Abstract
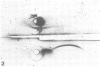
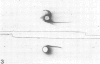
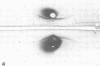
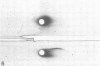
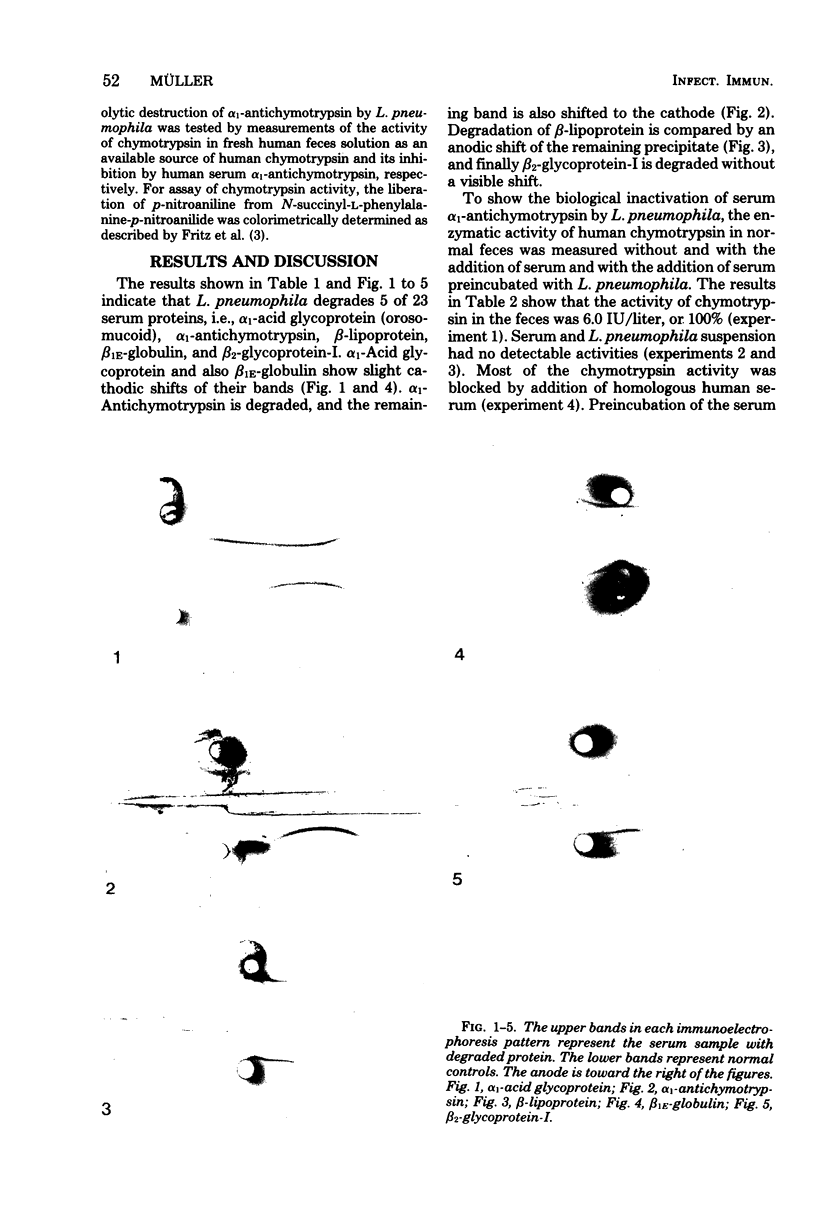
Proteolysis by four strains of Legionella pneumophila, the etiological agent of Legionnaires disease, was studied by the method of immunoelectrophoresis. Twenty-three human serum proteins were tested as substrates. Five proteins were degraded: alpha 1-acid glycoprotein, alpha 1-antichymotrypsin, beta-lipoprotein, beta 1E-globulin, and beta 2-glycoprotein-I. Moreover, the degradation of alpha 1-antichymotrypsin was demonstrated by investigation of an enzyme-blocking test. It is suggested that the proteolytic activity of L. pneumophila may bear some relationship to its pathogenic activity.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baine W. B., Rasheed J. K., Mackel D. C., Bopp C. A., Wells J. G., Kaufmann A. F. Exotoxin activity associated with the Legionnaires disease bacterium. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Mar;9(3):453–456. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.3.453-456.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gorman G. W., Weaver R. E., Mackel D. C., Smith H. W. Primary isolation media for Legionnaires disease bacterium. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):320–325. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.320-325.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Weaver R. E., Dees S. B., Cherry W. B. Cellular fatty acid composition of isolates from Legionnaires disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Aug;6(2):140–143. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.2.140-143.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller H. E. Immunelektrophoretisch nachweisbare Liquorproteinveränderungen bei bakteriellen Meningitiden. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1972;38(2):83–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller H. E., Marklein G. Untersuchungen zur proteolytischen Enzymaktivität bei Bacillus anthracis und Bacillus cereus. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1973;39(5):364–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller H. E. Methodische Untersuchungen in vitro zur Einwirkung bakterieller Proteasen auf menschliche Plasmaeiweisskörper, dargestellt am Beispiel von Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1971;216(1):79–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller H. E. Neuraminidase activity in Streptococcus sanguis and in the viridans group, and occurrence of acylneuraminate lyase in viridans organisms isolated from patients with septicemia. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):323–328. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.323-328.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller H. E., Sethi K. K. Proteolytic activity of Cryptococcus neoformans against human plasma proteins. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1972;158(2):129–134. doi: 10.1007/BF02120478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schallehn G., Müller H. E. Uber die Einwirkung proteolytischer Enzyme von Clostridium histolyticum und Clostridium novyi auf menschliche Plasmaeiweibbkörper in Wachstumskulturen. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1973 Jun;224(1):102–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi K. K., Müller H. E. Immunoelectrophoretic demonstration of proteolytic activity against human proteins by Mycoplasma laidlawii. Z Immunitatsforsch Allerg Klin Immunol. 1970 Aug;140(2):184–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner H., Müller H. E. Immunelektrophoretische Untersuchungen über die Einwirkung von Bacteroides-, Fusobacterium-, Leptotrichia- und Sphaerophorus-Arten auf menschliche Plasmaproteine. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1971;216(1):96–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]