Abstract
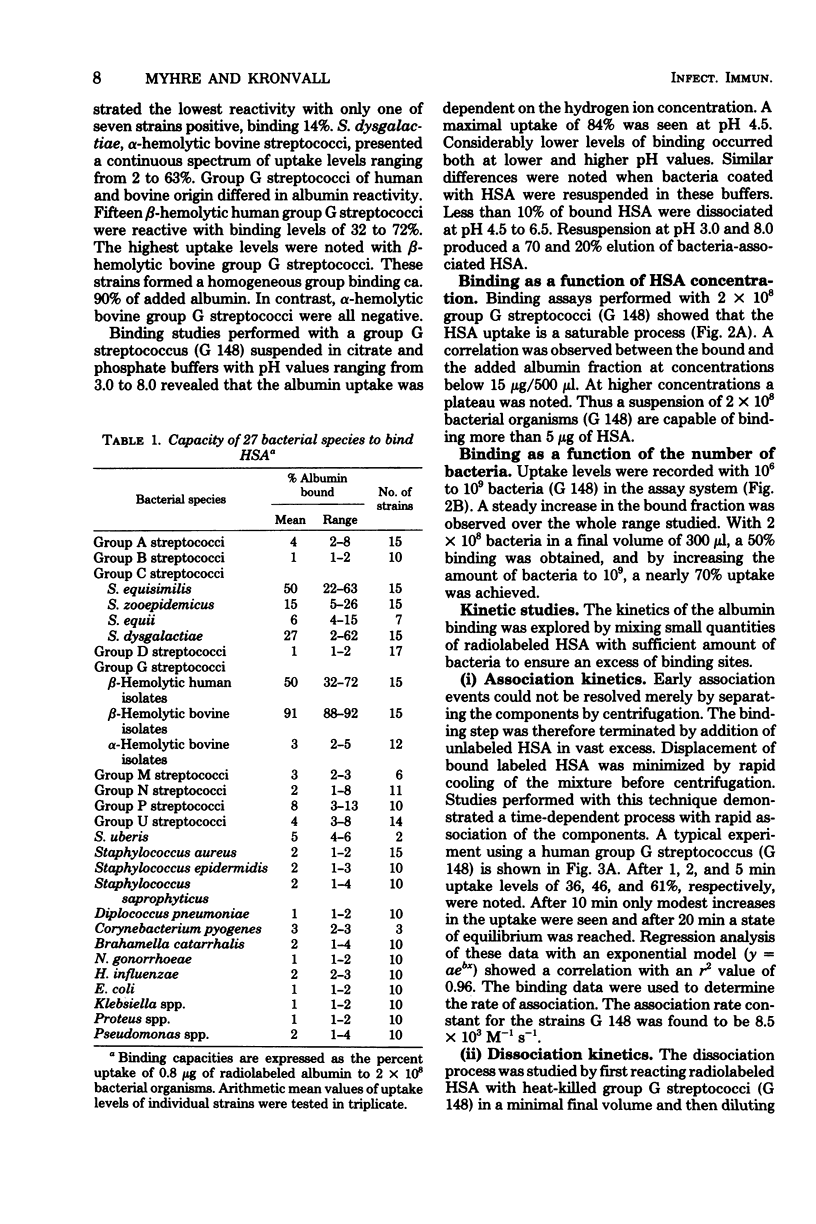
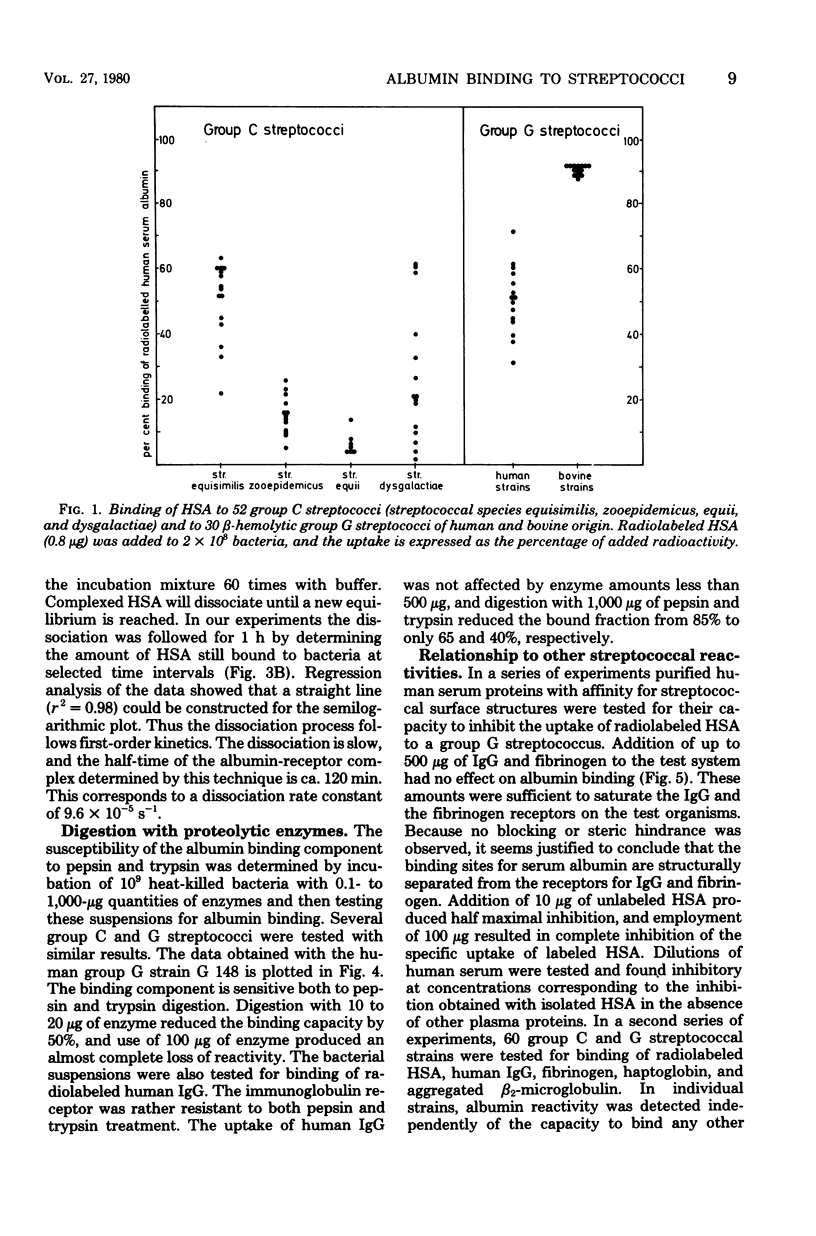
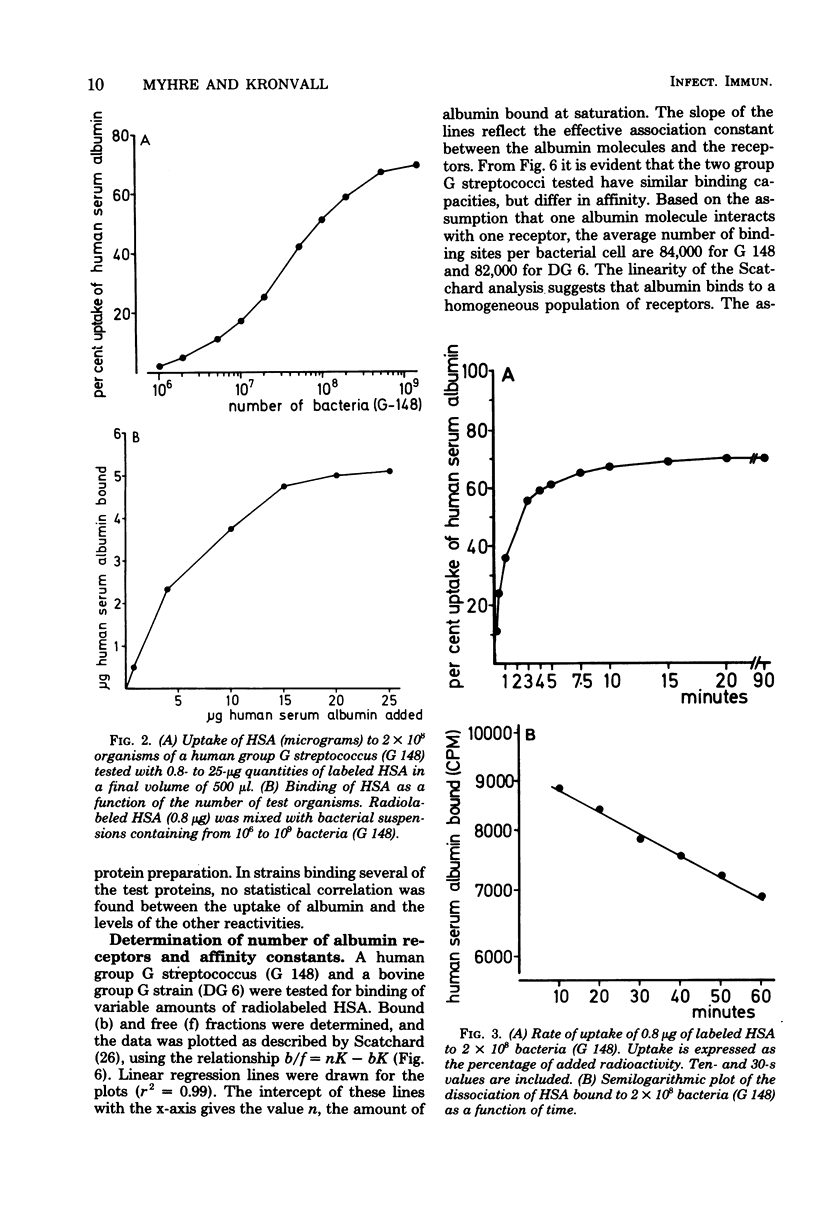
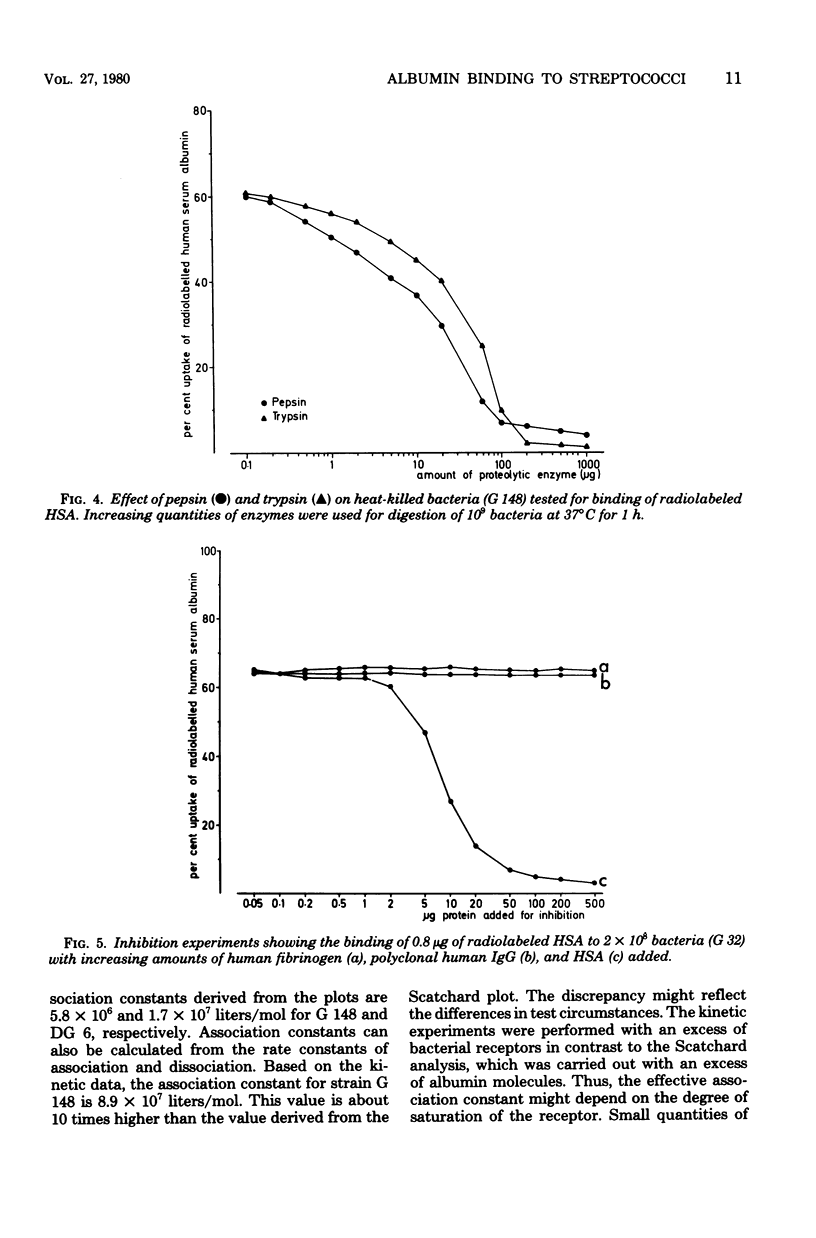
A total of 297 bacterial strains belonging to 27 species was tested for quantitative uptake of radiolabeled human serum albumin. Specific binding sites with high affinity for human serum albumin were found exclusively in group C and G streptococci. The albumin binding was found to be a time-dependent, saturable, and displaceable process which obeyed simple kinetic equations. Scatchard analysis revealed that human serum albumin bound to a homogeneous population of receptors with an affinity in the order ot 10(7) liters/mol and that the average bacterial cell carried more than 80,000 binding sites. The albumin receptor is a heat-stable component susceptible to proteolytic digestion. It has a surface localization separate from the receptors for immunolgobulin G, fibrinogen, aggregated beta 2-microglobulin, and haptoglobin. In individual strains, albumin reactivity was also detected independently of these other types of interactions with human proteins.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ankerst J., Christensen P., Kjellén L., Kronvall G. A rountine diagnostic test for IgA and IgM antibodies to rubella virus: absorption of IgG with Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):268–273. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Ofek I. Epithelial cell binding of group A streptococci by lipoteichoic acid on fimbriae denuded of M protein. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):759–771. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R. Games parasites play: how parasites evade immune surveillance. Nature. 1979 May 3;279(5708):21–26. doi: 10.1038/279021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen P., Kahlmeter G., Jonsson S., Kronvall G. New method for the serological grouping of Streptococci with specific antibodies adsorbed to protein A-containing staphylococci. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):881–885. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.881-885.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. A., Smithers S. R., Terry R. J. Acquisition of human antigens by Schistosoma mansoni during cultivation in vitro. Nature. 1971 Aug 27;232(5313):653–654. doi: 10.1038/232653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Hollenberg M. D. Membrane receptors and hormone action. Adv Protein Chem. 1976;30:251–451. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60481-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTHIE E. S. The action of fibrinogen on certain pathogenic cocci. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Oct;13(2):383–393. doi: 10.1099/00221287-13-2-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. B., Rombauer R. B., Campbell B. J. Thiol-disulfide interchange reactions between serum albumin and disulfides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 11;194(1):234–245. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90199-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe M., Fölling I. Recognition of two distinct groups of human IgM and IgA based on different binding to staphylococci. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(4):471–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B. G. Agarose gel electrophoresis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:7–19. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp W. M., Merritt S. C., Bogucki M. S., Rosier J. G., Seed J. R. Evidence for adsorption of heterospecific host immunoglobulin on the tegument of Schistosoma mansoni. J Immunol. 1977 Nov;119(5):1849–1854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Immunological properties of teichoic acids. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Jun;37(2):215–257. doi: 10.1128/br.37.2.215-257.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. A surface component in group A, C, and G streptococci with non-immune reactivity for immunoglobulin G. J Immunol. 1973 Nov;111(5):1401–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Myhre E. B., Björck L., Berggård I. Binding of aggregated human beta2-microglobulin to surface protein structure in group A, C, and G streptococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):136–142. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.136-142.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Simmons A., Myhre E. B., Jonsson S. Specific absorption of human serum albumin, immunoglobulin A, and immunoglobulin G with selected strains of group A and G streptococci. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):1–10. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.1-10.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler W., Prokop O. Relationship between haptoglobin and Streptococcus pyogenes T4 antigens. Nature. 1978 Jan 26;271(5643):373–373. doi: 10.1038/271373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallinson H., Roberts C., Bruce White G. B. Staphylococcal protein A; its preparation and an application to rubella serology. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Nov;29(11):999–1002. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.11.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhre E. B., Holmberg O., Kronvall G. Immunoglobulin-binding structure on bovine group G streptococci different from type III Fc receptors on human group G streptococci. Infect Immun. 1979 Jan;23(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.1.1-7.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhre E. B., Kronvall G. Heterogeneity of nonimmune immunoglobulin Fc reactivity among gram-positive cocci: description of three major types of receptors for human immunoglobulin G. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):475–482. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.475-482.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Beachey E. H., Jefferson W., Campbell G. L. Cell membrane-binding properties of group A streptococcal lipoteichoic acid. J Exp Med. 1975 May 1;141(5):990–1003. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.5.990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSA U., SCASSELLATI G. A., PENNISI F. LABELLING OF HUMAN FIBRINOGEN WITH 131-I BY ELECTROLYTIC IODINATION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jun 8;86:519–526. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher A., Hall B. F., Vadas M. A. Acquisition of murine major histocompatibility complex gene products by schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):46–57. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skaug K., Tjotta E. Diagnosis of recent Herpes simplex infections. A modified immunofluorescent test for the detection of specific Herpes simplex IgM antibodies after staphylococcal adsorption of IgG. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Jun;82(3):323–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torpier G., Capron A., Ouaissi M. A. Receptor for IgG(Fc) and human beta2-microglobulin on S. mansoni schistosomula. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):447–449. doi: 10.1038/278447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Lipoteichoic acids: a new class of bacterial antigen. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1161–1167. doi: 10.1126/science.46620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


