Abstract
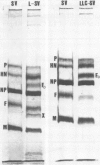
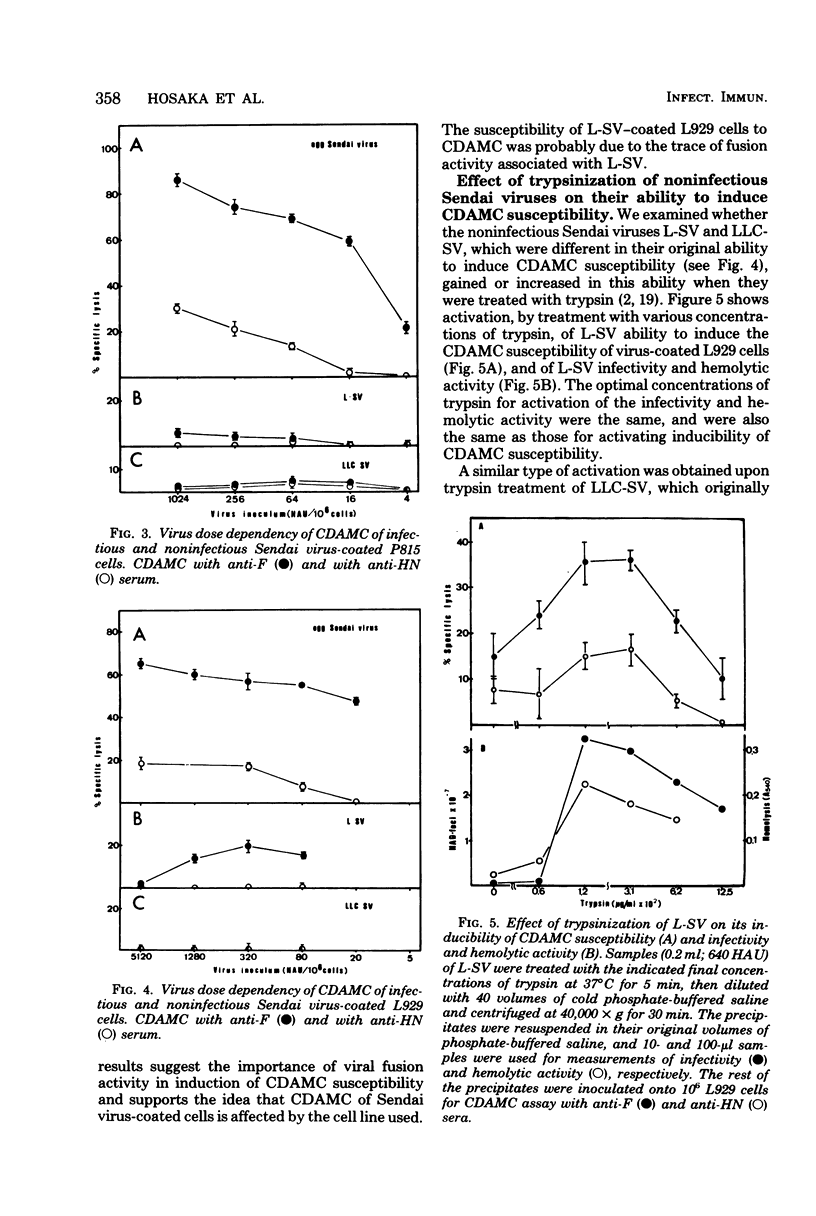
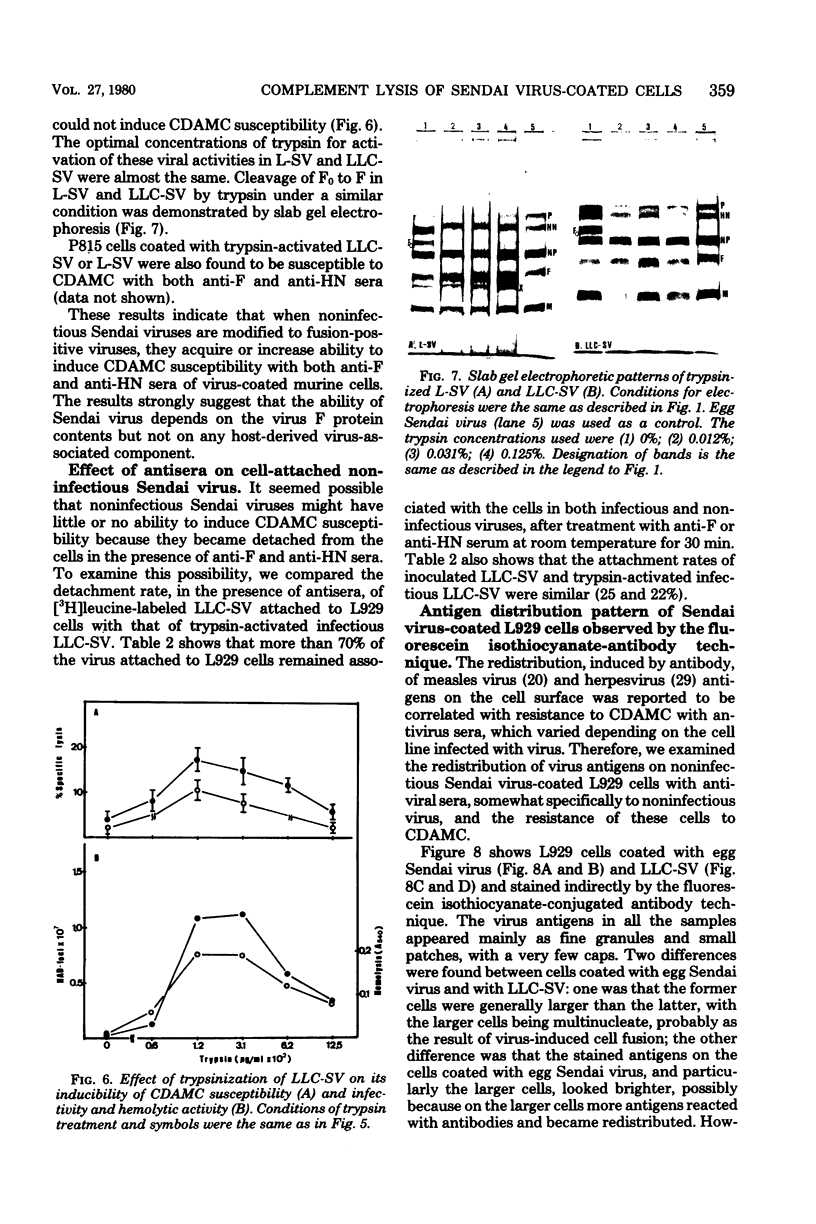
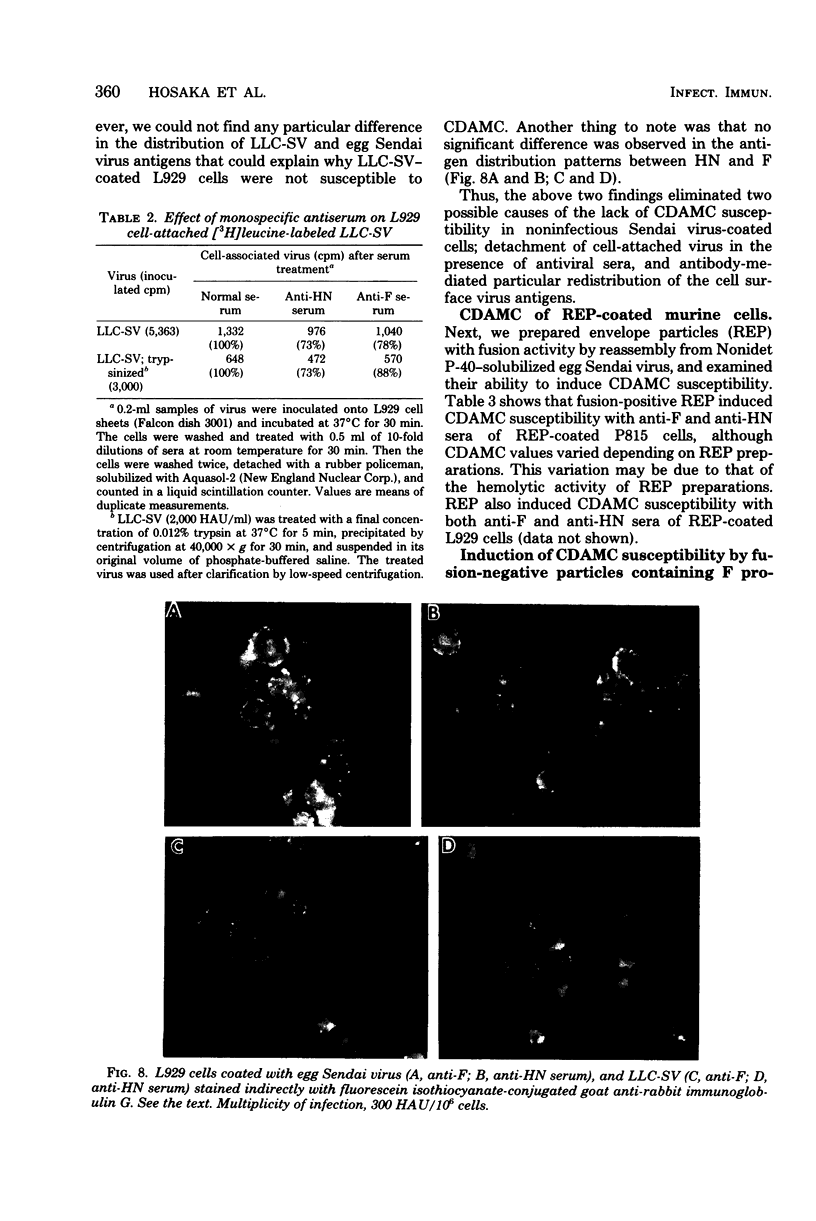
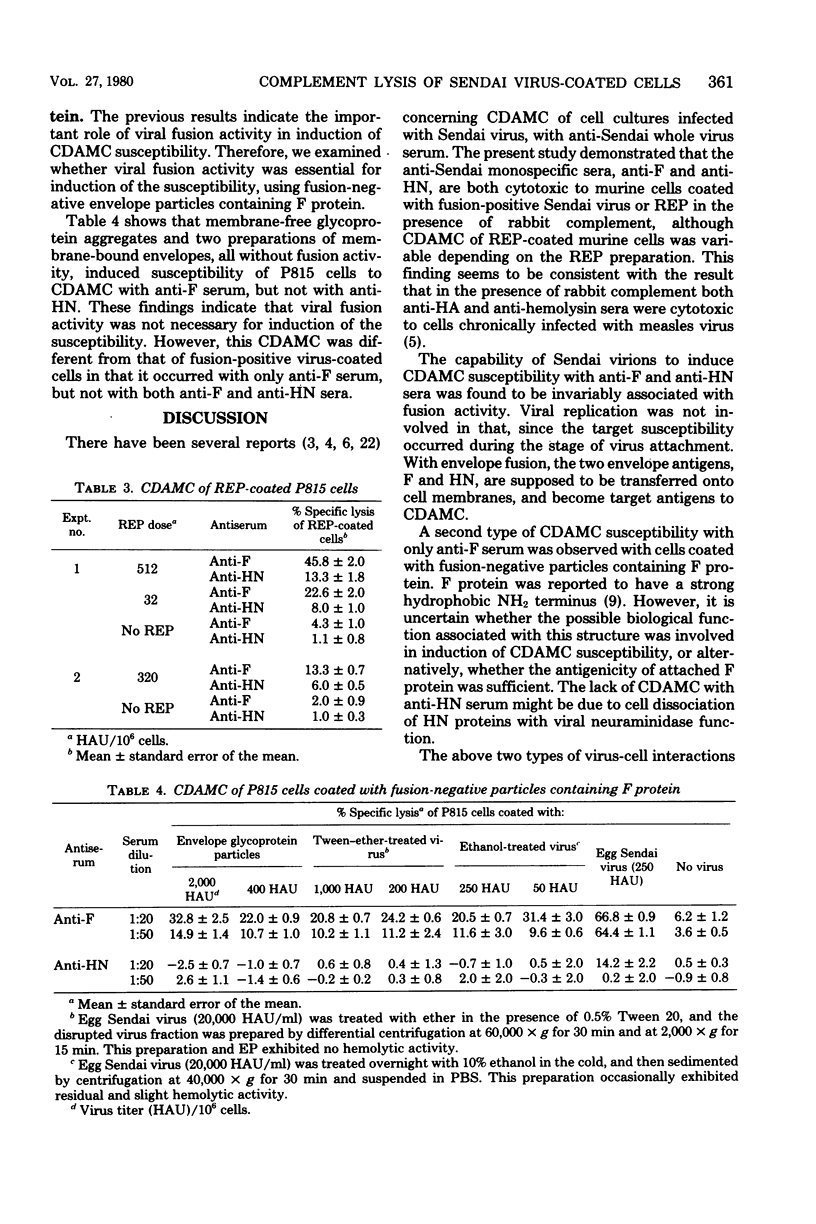
Complement-dependent antiviral antibody-mediated lysis of murine cells coated with Sendai virus or its envelope component (P815 mastocytoma cells and L929 cells) was studied with antiviral monospecific sera (anti-F and anti-HN sera). Three types of interactions different in terms of susceptibility of complement-dependent antibody-mediated lysis were distinguished: (i) fusion-positive Sendai viruses induced the susceptibility with both anti-F and anti-HN sera; (ii) fusion-negative envelope particles with F protein induced the susceptibility with only anti-F serum; (iii) noninfectious Sendai viruses with F0 protein induced no susceptibility. The lack of complement-dependent antibody-mediated cytolysis susceptibility in case (iii) was found to be due neither to detachment of cell-associated noninfectious virus in the presence of antiserum nor to antibody-mediated particular redistribution of cell surface virus antigens. Differences in virus or envelope component-cell association in these three cases were discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry D. M., Almeida J. D. The morphological and biological effects of various antisera on avian infectious bronchitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1968 Jul;3(1):97–102. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-3-1-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton M. D., Scala A. R. Further observations on the inhibitory effect of myxoviruses on a transplantable murine leukemia. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Oct;132(1):20–26. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton M. D., Scala A. R. Species source of complement in viral-immune and other cytolytic reactions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Feb;133(2):615–619. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrnst A. C. Characterization of measles virus-specific cytotoxic antibodies by use of a chronically infected cell line. J Immunol. 1975 Mar;114(3):1077–1082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan D. P., Sefton B. M. The entry into host cells of Sindbis virus, vesicular stomatitis virus and Sendai virus. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):985–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90282-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finberg R., Mescher M., Burakoff S. J. The induction of virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes with solubilized viral and membrane proteins. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1620–1627. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., White J. M., Waterfield M. D. Purification of the fusion protein of Sendai virus: analysis of the NH2-terminal sequence generated during precursor activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2737–2740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M., Koszinowski U., Waterfield M. Fusion of Sendai virus with the target cell membrane is required for T cell cytotoxicity. Nature. 1978 Aug 17;274(5672):689–691. doi: 10.1038/274689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt J. A., Nermut M. V. A morphological study of the M-protein of Sendai virus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jan;34(1):127–136. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-1-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Shimizu K., Shimizu Y. K., Ishida N. On the study of Sendai virus hemolysis. I. Complete Sendai virus lacking in hemolytic activity. Virology. 1976 May;71(1):41–47. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M. Trypsin action on the growth of Sendai virus in tissue culture cells. II. Restoration of the hemolytic activity if L cell-borne Sendai virus by trypsin. J Virol. 1972 May;9(5):829–835. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.5.829-835.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosaka Y., Shimizu Y. K. Artificial assembly of envelope particles of HVJ (Sendai virus). I. Assembly of hemolytic and fusion factors from envelopes solubilized by Nonidet P40. Virology. 1972 Sep;49(3):627–639. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90519-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAACS A., DONALD H. B. Particle counts of haemagglutinating viruses. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Apr;12(2):241–247. doi: 10.1099/00221287-12-2-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida N., Homma M. Sendai virus. Adv Virus Res. 1978;23:349–383. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph B. S., Oldstone M. B. Antibody-induced redistribution of measles virus antigens on the cell surface. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1205–1209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung H., Pfizenmaier K., Starzinski-Powitz A., Röllinghoff M., Wagner H. Primary in vitro sensitization of virus specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Immunology. 1978 Apr;34(4):763–769. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieling F., Bandlow G., Thomssen R. Cytotoxische Reaktionen an Sendai-virus infizierten Zellen. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972;36(1):123–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koszinowski U., Gething M. J., Waterfield M. T-cell cytotoxicity in the absence of viral protein synthesis in target cells. Nature. 1977 May 12;267(5607):160–163. doi: 10.1038/267160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurrle R., Röllinghoff M., Wagner H. H-2-linked murine cytotoxic T cell responses specific for sendai virus-infected cells. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Dec;8(12):910–912. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830081216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist S., Ostberg L., Persson H., Philipson L., Peterson P. A. Molecular association between transplantation antigens and cell surface antigen in adenovirus-transformed cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5674–5678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKADA Y., NISHIDA S., TADOKORO J. Correlation between the hemagglutination titer and the virus particle number of HVJ. Biken J. 1961 Sep;4:209–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. C., Lewandowski L. J., Waters D. Non-infectious virus induces cytotoxic T lymphocytes and binds to target cells to permit their lysis. Nature. 1977 Oct 13;269(5629):595–597. doi: 10.1038/269595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Isolation and purification of the envelope proteins of Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1973 Feb;11(2):263–271. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.2.263-271.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader J. W., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Functional interactions of viral and histocompatibility antigens at tumor cell surfaces. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5066–5070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader J. W., Edelman G. M. Joint recognition by cytotoxic T cells of inactivated Sendai virus and products of the major histocompatibility complex. J Exp Med. 1977 Mar 1;145(3):523–539. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.3.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y. K., Shimizu K., Ishida N., Homma M. On the study of Sendai virus hemolysis. II. Morphological study of envelop fusion and hemolysis. Virology. 1976 May;71(1):48–60. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugamura K., Shimizu K., Bach F. H. Involvement of fusion activity of ultraviolet light-inactivated Sendai virus in formation of target antigens recognized by cytotoxic T cells. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):276–287. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugamura K., Shimizu K., Zarling D. A., Bach F. H. Role of sendai virus fusion-glycoprotein in target cell susceptibility to cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1977 Nov 17;270(5634):251–253. doi: 10.1038/270251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling D. A., Keshet I., Watson A., Bach F. H. Association of mouse major histocompatibility and Rauscher murine leukaemia virus envelope glycoprotein antigens on leukaemia cells and their recognition by syngeneic virus-immune-cytotoxic T-lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1978;8(6):497–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00549.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]