Abstract
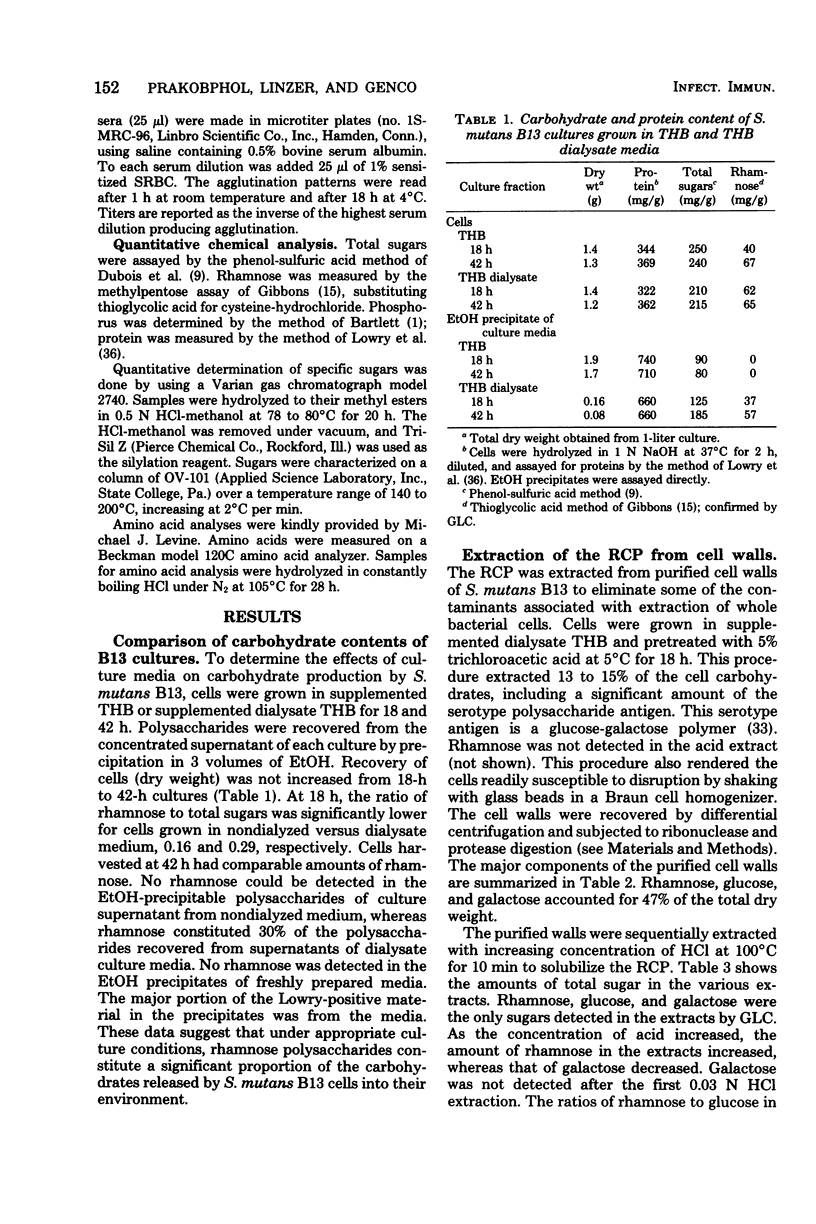
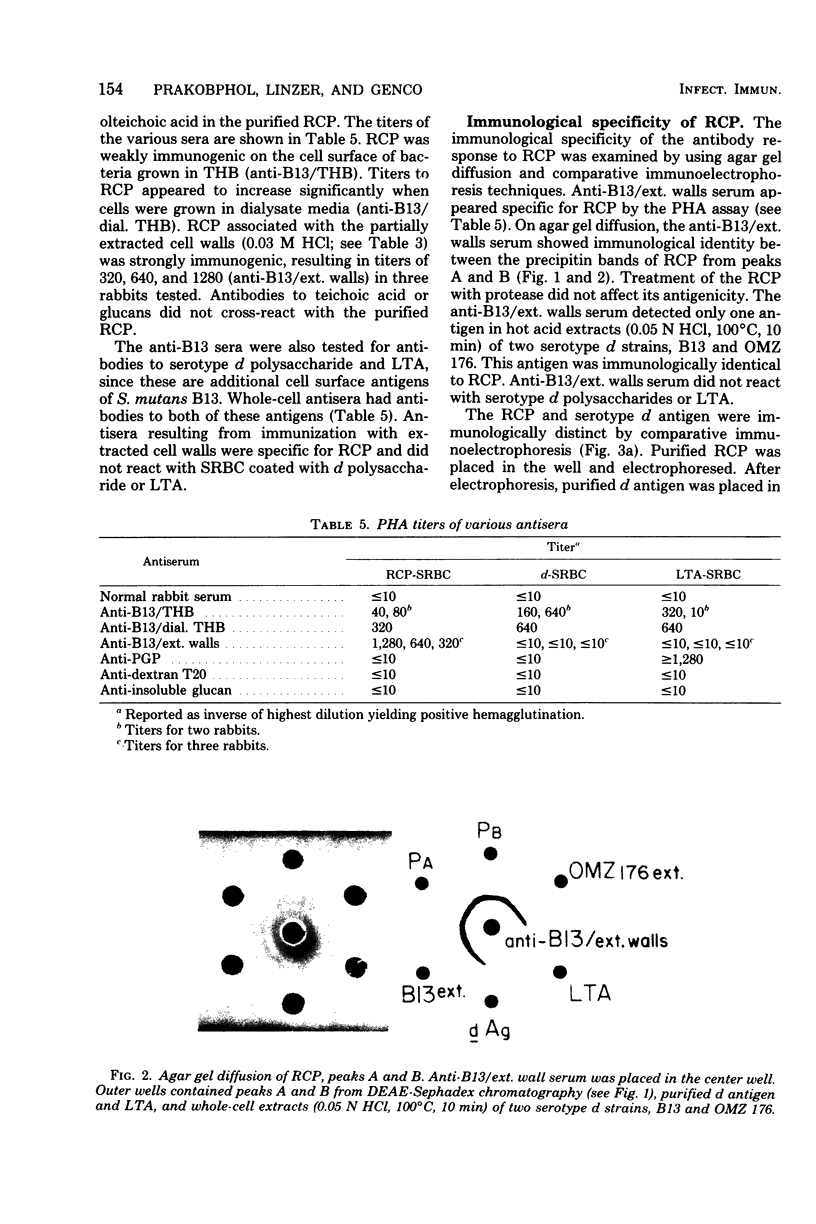
A rhamnose-containing polysaccharide (RCP) was extracted and purified from cell walls of Streptococcus mutans B13 (serotype d) and was chemically and immunologically characterized. Walls were initially extracted with 5% trichloroacetic acid at 4 degrees C to remove the serotype antigen and were then sequentially extracted with increasing concentrations of hot acid. Extracts lacking galactose were combined and chromatographed on a column of diethylaminoethyl--Sephadex A25. The purified RCP contained 90% carbohydrate, 1.4% protein, and 0.16% phosphorus. Analysis by gas chromatography indicated that the RCP was composed of rhamnose and glucose in a 1.6:1 ratio. RCP was immunogenic in rabbits when animals were immunized with whole cells or cell walls. Antisera prepared against partially extracted cell walls of B13 appeared specific for RCP. These sera were not reactive with purified serotype d antigen or lipoteichoic acid in passive hemagglutination assays or by agar gel diffusion. The RCP appeared to be a cell wall polysaccharide that was both chemically and immunologically distinct from the serotype d antigen.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratthall D. Demonstration of Streptococcus mutans strains in some selected areas of the world. Odontol Revy. 1972;23(4):401–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratthall D. Demonstration of five serological groups of streptococcal strains resembling Streptococcus mutans. Odontol Revy. 1970;21(2):143–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratthall D., Gibbons R. J. Antigenic variation of Streptococcus mutans colonizing gnotobiotic rats. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1231–1236. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1231-1236.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratthall D. Immunofluorescent identification of Streptococcus mutans. Odontol Revy. 1972;23(2):181–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. A., Bleiweis A. S. Chemical, immunochemical, and structural studies of the cross-reactive antigens of Streptococcus mutans AHT and B13. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):326–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.326-336.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. T., Emmings F. G., Genco R. J. Prevention of Streptococcus mutans infection of tooth surfaces by salivary antibody in Irus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis). Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):293–302. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.293-302.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZGERALD R. J., JORDAN H. V., STANLEY H. R. Experimental caries and gingival pathologic changes in the gnotobiotic rat. J Dent Res. 1960 Sep-Oct;39:923–935. doi: 10.1177/00220345600390052701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZGERALD R. J., KEYES P. H. Demonstration of the etiologic role of streptococci in experimental caries in the hamster. J Am Dent Assoc. 1960 Jul;61:9–19. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1960.0138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genco R. J., Evans R. T., Linzer E. R., Hall R., Emmings F. G., Huis J. H., Veld J. H. Antigenicity and immunogenicity of cell-associated glucans from Streptococcus mutans. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;107:783–790. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3369-2_88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genco R. J., Evans R. T., Taubman M. A. Specificity of antibodies to Streptococcus mutans; significance in inhibition of adherence. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1974;45(0):327–336. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-4550-3_39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenier E. M., Eveland W. C., Loesche W. J. Identification of Streptococcus mutans serotypes in dental plaque by fluorescent antibody techniques. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Jun;18(6):707–715. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenier E. M., Gray R. H., Loesche W. J., Eveland W. C. Microcapsules on Streptococcus mutans serotypes by electron microscopy. J Dent Res. 1977 Feb;56(2):166–176. doi: 10.1177/00220345770560021101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESS E. L., SLADE H. D. An electrophoretic examination of cell-free extracts from various serological types of group A hemolytic streptococci. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Mar;16(3):346–353. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall E. A., Knox K. W. Properties of the polysaccharide and mucopeptide components of the cell wall of Lactobacillus casei. Biochem J. 1965 Aug;96(2):310–318. doi: 10.1042/bj0960310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Gill K., Slade H. D. Chemical and immunological properties of the type f polysaccharide antigen of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):203–211. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.203-211.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Masuda N., Kotani S. Demonstration of serotype d and g specificities of Streptococcus mutans by immunodiffusion. Arch Oral Biol. 1978;23(6):495–499. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(78)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Purification and immunochemical characterization of type e polysaccharide antigen of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):68–76. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.68-76.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Tai S., Slade H. D. Selective adsorption of heterophile polyglycerophosphate antigen from antigen extracts of Streptococcus mutans and other gram-positive bacteria. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):903–910. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.903-910.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie J. M., Bowden G. H. Cell wall and serological studies on Streptococcus mutans. Caries Res. 1974;8(4):301–316. doi: 10.1159/000260120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hämmerling U., Westphal O. Synthesis and use of O-stearoyl polysaccharides in passive hemagglutination and hemolysis. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):46–50. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacono V. J., Taubman M. A., Smith D. J., Levine M. J. Isolation and immunochemical characterization of the group-specific antigen of Streptococcus mutants 6715. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):117–128. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.117-128.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasse B. Human streptococci and experimental caries in hamsters. Arch Oral Biol. 1966 Apr;11(4):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(66)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasse B., Jordan H. V., Edwardsson S., Svensson I., Trell L. The occurrence of certain "caries-inducing" streptococci in human dental plaque material with special reference to frequency and activity of caries. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 Aug;13(8):911–918. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Caldwell J., Challacombe S. J. Effects of immunisation on dental caries in the first permanent molars in rhesus monkeys. Arch Oral Biol. 1977;22(6):393–397. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(77)90062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer R., Gill K., Slade H. D. Chemical composition of Streptococcus mutans type c antigen: comparison to type a, b, and d antigens. J Dent Res. 1976 Jan;55:A109–A115. doi: 10.1177/002203457605500103011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer R., Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Serological purification of polysaccharide antigens from Streptococcus mutans serotypes a and d: characterization of multiple antigenic determinants. Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):791–798. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.791-798.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer R., Slade H. D. Characterization of an anti-glucosyltransferase serum specific for insoluble glucan synthesis by Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):494–500. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.494-500.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer R., Slade H. D. Purification and characterization of Streptococcus mutans group d cell wall polysaccharide antigen. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):361–368. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.361-368.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J., Rowan J., Straffon L. H., Loos P. J. Association of Streptococcus mutants with human dental decay. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1252–1260. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1252-1260.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalek S. M., McGhee J. R., Mestecky J., Arnold R. R., Bozzo L. Ingestion of Streptococcus mutans induces secretory immunoglobulin A and caries immunity. Science. 1976 Jun 18;192(4245):1238–1240. doi: 10.1126/science.1273589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Extraction, purification, and chemical and immunological properties of the Streptococcus mutans group "a" polysaccharide cell wall antigen. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):190–198. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.190-198.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Mechanism of adherence of Streptococcus mutans to smooth surfaces. I. Roles of insoluble dextran-levan synthetase enzymes and cell wall polysaccharide antigen in plaque formation. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):555–562. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.555-562.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson G. A., Bleiweis A. S., Small P. A., Jr Adherence inhibition of Streptococcus mutans: an assay reflecting a possible role of antibody in dental caries prophylaxis. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):419–427. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.419-427.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perch B., Kjems E., Ravn T. Biochemical and serological properties of Streptococcus mutans from various human and animal sources. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Jun;82(3):357–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbman M. A., Smith D. J. Effects of local immunization with Streptococcus mutans on induction of salivary immunoglobulin A antibody and experimental dental caries in rats. Infect Immun. 1974 Jun;9(6):1079–1091. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.6.1079-1091.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetherell J. F., Jr, Bleiweis A. S. Antigens of Streptococcus mutans: isolation of a serotype-specific and a cross-reactive antigen from walls of strain V-100 (serotype e). Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):160–169. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.160-169.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetherell J. R., Jr, Bleiweis A. S. Antigens of Streptococcus mutans: characterization of a polysaccharide antigen from walls of strain GS-5. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1341–1348. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1341-1348.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Studies on the group F antigen of lactobacilli: isolation of a teichoic acid-lipid complex from Lactobacillus fermenti NCTC 6991. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Mar;60(3):293–301. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-3-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZINNER D. D., JABLON J. M., ARAN A. P., SASLAW M. S. EXPERIMENTAL CARIES INDUCED IN ANIMALS BY STREPTOCOCCI OF HUMAN ORIGIN. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Mar;118:766–770. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachrisson B. U. Mast cells of the human gingiva. I. Investigations concerning the preservation and demonstration of mast cells in the gingival area. Odontol Revy. 1968;19(1):1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




