Abstract
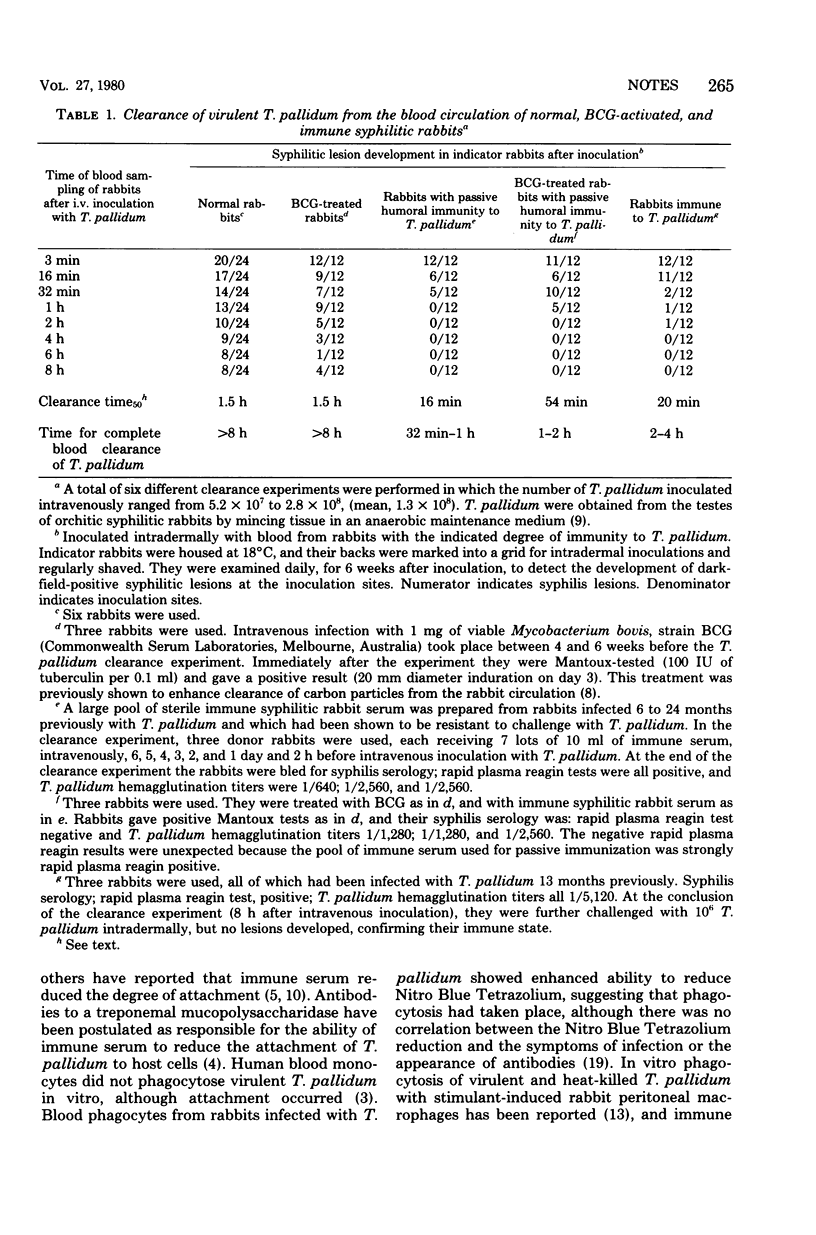
The rate of clearance of virulent Treponema pallidum (Nichols) from the blood stream of normal rabbits and rabbits previously treated with Mycobacterium bovis BCG was similar, there being treponemes still circulating 8 h after intravenous inoculation. In contrast, immune syphilitic rabbits cleared the virulent treponemes within 1 to 2 hours. Rabbits with passive humoral immunity to T. pallidum (after the transfer of 70 ml of immune serum) showed a similar clearance rate to that of the immune rabbits. Rabbits previously treated with BCG and with passive humoral immunity did not show a synergistic enhanced clearance rate, it being similar to that of immune rabbits.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baughn R. E., Musher D. M., Knox J. M. Effect of sensitization with Propionibacterium acnes on the growth of Listeria monocytogenes and Treponema pallidum in rabbits. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):109–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop N. H., Miller J. N. Humoral immunity in experimental syphilis. II. The relationship of neutralizing factors in immune serum to acquired resistance. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):197–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brause B. D., Roberts R. B. Attachment of virulent Treponema pallidum to human mononuclear phagocytes. Br J Vener Dis. 1978 Aug;54(4):218–224. doi: 10.1136/sti.54.4.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAZIER C. N., BENSEL A., KEUPER C. S. Further observations on the duration of spirochetemia in rabbits with asymptomatic syphilis. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1952 Mar;36(2):167–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAZIER C. N., BENSEL A., KEUPER C. S. Phenomena of disease in rabbits fed cholesterol and inoculated with treponema pallidum. II. Infectivity of blood. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1950 Sep 5;34(5):453–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Johnson R. C., Miller J. N., Sykes J. A. Characterization of the attachment of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) to cultured mammalian cells and the potential relationship of attachment to pathogenicity. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):467–478. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.467-478.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Johnson R. C. Mucopolysaccharidase of Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):261–268. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.261-268.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves S. R., Johnson R. C. Effect of pretreatment with Mycobacterium bovis (strain BCG) and immune syphilitic serum on rabbit resistance to Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1029–1036. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1029-1036.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves S. R., Sandok P. L., Jenkin H. M., Johnson R. C. Retention of motility and virulence of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) in vitro. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1116–1120. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1116-1120.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes N. S., Muse K. E., Collier A. M., Baseman J. B. Parasitism by virulent Treponema pallidum of host cell surfaces. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):174–186. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.174-186.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMANNA C., HOLLANDER D. H. Demonstration of particulate adhesion of the Rieckenberg type with the spirochete of syphilis. Science. 1956 Jun 1;123(3205):989–990. doi: 10.1126/science.123.3205.989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukehart S. A., Miller J. N. Demonstration of the in vitro phagocytosis of Treponema pallidum by rabbit peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):2014–2024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger M., Michalska E. Treponema pallidum opsonophagocytic test. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1974;22(6):745–758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Schell R. F., Knox J. M. The immunology of syphilis. Int J Dermatol. 1976 Oct;15(8):566–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1976.tb04891.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON R. A., Jr The immune-adherence phenomenon; an immunologically specific reaction between microorganisms and erythrocytes leading to enhanced phagocytosis. Science. 1953 Dec 18;118(3077):733–737. doi: 10.1126/science.118.3077.733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavis C. S., Folds J. D., Baseman J. B. Cell-mediated immunity during syphilis. Br J Vener Dis. 1978 Jun;54(3):144–150. doi: 10.1136/sti.54.3.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell R., Musher D., Jacobson K., Schwethelm P., Simmons C. Effect macrophage activation on infection with Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):505–511. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.505-511.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicher V., Blakowski S., Wicher K. Nitroblue tetrazolium test in experimental syphilis. Br J Vener Dis. 1977 Oct;53(5):292–294. doi: 10.1136/sti.53.5.292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


