Abstract
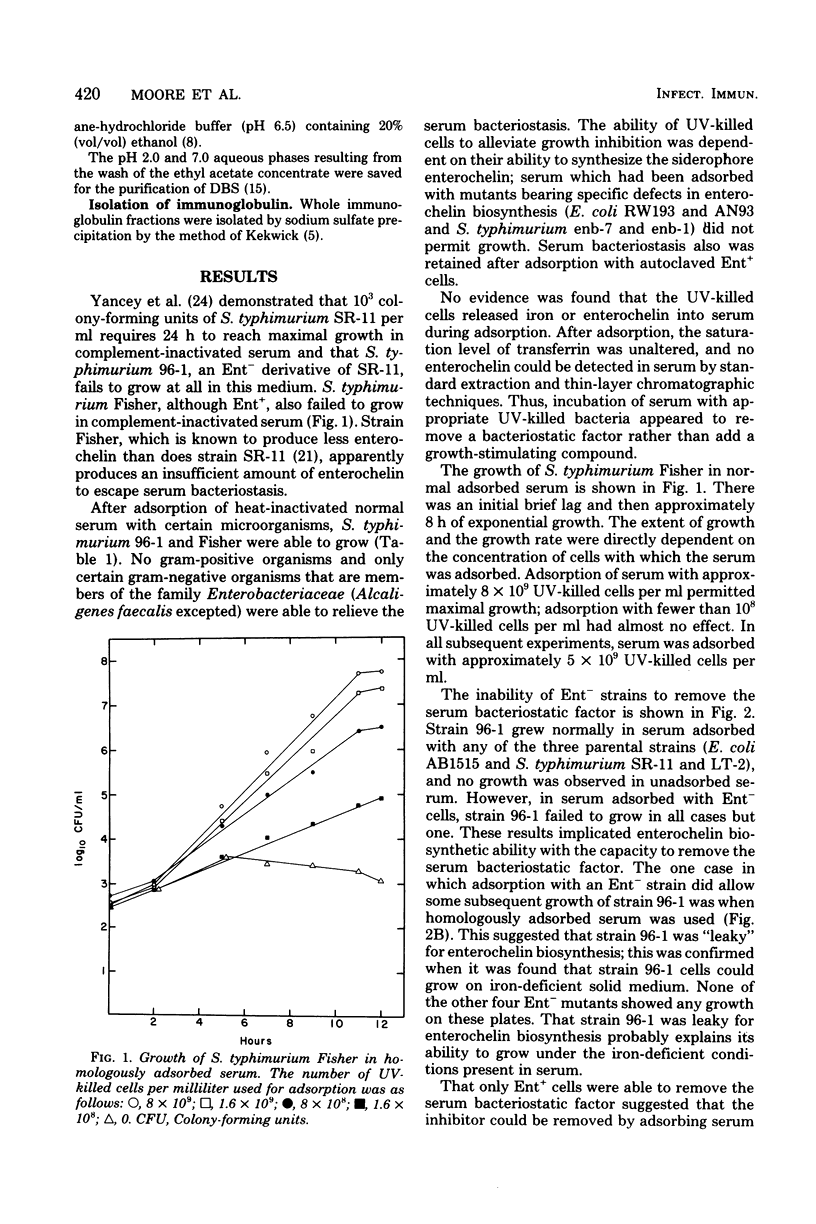
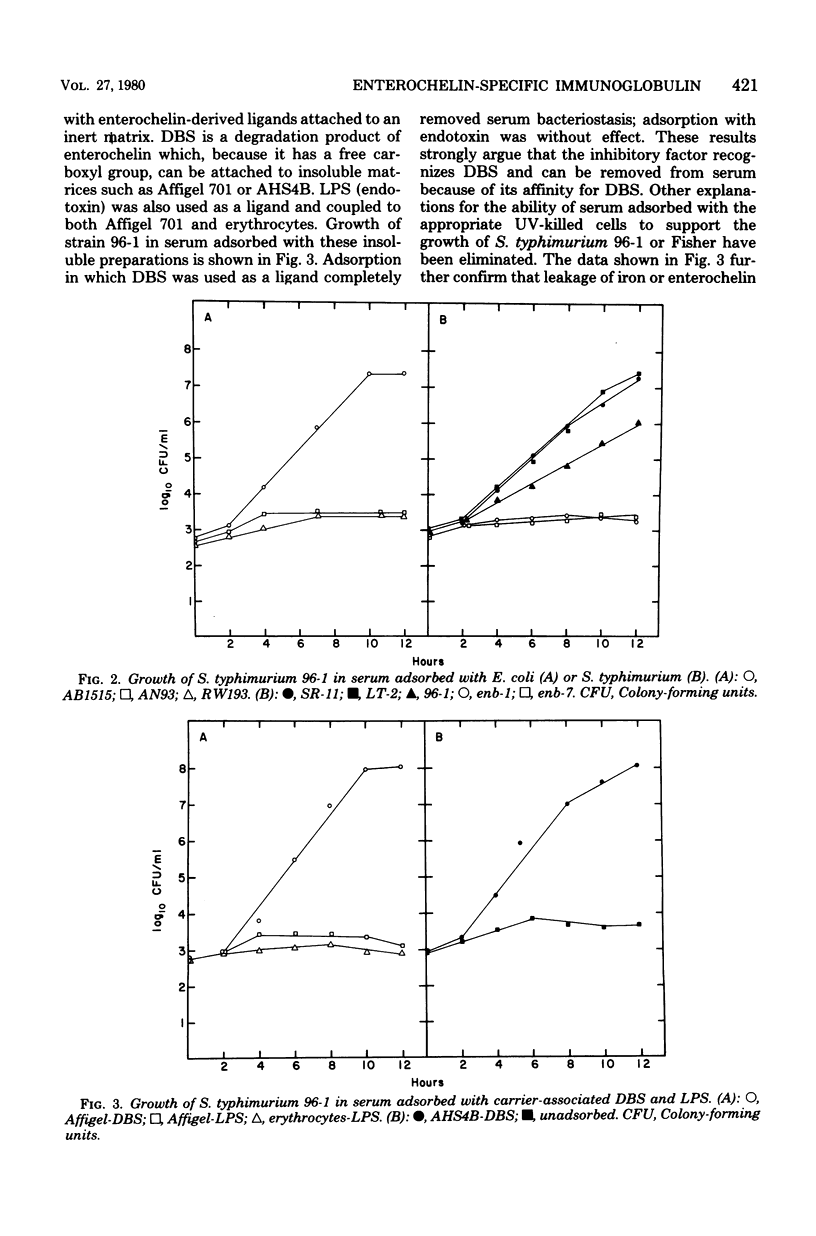
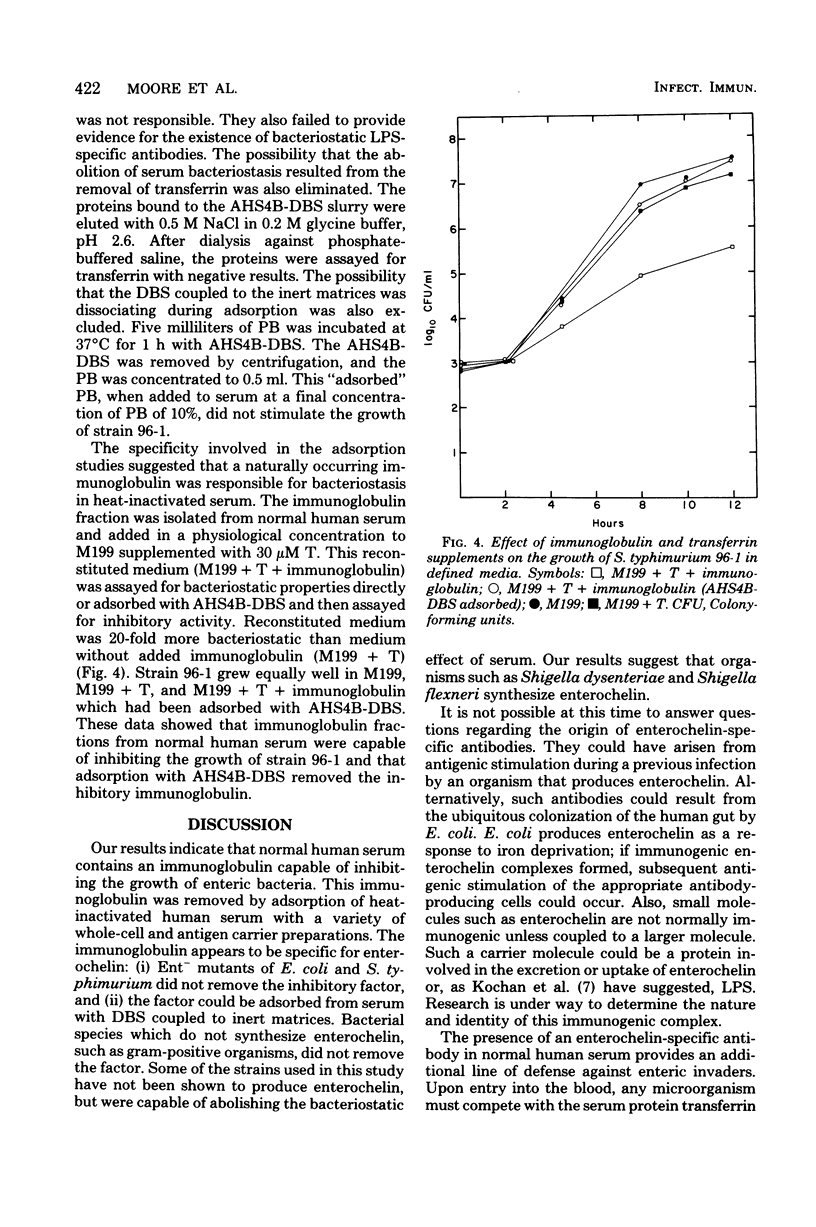
Heat-inactivated normal human serum produces iron-reversible bacteriostasis of a number of microorganisms. This inhibitory effect was abolished by adsorption of serum with ultraviolet-killed cells of species that produce the siderophore enterochelin. Bacteriostasis also was alleviated by adsorption of serum with 2,3-dihydroxy-N-benzoyl-L-serine, a degradation product of enterochelin, bound to the insoluble matrix AH-Sepharose 4B. The adsorption process did not add iron or enterochelin to serum, nor did it remove transferrin. The immunoglobulin fraction from normal human serum was isolated; when added to a defined medium (M199) prepared so as to mimic normal human serum, the immunoglobulin rendered the medium inhibitory to an enterochelin-defective strain of Salmonella typhimurium. Adsorption of this medium with AH-Sepharose 4B-2,3-dihydroxy-N-benzoyl-L-serine removed the inhibition. Our results indicate that enterochelin-specific immunoglobulins exist in normal human serum. These immunoglobulins may act synergistically with transferrin to effect bacteriostasis of enterochelin-producing pathogens.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bates G. W., Wernicke J. The kinetics and mechanism of iron(3) exchange between chelates and transferrin. IV. The reaction of transferrin with iron(3) nitrilotriacetate. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 10;246(11):3679–3685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambiaso C. L., Goffinet A., Vaerman J. P., Heremans J. F. Glutaraldehyde-activated aminohexyl- derivative of Sepharose 4B as a new verstile immunoabsorbent. Immunochemistry. 1975 Apr;12(4):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(75)90175-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. B., Gibson F., Luke R. K., Newton N. A., O'Brien I. G., Rosenberg H. Mutations affecting iron transport in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):219–226. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.219-226.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekwick R. A. The serum proteins in multiple myelomatosis. Biochem J. 1940 Sep;34(8-9):1248–1257. doi: 10.1042/bj0341248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochan I., Kvach J. T., Wiles T. I. Virulence-associated acquisition of iron in mammalian serum by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1977 Apr;135(4):623–632. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.4.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochan I. Mecahnism of tuberculostasis in mammalian serum. I. Role of transferrin in human serum tuberculostasis. J Infect Dis. 1969 Jan;119(1):11–18. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langman L., Young I. G., Frost G. E., Rosenberg H., Gibson F. Enterochelin system of iron transport in Escherichia coli: mutations affecting ferric-enterochelin esterase. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1142–1149. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1142-1149.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J., Neilands J. B. Mechanisms of siderophore iron transport in enteric bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):823–830. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.823-830.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON H. J., MORGAN J. F., PARKER R. C. Nutrition of animal cells in tissue culture. V. Effect of initial treatment of cultures on their survival in a synthetic medium. J Cell Physiol. 1951 Dec;38(3):389–400. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030380307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh M. A., Pickett C. L., Chenault S. S., Earhart C. F. Suppression of iron uptake deficiency in Escherichia coli K-12 by loss of two major outer membrane proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Apr 28;81(4):1106–1112. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91250-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien I. G., Cox G. B., Gibson F. Biologically active compounds containing 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid and serine formed by Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 24;201(3):453–460. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90165-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien I. G., Cox G. B., Gibson F. Enterochelin hydrolysis and iron metabolism in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 22;237(3):537–549. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90274-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack J. R., Ames B. N., Neilands J. B. Iron transport in Salmonella typhimurium: mutants blocked in the biosynthesis of enterobactin. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):635–639. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.635-639.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J. Ferric iron and the antibacterial effects of horse 7S antibodies to Escherichia coli O111. Immunology. 1976 Mar;30(3):425–433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J. Iron-Binding Catechols and Virulence in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):445–456. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.445-456.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Role of iron in host-parasite interactions. J Infect Dis. 1971 Oct;124(4):401–410. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.4.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins T. D., Lankford C. E. Production by Salmonella typhimurium of 2,3-dihydroxybenzoylserine, and its stimulation of growth in human serum. J Infect Dis. 1970 Feb;121(2):129–136. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.2.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams H. L., Conrad M. E. A one-tube method for measuring the serum iron concentration and unsaturated iron-binding capacity. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Jan;67(1):171–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey R. J., Breeding S. A., Lankford C. E. Enterochelin (enterobactin): virulence factor for Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):174–180. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.174-180.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young I. G. Preparation of enterochelin from Escherichia coli. Prep Biochem. 1976;6(2-3):123–131. doi: 10.1080/00327487608061607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



