Abstract
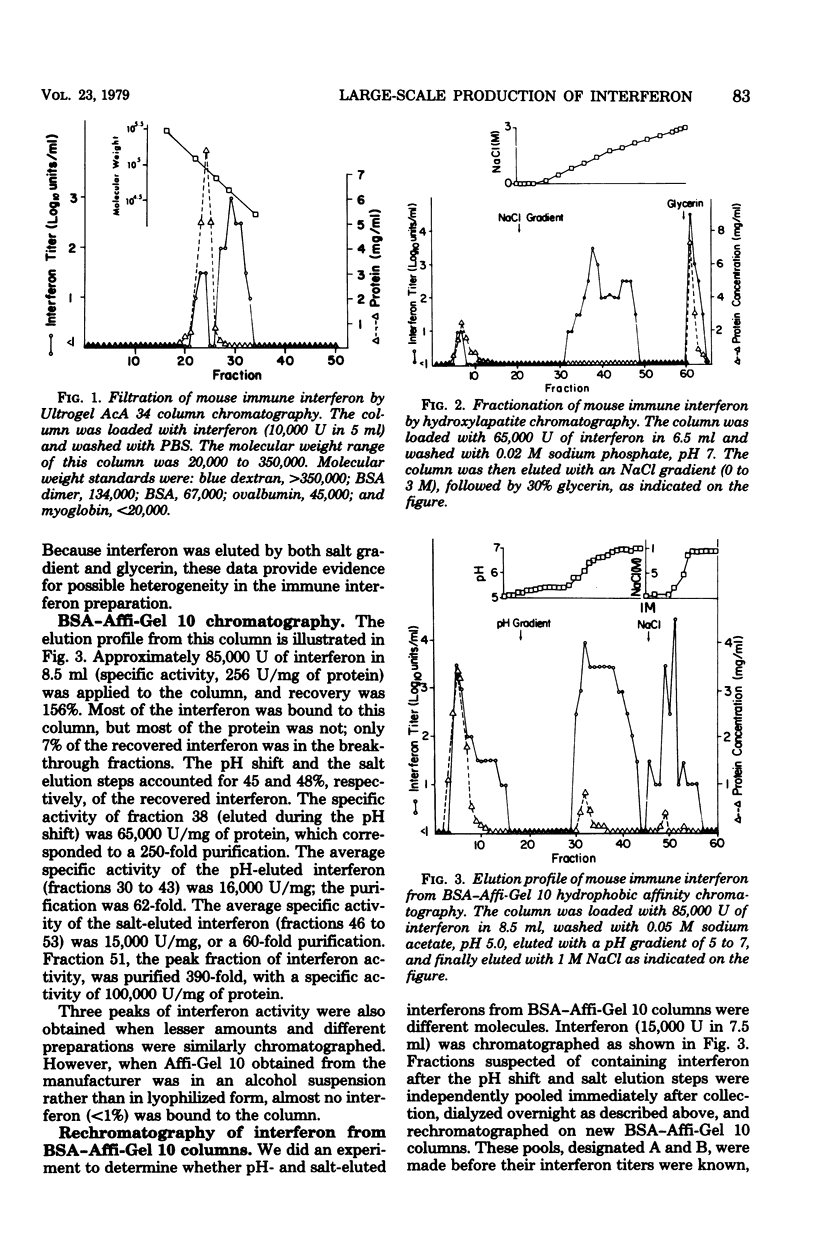
Large-scale production of high-titered (102.2 to 104 U/ml) immune interferon (type II) was carried out in roller cultures of mouse spleen cells by using the T-cell mitogen staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Precipitation of 90% of this interferon by 55 to 80% saturated ammonium sulfate resulted in a 20-fold concentration and a two- to sixfold purification. After application of this interferon to either bovine serum albumin (BSA)-Affi-Gel 10 or hydroxylapatite columns, 100% of the interferon activity was recovered. By BSA-Affi-Gel 10 chromatography, 7% of the recovered activity was not bound, 45% was eluted with pH gradient 5 to 7, and 48% was eluted with 1 M NaCl. The pH- and salt-eluted interferons from the BSA-Affi-Gel 10 column were purified 62- and 390-fold, respectively, when compared with the starting materials. Rechromatography of the pH- and salt-eluted interferon peaks from the BSA-Affi-Gel 10 column did not alter their elution patterns. Stepwise elution of interferon from the BSA-Affi-Gel 10 columns with buffers of various pH and salt contents also resulted in greater than 300-fold purification. Specific activities of up to 2 × 105 U of interferon per mg of protein were attained with either elution procedure from BSA-Affi-Gel 10 columns. By hydroxylapatite chromatography, 5% of the recovered activity was not bound, 20% was eluted with a salt gradient, and 75% was eluted with 30% glycerin. Purification was 107- and 16-fold, respectively, for the two fractions. Ultrogel AcA 34 chromatography of the interferon resulted in two peaks of activity, a major one with a molecular weight of approximately 40,000 and a minor peak of molecular weight 70,000 to 90,000. Thus, by different types of chromatography, immune interferon was found to be heterogeneous.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg K., Ogburn C. A., Paucker K., Mogensen K. E., Cantell K. Affinity chromatography of human leukocyte and diploid cell interferons on sepharose-bound antibodies. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 1):640–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridgen P. J., Anfinsen C. B., Corley L., Bose S., Zoon K. C., Rüegg U. T., Buckler C. E. Human lymphoblastoid interferon. Large scale production and partial purification. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6585–6587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhlen P., Stein S., Dairman W., Udenfriend S. Fluorometric assay of proteins in the nanogram range. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Mar;155(1):213–220. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(73)80023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. B., Grunberger T., Kochman M. A., White S. L. A microplaque reduction assay for human and mouse interferon. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Aug;21(8):1247–1253. doi: 10.1139/m75-186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey M. W., Sulkowski E., Carter W. A. Purification and characterization of mouse interferon with novel affinity sorbents. J Virol. 1976 Feb;17(2):439–445. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.2.439-445.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maeyer-Guignard J., Tovey M. G., Gresser I., De Maeyer E. Purification of mouse interferon by sequential affinity chromatography on poly(U)--and antibody--agarose columns. Nature. 1978 Feb 16;271(5646):622–625. doi: 10.1038/271622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edy V. G., Billiau A., de Somer P. Purification of human fibroblast interferon by zinc chelate affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 10;252(17):5934–5935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field A. K., Tytell A. A., Lampson G. P., Hilleman M. R. Inducers of interferon and host resistance. II. Multistranded synthetic polynucleotide complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1004–1010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. A., Cooperband S. R., Kibrick S. Immune specific induction of interferon production in cultures of human blood lymphocytes. Science. 1969 Jun 20;164(3886):1415–1417. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3886.1415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Berman B., Ogburn C. A., Berg K., Paucker K., Vilcek J. Two antigenically distinct species of human interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2185–2187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAACS A. INTERFERON. Adv Virus Res. 1963;10:1–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahrling P. B., Beall J. L. Chromatographic separations of alphavirus strains by hydroxylapatite. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Sep;6(3):238–243. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.3.238-243.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski W. J., Davey M. W., O'Malley J. A., Sulkowski E., Carter W. A. Molecular structure of human fibroblast and leukocyte interferons: probe by lectin and hydrophobic chromatography. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1124–1130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1124-1130.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Baron S. The nature of the suppressive effect of interferon and interferon inducers on the in vitro immune response. Cell Immunol. 1976 Jul;25(1):106–115. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M. Differentiation of the immunosuppressive and antiviral effects of interferon. Cell Immunol. 1978 Mar 15;36(2):220–230. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90266-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Stanton G. J., Baron S. Relative ability of mitogens to stimulate production of interferon by lymphoid cells and to induce suppression of the in vitro immune response. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Jan;154(1):138–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakita M., Cabrer B., Taira H., Rebello M., Slattery E., Weideli H., Lengyel P. Purification of interferon from mouse Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):598–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr Heterogeneity of purified mouse interferons. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4139–4144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr Interferon: purification and initial characterization from human diploid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):520–523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford M. P., Stanton G. J., Johnson H. M. Biological effects of staphylococcal enterotoxin A on human peripheral lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):62–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.62-68.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maehara N., Ho M., Armstrong J. A. Differences in mouse interferons according to cell source and mode of induction. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):572–579. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.572-579.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogburn C. A., Berg K., Paucker K. Purification of mouse interferon by affinity chromatography on anti-interferon globulin-sepharose. J Immunol. 1973 Oct;111(4):1206–1218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvin S. B., Youngner J. S., Lederer W. H. Migration inhibitory factor and interferon in the circulation of mice with delayed hypersensitivity. Infect Immun. 1973 Jan;7(1):68–75. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.1.68-75.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenfeld G., Mandel A. D., Merigan T. C. The immunosuppressive effect of type II mouse interferon preparations on antibody production. Cell Immunol. 1977 Dec;34(2):193–206. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90243-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stobo J., Green I., Jackson L., Baron S. Identification of a subpopulation of mouse lymphoid cells required for interferon production after stimulation with mitogens. J Immunol. 1974 Apr;112(4):1589–1593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulkowski E., Davey M. W., Carter W. A. Interaction of human interferons with immobilized hydrophobic amino acids and dipeptides. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5381–5385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Törmä E. T., Paucker K. Purification and characterization of human leukocyte interferon components. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 25;251(16):4810–4816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheelock E. F. Interferon-like virus-inhibitor induced in human leukocytes by phytohemagglutinin. Science. 1965 Jul 16;149(3681):310–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Salvin S. B. Production and properties of migration inhibitory factor and interferon in the circulation of mice with delayed hypersensitivity. J Immunol. 1973 Dec;111(6):1914–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



