir, and peramivir, that inhibit virus release.[1] Resistance to both classes of drugs, however, now necessitates the development of the next generation of anti-influenza drugs.[12] Amantadine and rimantadine are no longer recommended due to widespread drug resistance. Resistance to the only orally available drug, oseltamivir, continues to rise, and the 2008–2009 seasonal H1N1 strain was completely resistant to oseltamivir due to a H275Y mutation.[12] Influenza strains that are resistant to both classes of drugs have been repoted.[13, 14] Moreover, certain highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses such as H7N9 and H5N1, which have the potential to lead to the next influenza pandemic, are also resistant to oseltamivir.[15, 16] Thus the next generation of antiviral drugs with broad-spectrum antiviral activity against both drug-sensitive and drug-resistant influenza strains is clearly needed.[17, 18]
Fig. 1.
FDA-approved influenza antivirals.
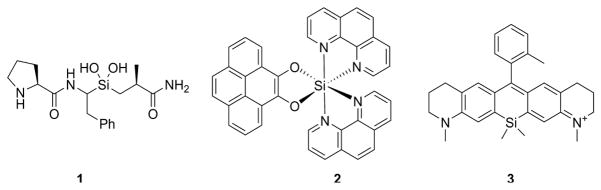
In pursuing the next generation of influenza antivirals, we chose the AM2-S31N mutant as the drug target. AM2 forms a proton-selective channel in the viral membrane and plays important roles during the viral replication cycle[19]: in the early stage AM2 facilitates viral uncoating by acidifying the viral interior, which leads to the dissociation of viral ribonucleoproteins from the matrix protein M1; in the late stage of viral replication AM2 equilibrates the pH across the Golgi apparatus and prevents the premature conformational change of hemagglutinin. More than 95% of currently circulating influenza A viruses carry the S31N mutant in their M2 genes, which renders them resistant to adamantanes.[20] The prevalence of this mutation thus makes AM2-S31N a desired target for drug design.[21] Propelled by structural and mechanistic understandings of AM2 proton conductance and drug inhibition,[21, 22] we successfully designed the first-in-class AM2-S31N inhibitors with both potent channel blockage and antiviral activity.[21, 23–26] Encouraged by this progress, in this study we report the design and expeditious synthesis of organosilane-based AM2-S31N inhibitors. Silicon is a bioisostere of carbon, and the design of organosilane-based bioactive molecules has been hotly pursued.[27, 28] Unique features of organosilanes include but are not limited to improved binding affinity, higher metabolism stability, and reduced cytotoxicity. More importantly, from the synthesis perspective, organosilanes are generally easier to synthesize than their carbon analogues. Furthermore, organosilanes have several unique properties that cannot be mimicked by their carbon analogues: (1) silicon can form stable silanediol to mimic the amide bond hydrolysis intermediate, and silanediols have been reported to be potent protease inhibitors (Fig. 2, compound 1).[29] (2) organosilanes can go beyond tetrahedral coordination to octahedral coordination (Fig. 2, compound 2) and such compounds can be used as DNA chelators.[30] (3) Incorporation of silicone into rhodamine results in Si-rhodamine, which emits in the near infrared region (650–900 nm) (Fig. 2, compound 3).[31] Such fluorescence probes have been successfully applied for live cell and in vivo imaging.[32]
Fig. 2.
Representative bioactive organosilanes. Compound 1 is a silanediol peptidomimetic and was designed as a serine protease inhibitor.[29] Compound 2 is an octahedral silicon complex and was designed as a DNA intercalator.[30] Compound 3 is a Si-rhodamine that emits in the near infrared region.[31]
2. Design rationale
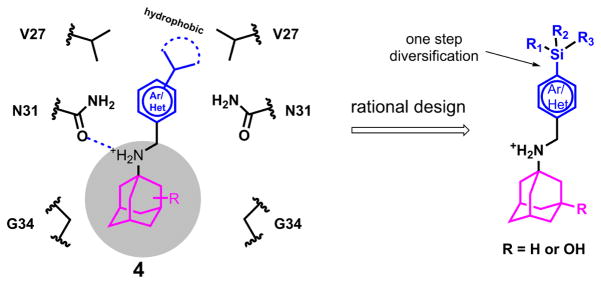
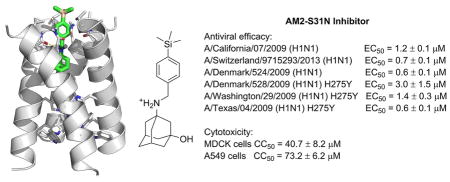
In light of advantages of exploring organosilanes as bioactive molecules, we are interested in designing organosilanes as AM2-S31N inhibitors. Three criteria were taken into consideration when designing AM2-S31N inhibitors: (1) the designed organosilanes should meet the pharmacophore requirements of AM2-S31N inhibitors. The pharmacophore of AM2-S31N inhibitors consists of a hydrophobic scaffold such as adamantane, a positively charged ammonium linker, and an aromatic head group with a hydrophobic substitution (Fig. 3, compound 4).[24–26] (2) The designed organosilanes should be easy to synthesize by late-stage diversification. (3) Introduction of silicon to a drug molecule increases its hydrophobicity, which might lead to enhanced cellular cytotoxicity; thus a hydroxyl group should be added to the 3-position of adamantane to reduce the overall hydrophobicity and thus cellular cytotoxicity. [24–26] Taking these factors into consideration, the designed organosilanes 5 contain an adamantane cage, an ammonium methylene linker, and a para-substituted aromatic/heterocyclic head group. Such a design allows the introduction of diverse silicon substitutions starting from a common intermediate.
Fig. 3.
Rational design of organosilanes as AM2-S31N inhibitors. Left is a cartoon representation of the pharmacophore of AM2-S31N inhibitors and the binding mode of AM2-S31N inhibitors in the AM2-S31N channel. Right is the designed AM2-S31N inhibitors.
3. Chemistry
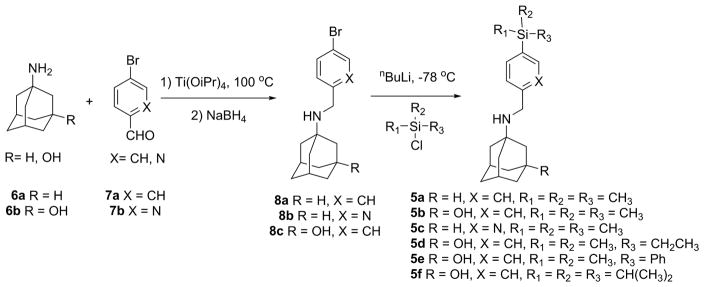
We then proceed to synthesize the designed organosilanes 5a–f (Fig. 4). Reductive amination of amantadine 6a or 3-amino-1-hydroxyadamantane 6b with 4-bromobenzaldehyde 7a or 5-bromo-2-pyridinecarbaldehyde 7b gave the intermediates 8a–8c. The yields range from 75% to 82%. In the next step, five equivalents of n-butyl lithium were used to generate the aryl lithium in the presence of a hydroxyl and an amine group. The resulting aryl lithium was then reacted with a variety of silyl chlorides to furnish the final products 5a–f. The yields range from 62% to 78%.
Fig. 4.
Expeditious synthesis of organosilanes as AM2-S31N inhibitors.
4. Results and discussion
4.1. Channel blockage, antiviral efficacy, and cytotoxicity of organosilane-based AM2-S31N inhibitors
To validate the design hypothesis, the synthesized organosilanes were tested for their AM2-S31N channel blockage, antiviral activity, and cellular cytotoxicity by electrophysiological two-electrode voltage clamp (TEVC) assay, plaque assay, and neutral red assay, respectively (Table 1). Two compounds, 9 and 10, which were the carbon analogues of compounds 5a and 5b, were also synthesized and used for comparison. It was found that organosilane 5a had similar channel blockage and antiviral activity as its carbon analogue 9. However, the difference between compounds 5b and 10 was more obvious, with the organosilane 5b being more potent than its carbon analogue 10 in blocking the AM2-S31N channel (86.7 ± 0.7% versus 75.4 ± 2.3%). Consistent with the electrophysiological assay results, the antiviral activity of organosilane 5b was 6-fold more potent than its carbon analogue 10 (0.4 ± 0.2 μM versus 2.5 ± 1.1 μM). The increased potency might be a result of the favorable hydrophobic interaction between the hydrophobic trimethylsilyl group from 5b and the valine side chain methyls located at the N-terminus of the AM2-S31N channel (Fig. 3). Substituting benzene with pyridine led to a slight increase in AM2-S31N channel inhibition (5c vs 5a). Further increase in the size of the silyl substitution led to compounds 5d–f. Compounds 5d and 5e both had slightly reduced percentage channel blockage against the AM2-S31N channel when compared with compound 5b, and both were also less potent than 5b in terms of their antiviral activity. Compound 5f with bulky triisopropylsilyl substitution was inactive in both electrophysiological and antiviral assays. All three compounds (5d–f) were more cytotoxic than 5b, probably due to increased clogP (Table 1). None of the compounds showed significant inhibition (>35%) against the AM2-WT channel, which was expected since these compounds were designed to target the drug-resistant AM2-S31N channel, not the WT-AM2. In summary, the most potent compound was 5b, which not only had potent channel blockage and antiviral activity, but also had the highest selectivity index (SI) of 101.8.
Table 1.
Channel blockage, antiviral activity, cytotoxicity, and hydrophobicity of organosilane AM2-S31N inhibitors.
| Compound structure and ID | a% AM2-S31N inhibition | a% AM2-WT inhibition | A/WSN/33 EC50 (μM)b | CC50 (μM) MDCKc and cLogPd |
|---|---|---|---|---|
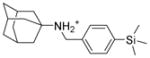 5a |
77.5 ± 0.1 | 21.8 ± 1.6 | 4.8 ± 1.8 | CC50 = 8.0 ± 0.6 clogP = 5.6 SI = 1.7 |
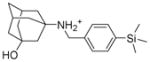 5b |
86.7 ± 0.7 | 9.5 ± 0.5 | 0.4 ± 0.2 | CC50 = 40.7 ± 8.2 clogP = 4.9 SI = 101.8 |
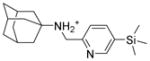 5c |
81.3 ± 2.1 | 5.9 ± 1.6 | 3.4 ± 0.5 | CC50 = 10.3 ± 0.2 clogP = 5.0 SI = 3.0 |
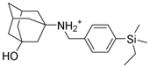 5d |
81.4 ± 0.8 | 18.2 ± 1.4 | 5.5 ± 0.4 | CC50 = 21.8 ± 0.5 clogP = 5.2 SI = 4.0 |
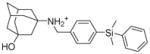 5e |
84.9 ± 1.5 | 33.6 ± 2.3 | 5.9 ± 2.2 | CC50 = 13.3 ± 1.0 clogP = 6.2 SI = 2.3 |
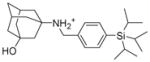 5f |
33.6 ± 2.0 | 17.8 ± 1.8 | >10 | CC50 = 11.4 ± 1.0 clogP = 6.5 |
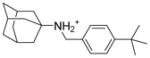 9 |
72.6 ± 1.4 | 9.9 ± 0.5 | 3.5 ± 1.2 | CC50 = 12.8 ± 0.6 clogP = 5.3 SI = 3.7 |
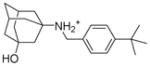 10 |
75.4 ± 2.3 | 22.3 ± 0.7 | 2.5 ± 1.1 | CC50 = 32.0 ± 1.21 clogP = 4.6 SI = 12.8 |
Values represent the mean of three independent measurements. Compounds were tested at 100 μM concentration.
Antiviral activity was tested with the A/WSN/33 (H1N1) virus, which contains the AM2-S31N mutant, in plaque assay. The experiments were done in duplicate.
Cytotoxicity was tested by incubating MDCK cells with compounds for 48 h and the cells were stained with neutral red.[33]
clogP values were calculated using Schrodinger Glide QikProp.
4.2. Broad-spectrum antiviral activity of organosilane 5b
To further characterize the therapeutic potential of organosilane 5b, its cytotoxicity against the human epithelial cell line A549 and antiviral activity against multidrug-resistant influenza A viruses were further evaluated (Table 2). Compound 5b was found to be less cytotoxic to A549 cells than to MDCK cells (CC50 = 73.2 ± 6.2 vs 40.7 ± 8.2 μM), resulting in an SI of 183. The antiviral efficacy of 5b against human clinical isolates of influenza A viruses was also profiled. The viruses tested include multidrug-resistant strains such as the A/Denmark/528/2009 (H1N1), A/Washington/29/2009 (H1N1), and A/Texas/04/2009 (H1N1), all of which are resistant to both amantadine and oseltamivir due to AM2-S31N and H275Y mutations in their M2 and neuraminidase genes, respectively. Encouragingly, compound 5b showed potent antiviral activity with single to submicromolar efficacy against all three multidrug-resistant strains. In addition, organosilane 5b also showed potent antiviral activity against oseltamivir-sensitive strains such as A/California/07/2009 (H1N1), A/Switzerland/9715293/2013 (H3N2), and A/Denmark/524/2009 (H1N1) with EC50 values ranging from 0.6 to 1.2 μM. The common feature among these influenza A strains is that they all contain the AM2-S31N mutation in their M2 genes, which explains their drug sensitivity to organosilane 5b. The selectivity index of 5b ranges from 24.4 to 122.0, which suggests that compound 5b might be a suitable lead compound to be further optimized.
Table 2.
Antiviral activity of organosilane 5b against drug-resistant influenza A viruses.
| Viruses | Resistance to oseltamivir | 5b EC50 (μM) | SI (A549) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A/California/07/2009 (H1N1) | NO | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 61.0 |
| A/Switzerland/9715293/2013 (H3N2) | NO | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 104.6 |
| A/Denmark/524/2009 (H1N1) | NO | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 122.0 |
| A/Denmark/528/2009 (H1N1) | YES (H275Y) | 3.0 ± 1.5 | 24.4 |
| A/Washington/29/2009 (H1N1) | YES (H275Y) | 1.4 ± 0.3 | 52.3 |
| A/Texas/04/2009 (H1N1) | YES (H275Y) | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 122.0 |
4.3. Molecular docking of organosilane 5b in the AM2-S31N channel
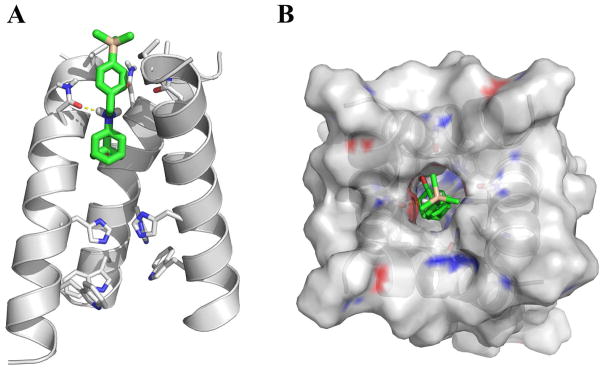
To gain further insights how organosilane 5b binds to the AM2-S31N channel, molecular docking was performed. The solution NMR structure of AM2-S31N channel (PDB: 2LY0) was used for the docking.[23] Consistent with the design principle, in the energy minimized pose (Fig. 5), organosilane 5b binds to the AM2-S31N channel with its trimethylsilyl-substituted benzene ring facing towards the N-terminus of the channel. The adamantane cage from 5b fits in a space created by G34, and the positively charged ammonium from 5b forms a hydrogen bond with one of the N31 side chain carbonyl. The trimethylsilyl is surrounded by a ring of methyls from V27. Based on this docking model, it is expected that compounds having a sterically bulky substitution at the 4-position of the benzyl ring, such as 5f, will experience steric clash with the V27 side chain methyls, thus will not be able to fit in the channel. This prediction is validated by the antiviral assay result which showed that compound 5f was not active in inhibiting the AM2-S31N-containing A/WSN/33 (H1N1) virus (EC50 > 10 μM, Table 1). Overall, the docking model is consistent with the experimental results and could serve as a reference for further lead optimization.
Fig. 5.
Docking model of organosilane 5b in the AM2-S31N channel. The solution NMR structurer of AM2-S31N (2LY0) was used for the docking.[23] Docking was performed using AutoDock Vina.[34] (A) Side view of the docking pose of organosilane 5b in AM2-S31N channel. The front helix was removed for clarity. (B) Top view of the docking pose of organosilane 5b in AM2-S31N channel.
5. Conclusions
In summary, guided by the pharmacophore of AM2-S31N inhibitors, we were able to design organosilanes as potent AM2-S31N channel blockers. Compared with its carbon analogue 10, the most potent organosilane, 5b, had improved antiviral activity in inhibiting the A/WSN/33 (H1N1) virus. Significantly, compound 5b was also highly active against both oseltamivir-sensitive and -resistant influenza A viruses, highlighting its promise for further development. Moreover, the synthesis of organosilanes is straightforward, and a diverse silyl groups can be installed in a onestep SN2 reaction, which would greatly facilitate the iterative cycles of design, synthesis, and biological characterization. In contrary, similar chemistry is not feasible for the corresponding carbon analogues. The major therapeutic importance of AM2-S31N inhibitors such as organosilane 5b is that they are active against both oseltamivir-sensitive and -resistant influenza viruses. Thus they can be used either alone to combat oseltamivir-resistant strains or used in combination with oseltamivir to delay the evolution of resistance. Overall, the results from this study reaffirm the advantages of exploring organosilanes as bioactive molecules, and organosilane therapeutics might become a reality in the near future.
6. Experimental section
6.1 Chemistry
6.1.1 General chemical methods
All chemicals were purchased from commercial vendors and used without further purification unless otherwise noted. 1H and 13C NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker-400 NMR spectrometer. Chemical shifts are reported in parts per million referenced with respect to residual solvent (CD3OD) 3.31 ppm and (Chloroform-d) 7.24 ppm or from internal standard tetramethylsilane (TMS) 0.00 ppm. The following abbreviations were used in reporting spectra: s, singlet; d, doublet; t, triplet; q, quartet; m, multiplet; dd, doublet of doublets; ddd, doublet of doublet of doublets. All reactions were carried out under N2 atmosphere, unless otherwise stated. HPLC-grade solvents were used for all reactions. Flash column chromatography was performed using silica gel (230–400 mesh, Merck). Low-resolution mass spectra were obtained using an ESI technique on a 3200 Q Trap LC/MS/MS system (Applied Biosystems). The purity was assessed by using Shimadzu LC-MS with Waters XTerra MS C-18 column (part #186000538), 50 × 2.1 mm, at a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min; λ = 250 and 220 nm; mobile phase A, 0.1% formic acid in H2O, and mobile phase B’, 0.1% formic in 60% isopropanol, 30% CH3CN and 9.9% H2O. All compounds submitted for testing in TEVC assay and plaque reduction assay were confirmed to be > 95.0% purity by LC-MS traces. All compounds were characterized by proton and carbon NMR and MS.
6.1.2 General procedures for the synthesis of organosilanes
Compounds 8a–8c, 9 and 10 were synthesized according to the following general procedure. General procedure of reductive amination (Fig. 4): Adamantane or 3-amino-1-adamantanol (1 equiv.) and aldehyde (1 equiv.) were mixed with 2 mL of titanium (IV) isopropoxide. The resulting slurry was heated in microwave at 120 °C for 30 minutes. Then the solution was cooled down and CH3OH (10 mL) was added. The mixture was cooled down to 0 °C using ice bath, then NaBH4 (4 equiv.) was added portionwise in 10 minutes. The solution was subsequently warmed to room temperature and stirred for 4 hours. The reaction was quenched with 1M NaOH and filtered through celite. The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure and was purified by silica gel flash column chromatography (5–10% CH3OH/CH2Cl2) to give the final product.
6.1.2.1. N-[(4-bromophenyl)methyl]adamantan-1-amine (8a)
Yield: 82.4%. 1HNMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.41 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.22 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 3.70 (s, 2H), 2.08 (s, 3H), 1.68–1.60 (m, 12 H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 140.43, 131.40, 129.82, 120.41, 50.09, 44.50, 42.64, 36.76, 29.71. EI-MS: m/z (M+H+): 320.1 (calculated), 320.0 (found). Compounds 8b and 8c were reported before.[25]
6.1.2.2. N-[(4-tert-butylphenyl)methyl]adamantan-1-amine (9)
Yield: 78.0%. 1HNMR (400 MHz, CD3Cl): δ 7.33 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.27 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 3.76 (s, 2H), 2.10 (m, 3H), 1.79–1.78 (m, 6H), 1.68–1.66 (m, 6H), 1.63 (s, 1H), 1.36 (s, 9H). 13NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 149.58, 137.97, 128.04, 125.32, 50.94, 44.69, 42.84, 36.80, 34.43, 31.38, 31.52, 29.68. EI-MS: m/z (M+H+): 298.2 (calculated), 298.0 (found).
6.1.2.3. 3-{[(4-tert-butylphenyl)methyl]amino}1adamantan-1-ol (10)
Yield: 75.3%. 1HNMR (400 MHz, CD3Cl): δ 7.33 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.27 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 3.75 (s, 2H), 2.29–2.28 (m, 2H), 1.77 (s, 2H), 1.68–1.67 (m, 6H), 1.66 (m, 4H), 1.54 (m, 2H), 1.43 (s, 9H). 13NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 149.91, 137.55, 128.11, 125.39, 69.77, 54.44, 50.22, 45.03, 44.48, 41.34, 35.24, 34.45, 31.38, 30.83. EI-MS: m/z (M+H+): 314.2 (calculated), 314.0 (found).
Compounds 5a–5f were synthesized according to the following general procedure.[35] General procedure of silylation (Fig. 4):
n-Butyllithium (1.6 M in hexanes; 5 equiv.) was added dropwise to a stirred solution of intermediate 8 (1 equiv.) in THF (15 mL) at −78 °C. The reaction was stirred at −78 °C for 1 hour, then silyl chloride (5 equiv.) was added dropwise, and the mixture was allowed to gradually warm to room temperature (4 hours) and stirred for another 12 hours. The reaction was quenched with water (10 ml), and the aqueous phase was separated and extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 30 mL). The combined organic portions were combined and dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. The mixture was then purified by silica gel flash column chromatography (0–10% CH3OH/CH2Cl2) to give the final products 5a–5f.
6.1.2.3. N-{[4-(trimethylsilyl)phenyl]methyladamantan-1-amine (5a)
Yield: 78.3%. 1HNMR (400 MHz, CD3Cl): δ 7.47 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.34 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 3.75 (s, 2H), 2.10 (m, 3H), 1.73–1.72 (m, 6H), 1.68–1.66 (m, 6H), 1.63 (s, 1H), 0.25 (s, 9H). 13NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 138.47, 133.37, 127.66, 50.90, 44.98, 42.78, 36.68, 29.57, −1.18. EI-MS: m/z (M+H+): 314.6 (calculated), 314.0 (found).
6.1.2.4. 3-({[4-(trimethylsilyl)phenyl]methyl}amino)adamantan-1-ol (5b)
Yield: 70.4 %. 1HNMR (400 MHz, CD3Cl): δ 7.47 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.33 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 3.75 (s, 2H), 2.28 (m, 2H), 1.71–1.64 (m, 12H), 1.55–1.53 (m, 2H), 0.25 (s, 9H). 13NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 141.65, 138.87, 133.62, 127.74, 69.78, 54.28, 50.34, 45.43, 44.51, 41.49, 35.62, 30.84, −1.08. EI-MS: m/z (M+H+): 330.6 (calculated), 331.0 (found).
6.1.2.5. N-{[5-(trimethylsilyl)pyridine-2-yl]methyladamantan-1-amine (5c)
Yield: 80.4%. 1HNMR (400 MHz, CD3Cl): δ 8.56 (s, 1H), 7.89 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.47 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 4.38 (s, 2H), 2.20 (m, 3H), 2.01 (s, 6H), 1.75–1.71 (m, 6H), 1.70–1.67 (m, 1H), 0.31 (s, 9H). 13NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 151.46, 150.37, 143.92, 122.95, 58.03, 41.91, 38.88, 35.50, 28.00, −1.46. EI-MS: m/z (M+H+): 315.5 (calculated), 316.0 (found).
6.1.2.6. 3-({[4-(ethyldimethylsilyl)phenyl]methyl}amino)adamantan-1-ol (5d)
Yield: 67.5%. 1HNMR (400 MHz, CD3Cl): δ 7.49 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.342 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 3.76 (s, 2H), 2.25 (m, 2H), 2.01 (s, 2H) 1.88–1.58 (m, 10H), 1.47 (m, 2H), 0.87 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 0.61 (q, J = 8.0 Hz, 3H), 0.12 (s, 6H). 13NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 139.58, 133.34, 129.60, 69.49, 48.21, 45.73, 43.20, 34.78, 30.06, 29.60, 7.33, 7.24, −3.43. EI-MS: m/z (M+H+): 344.6 (calculated), 345.0 (found).
6.1.2.7. 3-[({4-[dimethyl(phenyl)silyl]phenyl}methyl)amino]adamantan-1-ol (5e)
Yield: 68.7 %. 1HNMR (400 MHz, CD3Cl): δ 8.06 (s, 1H), 7.63 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.48 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.42–7.37 (m, 2H), 7.34–7.27 (m, 3H), 3.83 (s, 2H), 3.38 (s, 1H), 2.22 (m, 4H), 1.99–1.96 (m, 2H), 1.83–1.80 (m, 2H), 1.67–1.64 (m, 2H), 1.55–1.52 (m, 2H), 1.41 (s, 2H), 0.46 (s, 6H).13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 139.86, 137.52, 134.59, 134.04, 131.46, 130.30, 129.24, 127.87, 69.24, 61.55, 46.93, 44.99, 42.92, 36.86, 34.13, 30.25, −2.66. EI-MS: m/z (M+H+): 392.6 (calculated), 393.0 (found).
6.1.2.8. 3-[({4-[tris(propan-2-yl)silyl]phenylmethyl)amino]adamantan-1-ol (5f)
Yield: 62.3%. 1HNMR (400 MHz, CDCl3+ CD3OD): δ 7.58–7.47 (m, 4H), 3.83 (s, 2H), 3.88 (s, 2H), 2.32 (s, 2H), 1.88–1.87 (m, 2H), 1.83–1.85 (m, 4H), 1.70–1.63 (m, 4H), 1.52 (s, 2H), 1.37–1.30 (m, 3H), 1.00–0.97 (m, 18H). 13NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3+ CD3OD): δ 136.82, 135.97, 131.42, 128.99, 67.95, 60.00, 45.81, 43.85, 42.87, 36.26, 33.93, 30.34, 18.40, 10.85. EI-MS: m/z (M+H+): 414.7 (calculated), 415.0 (found).
6.2. Biological evaluation
6.2.1. Cell lines, viruses, and viral infection
Madin-Darby Canine Kidney (MDCK) cells were grown at 37°C in 5% CO2 atmosphere in DMEM media (high glucose, with L-glutamine) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 IU/ml penicillin and 100 μg/ml streptomycin. MDCK cells overexpressing ST6Gal I were obtained from Dr. Yoshihiro Kawaoka at the University of Wisconsin at Madison through material transfer agreement and were maintained in the presence of 7.5 μg/ml of puromycin, except when they were used for viral infection. Influenza A virus strains A/California/07/2009 (H1N1) and A/Texas/04/2009 (H1N1) were obtained from Dr. James Noah at the Southern Research Institute; influenza A virus strains A/Denmark/524/2009 (H1N1) and A/Denmark/528/2009 (H1N1) were obtained from Dr. Elena Govorkova at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital; influenza A virus strains A/Switzerland/9715293/2013 X-247 (H3N2), FR-1366, and A/Washington/29/2009 (H1N1), FR-460, were obtained through the Influenza Reagent Resource, Influenza Division, WHO Collaborating Center for Surveillance, Epidemiology and Control of Influenza, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, GA, USA. Virus stocks were amplified in MDCK cells in the presence of 2 μg/ml N-acetyl trypsin. Two days post infection, the culture media were harvested and cell debris was removed by centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 30 min. Virus titers were determined by plaque reduction assay using MDCK cells expressing ST6Gal I.
6.2.2. Plaque reduction assay
Plaque reduction assay were carried out as previously described,[36, 37] except MDCK cells expressing ST6Gal I were used instead of regular MDCK cells.
6.2.3. Cytotoxicity assay
Evaluation of the cytotoxicity of compounds was carried out using neutral red uptake assay.[33] Briefly, 80,000 cells/mL MDCK or A549 cells in DMEM medium supplemented with 10% FBS and 100 U/mL Penicillin-Streptomycin were dispensed into 96-well cell culture plates at 100 μL/well. Twenty-four hours later, the growth medium was removed and washed with 100 μL PBS buffer; then for cytotoxicity assay, 200 μL fresh DMEM (No FBS) medium contains serial diluted compounds was added to each well. After incubating for 48 hours at 37 °C with 5% CO2 in a CO2 incubator, the medium was removed and replaced with 100 μL DMEM medium contains 40 μg/mL neutral red for 4 hours 37 °C. The amount of uptaken neutral red was determined at absorbance 540 nm using a Multiskan FC Microplate Photometer (Fisher Scientific). The CC50 values were calculated from best-fit dose response curves with variable slope in Prism 5.
6.2.4. Electrophysiological TEVC assay
The compounds were tested in a two-electrode voltage clamp assay using Xenopus laevis frog oocytes microinjected with RNA expressing either the AM2-WT or the AM2-S31N mutant of the A/M2 proteins, as previously reported.[37] The potency of the inhibitors was expressed as percentage inhibition of AM2 current observed after 2 minutes of incubation with 100 μM of compounds at pH 5.5. All measurements were repeated three times with different oocytes.
6.3. Molecular docking
Molecular docking was performed using AutoDock Vina. The solution NMR structure of AM2-S31N (PDB: 2LY0) was used for the docking. The center of the grid box was set as the following: center_x = 0, center_y = 0, center_z = 11. The size of the grid box was set as the following: size_x = 22, size_y = 20, size_z = 18.
Supplementary Material
Highlights.
The first class of organosilane-based AM2-S31N inhibitors were rationally designed
An expeditious synthesis was developed to introduce diverse silyl groups
Compound 5b has potent efficacy against multidrug-resistant influenza A viruses
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by startup funding from the University of Arizona, the 2015 PhRMA Foundation Research Starter Grant in Pharmacology and Toxicology, and NIH grant AI119187 to J.W. We thank Dr. David Bishop for proofreading and editing the manuscript.
Abbreviations used
- WT
wild type
- DMEM
Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium
- MDCK
Madin–Darby Canine Kidney
- TEVC
two-electrode voltage clamps
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Loregian A, Mercorelli B, Nannetti G, Compagnin C, Palù G. Antiviral strategies against influenza virus: towards new therapeutic approaches. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014:1–25. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1615-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cox NJ, Subbarao K. Global epidemiology of influenza: past and present. Annual review of medicine. 2000;51:407–421. doi: 10.1146/annurev.med.51.1.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Thompson W, Shay D, Weintraub E, Brammer I, Bridges C, Cox N, Fukuda K. Influenza-associated hospitalizations in the United States. JAMA. 2004;292:1333–1340. doi: 10.1001/jama.292.11.1333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Thompson WW, Shay DK, Weintraub E, Brammer L, Cox N, Anderson LJ, Fukuda K. Mortality associated with influenza and respiratory syncytial virus in the United States. JAMA. 2003;289:179–186. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Horimoto T, Kawaoka Y. Influenza: lessons from past pandemics, warnings from current incidents. Nat Rev Micro. 2005;3:591–600. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Monto AS, Webster RG. Textbook of Influenza. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2013. Influenza pandemics: History and lessons learned; pp. 20–34. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lambert LC, Fauci AS. Influenza Vaccines for the Future. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:2036–2044. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1002842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Xie H, Wan XF, Ye ZP, Plant EP, Zhao YQ, Xu YF, Li X, Finch C, Zhao N, Kawano T, Zoueva O, Chiang MJ, Jing XH, Lin ZS, Zhang AD, Zhu YH. H3N2 Mismatch of 2014–15 Northern Hemisphere Influenza Vaccines and Head-to-head Comparison between Human and Ferret Antisera derived Antigenic Maps. Sci Rep. 2015;5 doi: 10.1038/srep15279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Houser K, Subbarao K. Influenza Vaccines: Challenges and Solutions. Cell Host & Microbe. 2015;17:295–300. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.02.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wong S, Webby R. Traditional and New Influenza Vaccines. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2013;26:476–492. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00097-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Osterholm M, Kelley N, Sommer A, Belongia E. Efficacy and effectiveness of influenza vaccines: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012;12:36–44. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(11)70295-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hurt AC. The epidemiology and spread of drug resistant human influenza viruses. Curr Opin Virol. 2014;8:22–29. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2014.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sheu T, Fry A, Garten R, Deyde V, Shwe T, Bullion L, Peebles P, Li Y, Klimov A, Gubareva L. Dual Resistance to Adamantanes and Oseltamivir Among Seasonal Influenza A(H1N1) Viruses: 2008–2010. J Infect Dis. 2011;203:13–17. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiq005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hayden FG, de Jong MD. Emerging Influenza Antiviral Resistance Threats. J Infect Dis. 2011;203:6–10. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiq012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ilyushina NA, Govorkova EA, Webster RG. Detection of amantadine-resistant variants among avian influenza viruses isolated in North America and Asia. Virology. 2005;341:102–106. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2005.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Orozovic G, Orozovic K, Lennerstrand J, Olsen B. Detection of resistance mutations to antivirals oseltamivir and zanamivir in avian influenza A viruses isolated from wild birds. PLoS One. 2011;6:e16028. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Arns S, Balgi AD, Shimizu Y, Pfeifer TA, Kumar N, Shidmoossavee FS, Sun S, Tai SSH, Agafitei O, Jaquith JB, Bourque E, Niikura M, Roberge M. Novel spirothiazamenthane inhibitors of the influenza A M2 proton channel. Eur J Med. 2016;120:64–73. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.05.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wang H, Xu RY, Shi YY, Si LL, Jiao PX, Fan ZB, Han X, Wu XY, Zhou XS, Yu F, Zhang YM, Zhang LR, Zhang LH, Zhou DM, Xiao SL. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel L-ascorbic acid-conjugated pentacyclic triterpene derivatives as potential influenza virus entry inhibitors. Eur J Med. 2016;110:376–388. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wang J, Qiu JX, Soto C, DeGrado WF. Structural and dynamic mechanisms for the function and inhibition of the M2 proton channel from influenza A virus. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2011;21:68–80. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2010.12.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Dong G, Peng C, Luo J, Wang C, Han L, Wu B, Ji G, He H. Adamantane-Resistant Influenza A Viruses in the World (1902–2013): Frequency and Distribution of M2 Gene Mutations. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0119115. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wang J, Li F, Ma C. Recent progress in designing inhibitors that target the drug-resistant M2 proton channels from the influenza A viruses. Biopolymers. 2015;104:291–309. doi: 10.1002/bip.22623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hong M, DeGrado WF. Structural basis for proton conduction and inhibition by the influenza M2 protein. Protein Sci. 2012;21:1620–1633. doi: 10.1002/pro.2158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wang J, Wu Y, Ma C, Fiorin G, Wang J, Pinto LH, Lamb RA, Klein ML, DeGrado WF. Structure and inhibition of the drug-resistant S31N mutant of the M2 ion channel of influenza A virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:1315–1320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1216526110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Li F, Ma C, DeGrado WF, Wang J. Discovery of Highly Potent Inhibitors Targeting the Predominant Drug-Resistant S31N Mutant of the Influenza A Virus M2 Proton Channel. J Med Chem. 2016;59:1207–1216. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Li F, Ma C, Hu Y, Wang Y, Wang J. Discovery of Potent Antivirals against Amantadine-Resistant Influenza A Viruses by Targeting the M2-S31N Proton Channel. ACS Infect Dis. 2016;2:726–733. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.6b00130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Li F, Hu YM, Wang YX, Ma CL, Wang J. Expeditious Lead Optimization of Isoxazole-Containing Influenza A Virus M2-S31N Inhibitors Using the Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-Coupling Reaction. J Med Chem. 2017;60:1580–1590. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Franz AK, Wilson SO. Organosilicon molecules with medicinal applications. J Med Chem. 2013;56:388–405. doi: 10.1021/jm3010114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wang J, Ma C, Wu Y, Lamb RA, Pinto LH, DeGrado WF. Exploring Organosilane Amines as Potent Inhibitors and Structural Probes of Influenza A Virus M2 Proton Channel. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:13844–13847. doi: 10.1021/ja2050666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Singh S, Sieburth SM. Serine Protease Inhibition by a Silanediol Peptidomimetic. Org Lett. 2012;14:4422–4425. doi: 10.1021/ol301933n. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Xiang YG, Fu C, Breiding T, Sasmal PK, Liu HD, Shen Q, Harms K, Zhang LL, Meggers E. Hydrolytically stable octahedral silicon complexes as bioactive scaffolds: application to the design of DNA intercalators. Chem Commun. 2012;48:7131–7133. doi: 10.1039/c2cc32506c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yuan L, Lin W, Zheng K, He L, Huang W. Far-red to near infrared analyte-responsive fluorescent probes based on organic fluorophore platforms for fluorescence imaging. Chem Soc Rev. 2013;42:622–661. doi: 10.1039/c2cs35313j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Koide Y, Urano Y, Hanaoka K, Piao W, Kusakabe M, Saito N, Terai T, Okabe T, Nagano T. Development of NIR Fluorescent Dyes Based on Si–rhodamine for in Vivo Imaging. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:5029–5031. doi: 10.1021/ja210375e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Repetto G, del Peso A, Zurita JL. Neutral red uptake assay for the estimation of cell viability/cytotoxicity. Nat Protoc. 2008;3:1125–1131. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Trott O, Olson AJ. AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem. 2010;31:455–461. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ball LT, Lloyd-Jones GC, Russell CA. Gold-catalyzed oxidative coupling of arylsilanes and arenes: origin of selectivity and improved precatalyst. J Am Chem Soc. 2014;136:254–264. doi: 10.1021/ja408712e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Jing X, Ma C, Ohigashi Y, Oliveria FA, Jardetzky TS, Pinto LH, Lamb RA. Functional studies indicate amantadine binds to the pore of the influenza A virus M2 proton-selective ion channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:10967–10972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0804958105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Balannik V, Wang J, Ohigashi Y, Jing X, Magavern E, Lamb RA, DeGrado WF, Pinto LH. Design and Pharmacological Characterization of Inhibitors of Amantadine-Resistant Mutants of the M2 Ion Channel of Influenza A Virus. Biochemistry. 2009;48:11872–11882. doi: 10.1021/bi9014488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.