Abstract
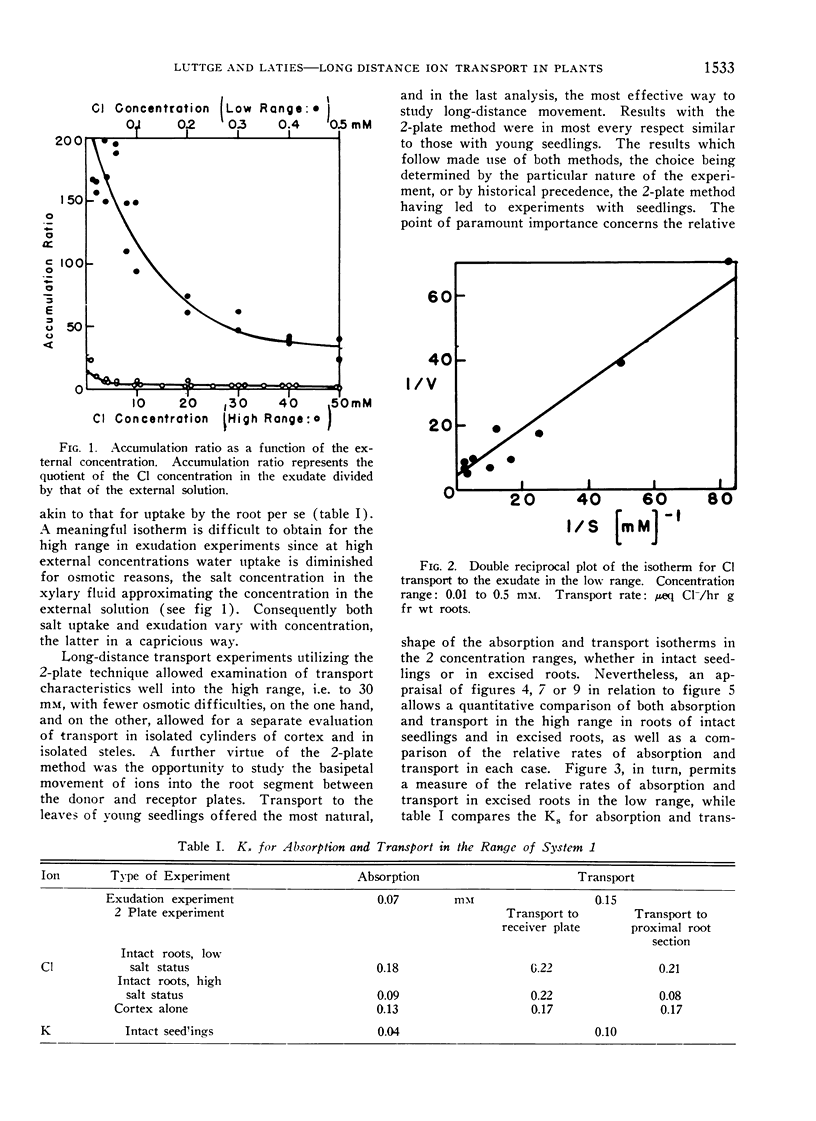
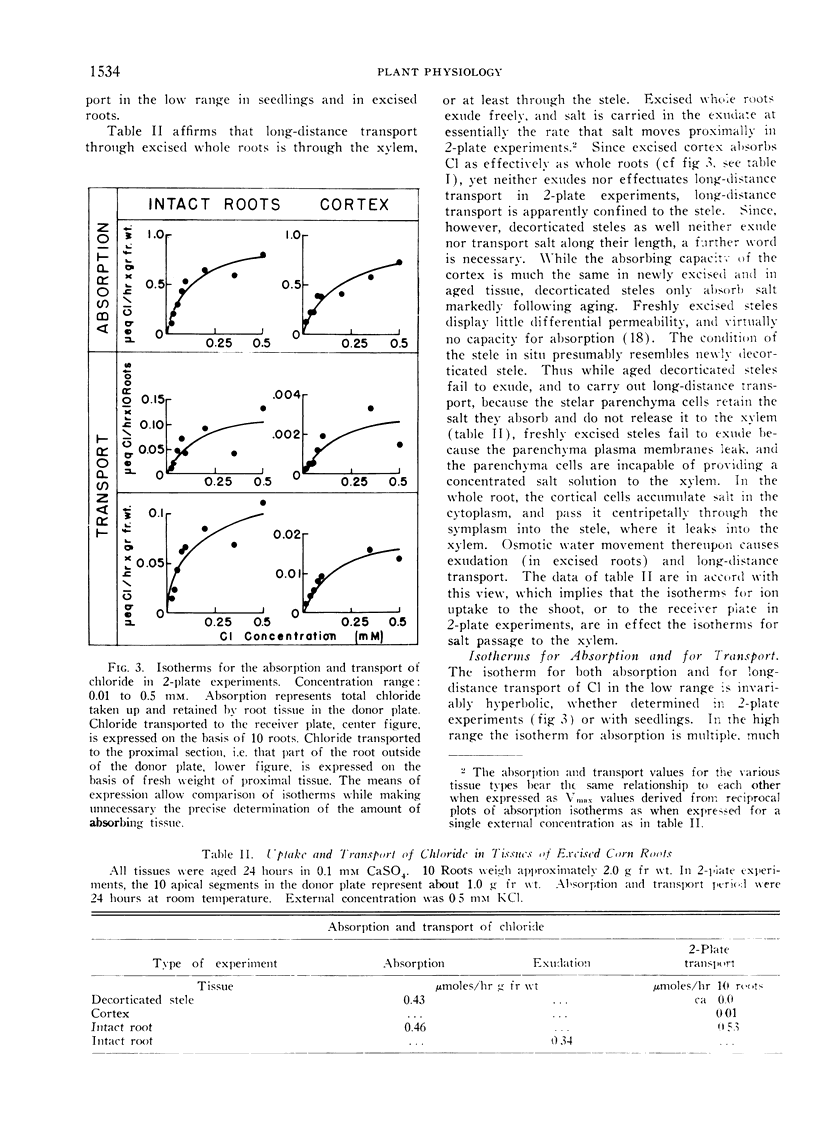
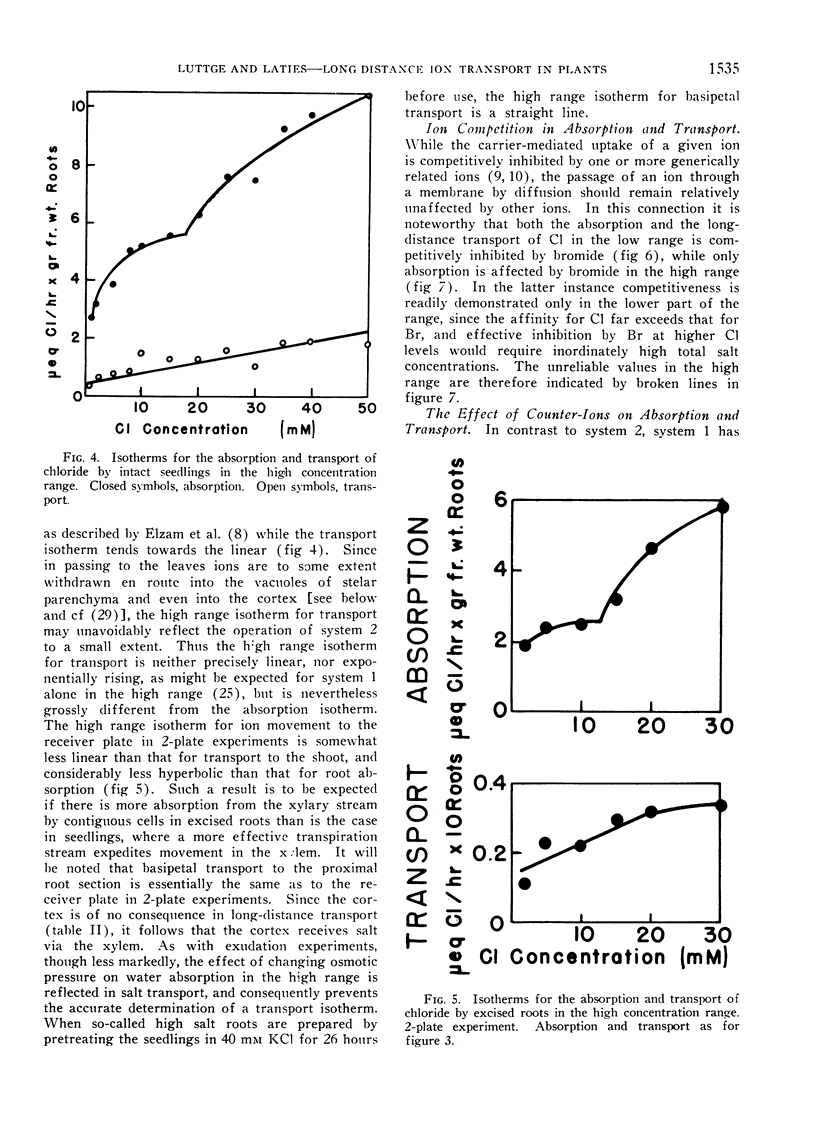
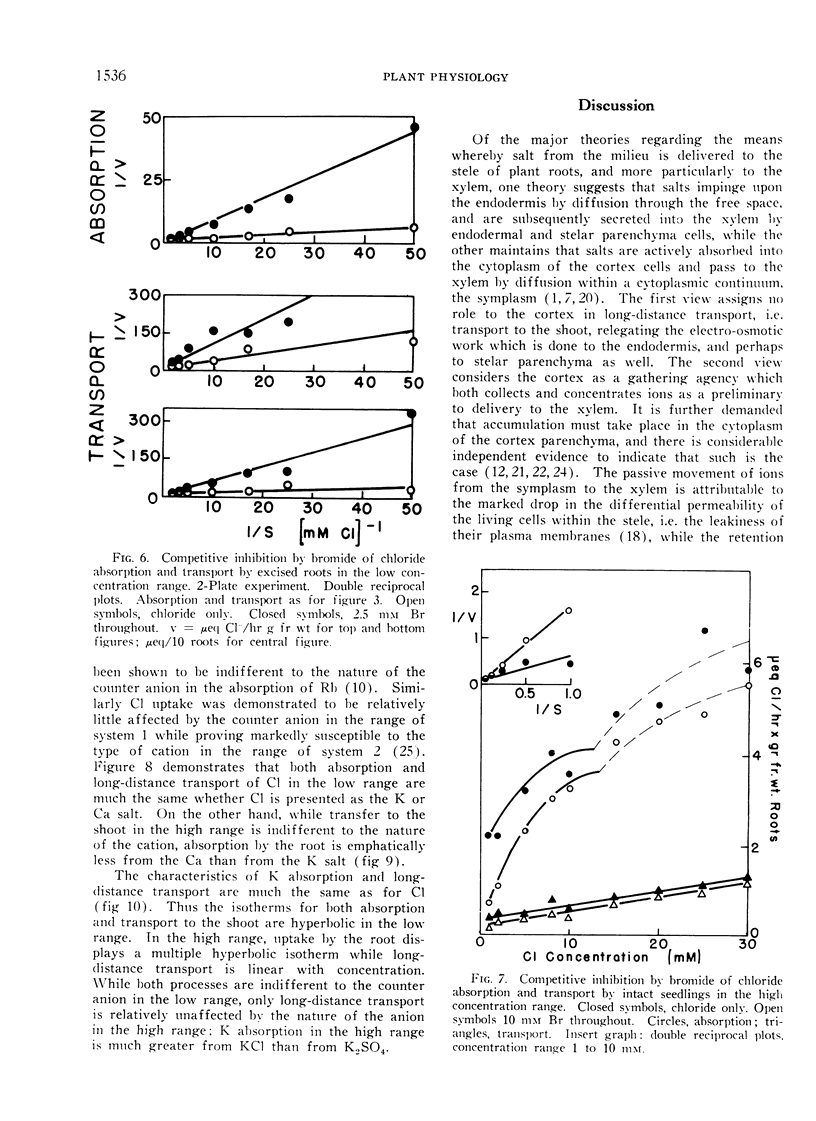
The characteristics of ion transport to the shoots of young corn seedlings were studied with respect to the nature of the isotherm through a wide concentration range, the competitive influence of closely related ions upon the transport of a given ion, and the influence of the counter-ion. Both with respect to 36Cl and 86Rb transport, the characteristics of the process in every way resemble uptake by non-vacuolate root tips wherein the plasma membrane is the only membrane involved in absorption, and where system 1 — of the 2 systems which can be shown to participate in absorption by vacuolate tissue — is the only system operative. Net ion uptake by the roots per se was shown to display both the high affinity (system 1) and low affinity (system 2) mechanisms. It is concluded that the symplastic theory of ion movement to the xylem is valid, and that the contention that system 1 operates at the plasma membrane while system 2 functions at the tonoplast is strengthened.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Branton D., Jacobson L. Iron Transport in Pea Plants. Plant Physiol. 1962 Jul;37(4):539–545. doi: 10.1104/pp.37.4.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyer T. C. FURTHER OBSERVATIONS ON THE ABSORPTION AND TRANSLOCATION OF INORGANIC SOLUTES USING RADIOACTIVE ISOTOPES WITH PLANTS. Plant Physiol. 1950 Jul;25(3):367–376. doi: 10.1104/pp.25.3.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budd K., Laties G. G. Ferricyanide-Mediated Transport of Chloride by Anaerobic Corn Roots. Plant Physiol. 1964 Jul;39(4):648–654. doi: 10.1104/pp.39.4.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ETHERTON B., HIGINBOTHAM N. Transmembrane potential measurements of cells of higher plants as related to salt uptake. Science. 1960 Feb 12;131(3398):409–410. doi: 10.1126/science.131.3398.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elzam O. E., Rains D. W., Epstein E. Ion transport kinetics in plant tissue: complexity of the chloride absorption isotherm. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 Mar 26;15(3):273–276. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90159-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E., Hagen C. E. A KINETIC STUDY OF THE ABSORPTION OF ALKALI CATIONS BY BARLEY ROOTS. Plant Physiol. 1952 Jul;27(3):457–474. doi: 10.1104/pp.27.3.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E., Rains D. W. CARRIER-MEDIATED CATION TRANSPORT IN BARLEY ROOTS: KINETIC EVIDENCE FOR A SPECTRUM OF ACTIVE SITES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jun;53(6):1320–1324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.6.1320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E., Rains D. W., Elzam O. E. RESOLUTION OF DUAL MECHANISMS OF POTASSIUM ABSORPTION BY BARLEY ROOTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 May;49(5):684–692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.5.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Noggle J. C. Multiple Site Uptake of Individual Cations by Roots as Affected by Hydrogen Ion. Plant Physiol. 1958 Mar;33(2):139–144. doi: 10.1104/pp.33.2.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges T. K., Vaadia Y. Chloride Uptake and Transport of Different Salt Status. Plant Physiol. 1964 Jan;39(1):109–114. doi: 10.1104/pp.39.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges T. K., Vaadia Y. Uptake and Transport of Radiochloride and Tritiated Water by Various Zones of Onion Roots of Different Chloride Status. Plant Physiol. 1964 Jan;39(1):104–108. doi: 10.1104/pp.39.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laties G. G., Budd K. THE DEVELOPMENT OF DIFFERENTIAL PERMEABILITY IN ISOLATED STELES OF CORN ROOTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Aug;52(2):462–469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.2.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torii K., Laties G. G. Dual mechanisms of ion uptake in relation to vacuolation in corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1966 May;41(5):863–870. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.5.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


