Abstract
Background
Heart rate variability (HRV) has been used to assess cardiac autonomic activity in critically ill patients, driven by translational and biomarker research agendas. Several clinical and technical factors can interfere with the measurement and/or interpretation of HRV. We systematically evaluated how HRV parameters are acquired/processed in critical care medicine.
Methods
PubMed, MEDLINE, EMBASE and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (1996–2016) were searched for cohort or case–control clinical studies of adult (>18 years) critically ill patients using heart variability analysis. Duplicate independent review and data abstraction. Study quality was assessed using two independent approaches: Newcastle–Ottowa scale and Downs and Black instrument. Conduct of studies was assessed in three categories: (1) study design and objectives, (2) procedures for measurement, processing and reporting of HRV, and (3) reporting of relevant confounding factors.
Results
Our search identified 31/271 eligible studies that enrolled 2090 critically ill patients. A minority of studies (15; 48%) reported both frequency and time domain HRV data, with non-normally distributed, wide ranges of values that were indistinguishable from other (non-critically ill) disease states. Significant heterogeneity in HRV measurement protocols was observed between studies; lack of adjustment for various confounders known to affect cardiac autonomic regulation was common. Comparator groups were often omitted (n = 12; 39%). This precluded meaningful meta-analysis.
Conclusions
Marked differences in methodology prevent meaningful comparisons of HRV parameters between studies. A standardised set of consensus criteria relevant to critical care medicine are required to exploit advances in translational autonomic physiology.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s40635-017-0146-1) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Autonomic, Heart rate variability, Human, Systematic review
Background
Autonomic changes are evident from the onset of acute pathology requiring critical care. Cardiac autonomic function can be derived by analysing variability between heart beats to yield time domain and frequency domain (power spectral density) measures that reflect autonomic modulation of cardiac frequency [1, 2]. Heart rate variability (HRV) appears to contribute diagnostic and prognostic value in various cardiometabolic conditions associated with subclinical autonomic dysfunction that predispose to critical illness including hypertension, coronary artery disease, heart failure and diabetes [3–7]. Similarly, HRV has been proposed to serve as a potential diagnostic and prognostic tool in critically ill patients [8].
However, HRV measures in critically ill patients are fraught with potential problems. [9] Although population norms for HRV parameters have been reported in healthy populations [10], the impact of multiple physiological, procedural and technical factors in critically ill patients has not undergone systematic scrutiny in critical care medicine [11]. Moreover, the validity of HRV as a tool to interrogate autonomic function is increasingly under physiological scrutiny [12, 13], since a strong correlation between HRV and morbidity/mortality appears to be largely attributable to incident heart rate. In addition, recording technique, clinical context and adjustment for incident heart rate are key factors to consider when interpreting the translational relevance of HRV in critically ill patients.
Here, we sought to systematically evaluate the methodology and design of HRV studies in critical care medicine. We focused on whether recommended standards for measurement and reporting have been employed [14, 15], with the aim of identifying areas to refine in future HRV experimental design in critical care medicine.
Methods
Identification of studies
A literature review was performed based on the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines for systematic reviews [16]. The summary of the search strategy employed is shown in Additional file 1.
We searched the electronic databases PubMed, EMBASE, MEDLINE and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Clinical Trials for articles investigating HRV measurement in intensive care patients. Inclusion criteria were full-text studies written in English involving adult patients, published after 1996 (following published guidelines) and reporting traditional time and frequency domain parameters [15]. Studies which reported newer analysis techniques of HRV (e.g. entropy analysis) were excluded, as we focussed on those reporting measures in line with recent European guidance [17]. The following Medical Subject Headings (MESH) were used to identify pertinent articles: “Heart rate variability OR HRV AND Sepsis”, “Heart rate variability OR HRV AND multiple organ dysfunction OR MODS”, “Heart rate variability OR HRV AND critical illness”, “Heart rate variability OR HRV AND intensive care OR ICU”. The last search took place on 9 November 2016. We screened articles by title search and abstract review. Relevant articles were analysed for eligibility, and further articles were identified from reference lists. Articles were excluded based on the following criteria: experimental studies, incorrect target population (adult; >18 years old), medical field other than intensive care, not original research, topic not within scope or traditional HRV parameters not reported.
Data extraction
Data was extracted by two independent reviewers (S.K and A.S) and recorded into a standardised excel sheet recording: author, year of publication, study design, number of subjects, mean patient age, proportion of male subjects, risk stratification score, comparator groups, study aim and outcome, study design, protocol for measurement, processing, analysis and reporting of HRV parameters, adjustment and reporting of confounding factors and quality assessment. We identified the following clinical confounding factors: age, gender, average heart rate, average respiratory rate, co-morbidities, drugs, sedative drugs, vasoactive drugs, enteral nutrition and mechanical ventilation. Full details of the impact on HRV of these parameters are provided in Additional file 1. For reporting and analysis purposes, we selected the most commonly used time and frequency domain HRV parameters [15].
Risk of bias and study quality assessment
The quality of studies was assessed by two assessors independently (SK, SM) using two established tools (Newcastle–Ottowa scale, Downs and Black Instrument). The Downs and Black instrument is recommended by the Cochrane Collaboration for use in non-randomised and observational studies (Additional file 1) [18, 19]. Inter-observer reliability evaluating quality within five domains: reporting, external validity, bias, confounding and power. Five questions were omitted because they are designed for interventional trials. The version which we employed in this study therefore has a maximum score of 22. Differences between reviewers were resolved by panel consensus opinion following further review of the article(s) in question by the senior author.
Results
Study selection
We identified 238 studies which underwent screening by title search and abstract review. From these, 31 articles involving 2090 patients (including controls) met the inclusion criteria for assessing the role of HRV in critically ill patients [20–53]. Two articles analysed the same cohort of patients [34, 37].
Study characteristics
Demographic and clinical data, including comparator groups are summarised in Table 1. All articles reported cohort or case–control studies. The average age of patients was 60 ± 7 years. The majority of studies (22/31; 71%) explored the association between HRV measures, morbidity and mortality. Key clinical findings from these studies are summarised in Table 2. Due to significant differences in trial design, methodology, confounding, non-standardised comparator groups and inconsistent reporting of summary data, a meta-analysis could not be performed. However, there was consistency between studies in their findings that LF/HF ratio was inversely associated with increased disease severity or mortality. For illustrative purposes, the individual effect sizes across six studies reporting mean and standard deviation data looking at disease severity and mortality using the most commonly reported HRV parameter (LF/HF ratio) are shown (Fig. 1).
Table 1.
Demographics and study design of studies
| Reference number. author | Year | Study design | Study populations (± comparator group) | Patients (n) | Age (mean ± SD or mean [range]) | Male (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20. Annane | 1999 | Case–control | Sepsis (healthy controls) | 26 | Septic shock 52 ± 14 Sepsis 54 ± 17 Control 43 ± 11 |
65 |
| 21. Korach | 2001 | Cohort | Sepsis | 41 | 50 [20–90] | 44 |
| 22. Barnaby | 2002 | Cohort | Sepsis | 15 | 59 [39–85] | – |
| 23. Pontet | 2003 | Case–control | Sepsis + MODS (Sepsis − MODS) |
22 | MODS 59.5 ± 17.8 Non-MODS 60 ± 10.4 |
64 |
| 24.Shen | 2003 | Cohort | Weaning | 24 | Successful wean 76 ± 12.9 Unsuccessful wean 69.8 ± 17.8 |
42 |
| 25. Schmidt | 2005 | Cohort | MODS (literature values) |
85 | 60.4 ± 14 | 62 |
| 26. Papaioannou | 2006 | Cohort | MODS | 53 | 63.02 ± 14.68 | 58 |
| 44. Bourgault | 2006 | Cohort | Mixed aetiology | 18 | 60 [33–82] | 72 |
| 45. Chen | 2007 | Cohort | Sepsis | 81 | 67 [30–84] | 41 |
| 50. Passariello | 2007 | Case–control | Ischaemic sudden death | 40 | Sudden death 66 ± 8 Pathology matched controls 68 ± 8 |
|
| 46. Chen | 2008 | Cohort | Sepsis | 132 | 67 [27–86] | 47 |
| 47. Aboab | 2008 | Case–control | Sepsis ± adrenal insufficiency (healthy controls) |
81 | Septic shock and adrenal failure 55 ± 16 Septic shock 58 ± 19 Healthy controls (not provided) |
36 |
| 27. Nogueira | 2008 | Cohort | Sepsis | 31 | Survivors 44.9 ± 5.9 Non-survivors 55.6 ± 4.63 |
74 |
| 28. Papaioannou | 2009 | Cohort | Sepsis (Sepsis SOFA <10) |
45 | 57.8 | – |
| 51. Tiainen | 2009 | Cohort | Out of hospital cardiac arrest | 70 | Hypothermia 60 (23–75) Normothermia 59 (18–75) |
86 |
| 29. Schmidt | 2010 | Case–controla | MODS | 178 | 61.1 ± 13.2 | 67 |
| 30. Kasaoka | 2010 | Cohort | SIRS | 10 | 53 ± 15 | 70 |
| 31. Chen | 2012 | Case–control | Sepsis and out of hospital cardiac arrest (Non-severe sepsis and healthy controls) |
210 | Out of hospital cardiac arrest 68 ± 10 Severe sepsis and mechanical ventilation 66 ± 8 Severe sepsis 68 ± 7 Sepsis 67 ± 6 Healthy 66 ± 6 |
55 |
| 32.Gomez Duque | 2012 | Cohort | Sepsis (literature values) |
100 | 55 [18–88] | 42 |
| 33. Brown | 2013 | Cohort | Sepsis | 48 | 57 [40–63] | 46 |
| 34. Green | 2013 | Cohort | MODS | 33 | 56.5 ± 15.9 | 61 |
| 35.Wieske | 2013 | Cohort | ICU acquired weakness | 83 | ICU acquired weakness 60 ± 13 No ICU acquired weakness 59 ± 16 |
60 |
| 36. Wieske | 2013 | Cohort | Mixed aetiology (healthy controls) |
32 | Patients 54 ± 15 Healthy control 36 ± 2 |
70 |
| 37. Bradley | 2013 | Cohort | Mixed aetiology | 33 | 56.5 ± 15.9 | 61 |
| 38. Huang | 2014 | Cohort | Mixed aetiology | 101 | Successful 65 ± 18 Unsuccessful 71 ± 16 |
65 |
| 39. Zhang | 2014 | Cohort | SIRS/MODS (non-MODS) |
41 | 47 [34–59] | 54 |
| 40. Schmidt | 2014 | Case–controla | CCF and MODS (literature values) |
130 | CCF 63 ± 10.1 MODS 62.8 ± 10.2 |
63 |
| 52. Tang | 2014 | Case–control | Stroke | 227 | AF stroke 74 ± 12 Non-AF stroke 62 ± 15 Age/sex-matched controls 61 ± 10 |
40 |
| 41. Zaal | 2015 | Case–control | ICU delirium (no delirium) |
25 | ICU delirium 67 ± 12 No ICU delirium 57 ± 16 |
72 |
| 42. Hammash | 2015 | Cohort | Weaning | 35 | 53.3 ± 14.6 | 66 |
| 53. Nagaraj | 2016 | Case seriesa | Not specified | 40 | 56.3 ± 16.8 | 62.5 |
Reference for each paper is shown before first author (first column)
CCF congestive cardiac failure, MODS multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, SIRS systemic inflammatory response syndrome, SOFA sequential organ failure assessment
aRetrospective analysis
Table 2.
Study objectives and key findings
| Author | Year | Study objectives | Key findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annane | 1999 | Compare HRV between sepsis, septic shock and healthy volunteers | TP, LF, LFnu, LF/HF lower in septic shock vs sepsis |
| Korach | 2001 | Effects of sepsis, age, sedation, catecholamines and illness severity on sympathovagal balance (LF/HF) | LF/HF ratio <1.5 was associated with sepsis and mortality |
| Barnaby | 2002 | Assess if HRV can predict sepsis severity | Negative correlation between LFnu, LF/HF and SOFA score |
| Pontet | 2003 | Assess if HRV can predict MODS in sepsis | Low LF and RMSSD associated with MODS |
| Shen | 2003 | Assess changes in cardiac autonomic activity during weaning from mechanical ventilation | HF, LF and TP decreased in unsuccessful group during spontaneous breathing trial |
| Schmidt | 2005 | Effects of MODS, age, sedation, catecholamines, mechanical ventilation on HRV Assess if HRV can predict mortality in MODS |
Time and frequency domain reduced in MODS HRV indices affected by mechanical ventilation but not age, sedation or catecholamines LnVLF associated with 28-day survival. |
| Papaioannou | 2006 | Assess if HRV associated with disease severity and mortality | LF/HF ratio negatively correlated with SOFA score |
| Bourgault | 2006 | Effects of endotracheal suction on HRV | No significant differences found in HRV indices between closed or open suctioning |
| Chen | 2007 | Assess if HRV can predict sepsis severity | Septic shock associated lower LF, LFnu, LF/HF, and higher RMSSD, HF, HFnu |
| Passariello | 2007 | Assess if HRV can predict ischaemic sudden cardiac death | SDNN decreases shortly before ischaemic sudden death |
| Chen | 2008 | Assess if HRV can predict 28-day mortality | Low SDNN, TP, VLF, LF and LF/HF associated with increased 28-day mortality |
| Aboab | 2008 | Assess effect of steroids on HRV in patients with sepsis | LF, LFnu, LF/HF lower in septic shock. Corticosteroids helped increase LFnu values in adrenal insufficiency group. |
| Nogueira | 2008 | Assess relationship between HRV, markers of myocardial damage and free fatty acids in sepsis | Low LF, HF and LF/HF associated with mortality |
| Papaioannou | 2009 | Assess relationship between HRV and biomarkers of inflammation (CRP, IL-6, IL-10) in patients with sepsis | There is a negative correlation between LFnu, LF/HF and CRP, IL-6, IL-10, SOFA score |
| Tiainen | 2009 | Assess if HRV changes (and has prognostic ability) with therapeutic cooling of resuscitated cardiac arrest patients | Higher SDNN, SDANN, TP, LF, HF in the first 48 h of cooling. SDNN >100 ms predicts better neurological outcome |
| Schmidt | 2010 | To assess if ACE-I therapy affects short (28-day) and long (365-day) mortality in patients with MODS | ACE-I associated with preserved VLF, LF, HF, TP and survival (28-day and 365-day) |
| Kasaoka | 2010 | To trial a real-time HRV measurement and analysis system | LF, HF and LF/HF higher in patients spontaneously breathing compared to mechanical ventilation |
| Chen | 2012 | To compare HRV between post-resuscitation cardiac arrest patients and patients with severe sepsis | No significant differences in HRV indices between OOHCA and Severe Sepsis patients Low LF, LFnu, LF/HF associated with mortality |
| Gomez Duque | 2012 | To investigate the incidence of cardiovascular adverse events in patients with sepsis | Deceased patients demonstrated lower SDNN than survivors |
| Brown | 2013 | Assess if HRV can predict vasopressor dependence at 24 h in sepsis | Traditional HRV indices not associated with vasopressor requirement after controlling for HR |
| Green | 2013 | Association of HRV and illness severity in MODS | Low LFnu and LF/HF associated with increased MODS |
| Wieske | 2013 | Relationship between autonomic dysfunction (HRV) and ICU-acquired weakness | Artefacts, mechanical ventilation, sedation, catecholamines and heart rate all associated with TP % artefacts were associated with TP and LF/HF No association between HRV and ICU-acquired weakness |
| Wieske | 2013 | Compare different autonomic function tests in critically unwell patients (CFT, SWT and HRV) | Only HRV tests associated with SOFA score |
| Bradley | 2013 | Impact of sedation and sedation interruptions on HRV | SDNN, RMSSD and HF all increased during sedation interruption (more pronounced in less unwell patients) |
| Huang | 2014 | Assess if HRV associated with weaning success or failure | Reduction in TP during SBT associated with failure |
| Tang | 2014 | Assess if HRV predicts outcome in ICU stroke patients | Traditional HRV indices were unable to predict outcome |
| Zhang | 2014 | Asses if HRV can predict infected pancreatic necrosis or MODS in patients with severe acute pancreatitis | Low LFnu, LF/HF and high HFnu associated with increased MODS and mortality |
| Schmidt | 2014 | Assess relationship between HRV and illness severity in CCF and MODS | MODS patients demonstrated lower HRV indices in all parameters compared to CCF patients. |
| Zaal | 2015 | To assess if HRV is abnormal in patients with ICU delirium. | No association between HRV and delirium found |
| Hammash | 2015 | Assess relationship between HRV and incidence of dysrhythmias during weaning | LF was higher during spontaneous breathing than during controlled mechanical ventilation. |
| Nagaraj | 2016 | Assess if sedation levels can be classified by HRV algorithms | Algorithms using composite measures of HRV may discriminate between levels of sedation in ICU patients |
ACE-I angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, CCF congestive cardiac failure, CFT cold face test, CRP C-reactive protein, HF high frequency, HFnu high frequency normalised unit, HRV heart rate variability, IL-6 interleukin 6, IL-10 interleukin 10, LF low frequency, LFnu low frequency normalised unit, MODS multiple organ dysfunction, RMSSD root mean square of successive differences, SOFA sequential organ failure assessment, SBT spontaneous breathing trial, SWT skin wrinkle test, TP total power, VLF very low frequency, LnVLF natural logarithm of very low frequency
Fig. 1.
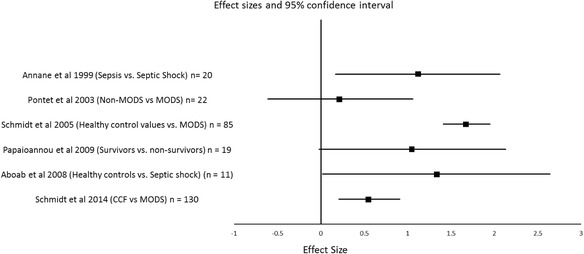
Forest plot of individual effect sizes (Cohen’s d) across six studies investigating the relationship between LF/HF ratio and disease severity and mortality
Quality of studies
No studies reported Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) guidelines. Two studies analysed data retrospectively. A minority of studies (n = 5; 16%) used individualised HRV data—i.e. patients serving as their own control, prior to an intervention. More than one third of studies (n = 13; 42%) did not describe any comparator group. The remainder of studies used non-age matched healthy volunteers, non-critically ill patients with established cardiovascular disease or HRV values derived from the literature. External validity (as adjudged by the Down and Black assessment tool) was poor, with the majority of studies achieving a score of 1.
Risk of bias assessment
We found recurring potential sources of bias in study design, with 19 (61%) studies failing to report whether HRV data analysers were masked to the patient condition/outcome (Additional file 1). Only one study performed a power calculation [41].
Data acquisition and preparation
Details on short-term recordings, including source of heart rate periods [54, 55], duration of recordings, epochs used for analysis and patient position [56] were variable or not reported. Fourteen (45%) studies did not describe the sampling frequency of recordings; four (13%) studies used sampling rates below the recommended 250 Hz [15].
ECG recording in the critically ill population is frequently contaminated by electrical and physiological artefacts. Thus, detailing methods to detect artefact (manual or automated) and its management (segment selection, deletion or interpolation) is important for data interpretation [57]. Fourteen (45%) studies reported automated and/or manual editing of the raw ECG to remove artefact by replacing the missing data with cubic spline or linear interpolation methods. In keeping with guidelines, the majority of studies used interpolation methods as opposed to deletion of abnormal beats to avoid a loss of information [15].
HRV analysis
Measurement protocols, processing and reporting of HRV data are summarised in Table 3.
Table 3.
Procedures for measurement, processing and reporting of HRV
| Author | Year | Recording protocol (duration/position/time) | Monitor | Sampling frequency (Hz) | Management of artefact | Data presented |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annane | 1999 | 5 min/–/– | PRV | 500 | Interpolation | TP, LF, HF, LF/HF, Lfnu, Hfnu |
| Korach | 2001 | 30 min supine/0800–1200 | ECG | 5 | Interpolation | Lfnu, Hfnu, LF/HF |
| Barnaby | 2002 | 5 min/–/– | ECG | – | Interpolation | TP, LF, HF, Lfnu, Hfnu, LF/HF |
| Pontet | 2003 | 10 min/supine/2100–2300 | ECG | >500 | Interpolation | SDNN, RMSSD, LF, HF, Lfnu, Hfnu, LF/HF |
| Shen | 2003 | 90 min/semi recumbent/1000–1400 | ECG | – | Interpolation | TP, LnLF, LnHF, Lfnu, Hfnu, LF/HF |
| Schmidt | 2005 | 24 hours | ECG | 256 | Interpolation | SDNN, SDANN, RMSSD, pNN50, VLF, LF, HF, LF/HF |
| Papaioannou | 2006 | 10 min/supine/morning | ECG | 250 | Segment selection | LF/HF |
| Bourgault | 2006 | 20 min/–/day and night | ECG | 1000 | – | LF, HF, LF/HF, TP |
| Chen | 2007 | 10 min/supine/day and night | ECG | – | Interpolation | RMSSD, TP, LF, HF, Lfnu, Hfnu, LF/HF |
| Passariello | 2007 | 24 h | ECG | – | – | SDNN, SDANN, pNN50, RMSSD |
| Chen | 2008 | 10 min/supine/day and night | ECG | – | Interpolation | SDNN, RMSSD, TP, LF, HF, Lfnu, Hfnu, LF/HF |
| Aboab | 2008 | 5 min/supine/– | PRV | – | Interpolation | TP, Lfnu, Hfnu, LF/HF |
| Nogueira | 2008 | 30 min/supine/morning | ECG | – | – | LF, HF, LF/HF |
| Papaioannou | 2009 | 10 min/–/– | ECG | 250 | Segment selection | SDNN, Lfnu, Hfnu, LF/HF |
| Tiainen | 2009 | 24 h | ECG | – | – | SDNN, SDANN, TP, LF, HF, |
| Schmidt | 2010 | 24 h | ECG | 256 | Interpolation | LnTP, LnVLF, LnHF, LnLF, LF/HF |
| Kasaoka | 2010 | 5 min/supine/– | ECG | – | – | LnLF, LnHF, LF/HF |
| Chen | 2012 | 10 min/supine/day and night | ECG | – | Interpolation | SDNN, TP, VLF, LF, HF, Hfnu, Lfnu, LF/HF |
| Gomez Duque | 2012 | 24 h | ECG | – | – | SDNN, PNN50 |
| Brown | 2013 | 6 h/–/– | ECG | 500 | Deletion | SDNN, pNN50, Lfnu, Hfnu, LF/HF |
| Green | 2013 | 24 h | ECG | 125 | Deletion | SDNN, RMSSD, Lfnu, Hfnu, LF/HF |
| Wieske | 2013 | 5 min/–/– | ECG | 250 | Interpolation | HR, TP, LF/HF |
| Wieske | 2013 | 5 min/supine/– | ECG | 250 | Deletion | LF, HF, Lfnu, Hfnu, LF/HF |
| Bradley | 2013 | 24 h | ECG | 125 | Deletion | SDNN, RMSSD, LF, HF, LF/HF |
| Huang | 2014 | 5 min/semi-recumbent/0800–1200 | ECG | – | – | LnTP, LnVLF, Hfnu, Lfnu, LF/HF |
| Tang | 2014 | 60 min/–/– | ECH | 512 | – | SDNN, RMSSD, LF, HF, LF/HF |
| Zhang | 2014 | 5 min/–/0900–1100 | ECG | – | Deletion | SDNN, RMSSD, TP, VLF, LF, HF, Lfnu, Hfnu, LF/HF |
| Schmidt | 2014 | 24 h | ECG | 256 | Interpolation | SDNN, SDANN, SDNNi, RMSSD, pNN50, VLF, LF, HF, LnLF, LnHF, LF/HF |
| Zaal | 2015 | 15 min/supine, 0800–1700 | ECG | 500 | Segment selection | LnLF, LnHF, Hfnu, LF/HF |
| Hammash | 2015 | 24 h | ECG | – | Interpolation | VLF, HF, LF |
| Nagaraj | 2016 | 24 h (5 min epochs) | ECG | 240 | Thresholding | SDNN, RMSSD, VLF, LF, HF, LF/HF, LFnu, HFnu |
ECG electrocardiogram, HF high frequency, HFnu high frequency normalised unit, LF low frequency, LFnu low frequency normalised unit, Ln natural logarithm, pNN50 percentage of normal–normal intervals >50 ms, PRV pulse rate variability, RMSSD root mean square of successive differences, SDANN standard deviation of average normal–normal intervals, SDNN standard deviation of normal–normal intervals, TP total power
A minority of studies (14; 45%) reported both frequency and time domain data (Table 3). A minority of studies (9; 29%) reported frequency data in normalised units together with absolute values, in keeping with established recommendations. Summary values for commonly reported HRV parameters revealed a wide range of non-normally distributed data for each (Additional file 1: Table S3). Reporting and/or adjustment for heart rate and respiratory rate, which dramatically alter both high and low frequency spectral components [58] was inconsistent between studies. A small majority of studies (17; 55%) reported average heart rate, whilst a minority (6; 19%) adjusted for, or reported, respiratory rate during data acquisition.
Pharmacologic and clinical interventions
Studies varied in their exclusion criteria and reporting of potential confounding factors including age, gender, body mass index [59], common comorbidities [60–63], drug therapy [64–68] and/or ICU interventions (Tables 4 and 5). Exclusion criteria used and comorbidities/drugs are summarised in Additional file 1. A minority of studies (12; 39%) excluded patients with chronic comorbidities that are commonly associated with autonomic dysfunction. Reporting of drugs that directly affect autonomic function was highly variable across studies. A majority of studies (25; 81%) did not detail drug therapy. Around 22% studies did not report the use of mechanical ventilation, and more than 25% failed to report whether sedation and/or vasoactive drugs were used at the time of HRV recordings.
Table 4.
Reporting of potential clinical confounders
| Author | Year | Comorbidities | Drugs | Mechanical ventilation (% patients) | Sedation (% patients) | Catecholamines (% patients) | Feeding | HR/RR reported |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annane | 1999 | Excluded | – | 100% | 0% | 0% | – | HR/RR |
| Korach | 2001 | – | – | 41.5%. | 19.5% | 12.20% | – | – |
| Barnaby | 2002 | – | – | 0% | – | 0% | – | HR/RR |
| Pontet | 2003 | Excluded | Excluded | 38.5% | – | 17.90% | – | HR |
| Shen | 2003 | + | + | 100% | 0% | 0% | – | HR/RR |
| Schmidt | 2005 | – | – | 71% | 61% | 62% | – | – |
| Papaioannou | 2006 | + | – | – | + | – | – | – |
| Bourgault | 2006 | Excluded | Excluded | 100% | 33% | 0% | – | HR |
| Chen | 2007 | Excluded/+ | – | – | – | 0% | – | HR/RR |
| Passriello | 2007 | + | + | – | – | – | – | HR |
| Chen | 2008 | + | – | 0% | – | – | – | HR |
| Aboab | 2008 | Excluded | – | 100% | 80.9% | 100% | – | HR |
| Nogueira | 2008 | Excluded | – | 100% | – | 100% | – | RR |
| Papaioannou | 2009 | – | Excluded | 100% | 100% | – | – | – |
| Tiainen | 2009 | + | – | 100% | 100% | 87% | – | HR |
| Schmidt 0 | 2010 | + | – | 88% | 89% | 74% | – | – |
| Kasaoka 1 | 2010 | – | – | 100% | 100% | – | – | – |
| Chen | 2012 | + | – | OHCA 100%, SS + MV 100%, SS 0%, S 0% | OHCA 81, SS + MV 63%, SS 59%, S 0% | OHCA 100%, SS + MV 9%, SS 18.8%, S 0% | – | HR |
| Gomez Duque | 2012 | Excluded/+ | – | – | – | 72% | – | – |
| Brown | 2013 | – | – | – | – | 63% | – | HR |
| Green | 2013 | – | – | 90.90% | + | 78.80% | – | HR |
| Wieske | 2013 | Excluded/+ | + | + | + | + | – | HR |
| Wieske | 2013 | Excluded/+ | – | 100% | – | – | – | – |
| Bradley | 2013 | – | – | + | + | + | – | HR |
| Huang | 2014 | Excluded/+ | Excluded/+ | 100% | – | – | – | RR |
| Zhang | 2014 | – | – | – | – | 12% | – | – |
| Schmidt | 2014 | – | + | 89.2% | 72.3% | 72.3% | – | HR |
| Tang | 2014 | + | + | – | – | – | – | HR |
| Zaal | 2015 | Excluded | Excluded | 60% | 20% | 0% | – | – |
| Hammash | 2015 | Excluded/+ | – | 100% | – | – | – | – |
| Nagaraj | 2016 | – | – | 100% | 100% | – | – | HR |
Excluded refers to specific comorbidities or drugs were part of exclusion criteria of study
HR heart rate, RR respiratory rate, + reported but proportion of patients not provided, – not reported
Table 5.
Reporting of potential confounders
| Author | Year | Comorbidities | Drugs | Mechanical ventilation (% patients) | Sedation (% patients) | Catecholamines (% patients) | Feeding | HR/RR reported |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annane [17] | 1999 | Excluded | – | 100% | 0% | 0% | – | HR/RR |
| Korach [18] | 2001 | – | – | 41.5%. | 19.5% | 12.20% | – | – |
| Barnaby [19] | 2002 | – | – | 0% | – | 0% | – | HR/RR |
| Pontet [20] | 2003 | Excluded | Excluded | 38.5% | – | 17.90% | – | HR |
| Shen [21] | 2003 | + | + | 100% | 0% | 0% | – | HR/RR |
| Schmidt [22] | 2005 | – | – | 71% | 61% | 62% | – | – |
| Papaioannou [23] | 2006 | + | – | – | + | – | – | – |
| Bourgault [24] | 2006 | Excluded | Excluded | 100% | 33% | 0% | – | HR |
| Chen [25] | 2007 | Excluded/+ | – | – | – | 0% | – | HR/RR |
| Passriello | 2007 | + | + | – | – | – | – | HR |
| Chen [26] | 2008 | + | – | 0% | – | – | – | HR |
| Aboab [27] | 2008 | Excluded | – | 100% | 80.9% | 100% | – | HR |
| Nogueira [28] | 2008 | Excluded | – | 100% | – | 100% | – | RR |
| Papaioannou [29] | 2009 | – | Excluded | 100% | 100% | – | – | – |
| Tiainen | 2009 | + | – | 100% | 100% | 87% | – | HR |
| Schmidt [30] | 2010 | + | – | 88% | 89% | 74% | – | – |
| Kasaoka [31] | 2010 | – | – | 100% | 100% | – | – | – |
| Chen [32] | 2012 | + | – | OHCA 100%, SS + MV 100%, SS 0%, S 0% | OHCA 81, SS + MV 63%, SS 59%, S 0% | OHCA 100%, SS + MV 9%, SS 18.8%, S 0% | – | HR |
| Gomez Duque [33] | 2012 | Excluded/+ | – | – | – | 72% | – | – |
| Brown [34] | 2013 | – | – | – | – | 63% | – | HR |
| Green [35] | 2013 | – | – | 90.90% | + | 78.80% | – | HR |
| Wieske [36] | 2013 | Excluded/+ | + | + | + | + | – | HR |
| Wieske [37] | 2013 | Excluded/+ | – | 100% | – | – | – | – |
| Bradley [38] | 2013 | – | – | + | + | + | – | HR |
| Huang [39] | 2014 | Excluded/+ | Excluded/+ | 100% | – | – | – | RR |
| Zhang [40] | 2014 | – | – | – | – | 12% | – | – |
| Schmidt [41] | 2014 | – | + | 89.2% | 72.3% | 72.3% | – | HR |
| Tang | 2014 | + | + | – | – | – | – | HR |
| Zaal [42] | 2015 | Excluded | Excluded | 60% | 20% | 0% | – | – |
| Hammash [43] | 2015 | Excluded/+ | – | 100% | – | – | – | – |
| Nagaraj | 2016 | – | – | 100% | 100% | – | – | HR |
Excluded refers to specific comorbidities or drugs were part of exclusion criteria of study
HR heart rate, RR respiratory rate, + reported but proportion of patients not provided, – not reported
Discussion
This review is the first to systematically explore how HRV analyses are undertaken and/or reported in critically ill patients. Despite a wealth of laboratory and translational data suggesting that HRV may offer diagnostic and prognostic utility, significant heterogeneity in methodology between HRV articles precluded comparisons across studies and meta-analysis. Our review identifies several areas that require greater scrutiny in future, highlighting the need to develop consensus guidelines that are relevant and tailor-made for the challenges faced by researchers in critical care medicine.
Well-recognised technical, physiologic and clinical factors impact on the measurement, and interpretation of HRV [69, 70]. We found highly variable practice in three key technical areas. Low sampling rates (<250 Hz) impair the precise detection of the R wave fiducial point in the ECG waveform, which consequently affects the power spectrum [15]. This is particularly relevant for studies that derived R–R intervals from arterial pressure waveform analysis [20, 47], since non-neural respiratory influences (e.g. changes in ventricular mechanics) differentially affect mechanical pulse waves and electrical R waves [55]. Manual inspection of the raw ECG to identify artefact is preferred to automated methods to avoid the introduction of false frequency components into the power spectrum [57]. The variable (or unstated) masking of HRV analysers to clinical data also introduces potential significant bias.
From a physiologic perspective, reporting and/or adjustment for heart rate and respiratory rate was inconsistent between studies, with heart rate frequently not reported. Across species with highly variable heart rates, HRV appears to be largely attributable to incident heart rate. If heart rate is not taken into account, erroneous conclusions regarding HRV are likely since differences may merely reflect lower heart rate [12]. This is particularly of relevance to hemodynamically unstable critically ill patients, in whom heart rate may rapidly change. Similarly, increases in respiratory frequency and tidal volume affect both high and low frequency spectral components [58]. Hence, standardised criteria for ventilatory and heart rate reporting are required for the interpretation of HRV data between studies (and hence, potentially, meta-analysis).
From a clinical perspective, HRV parameters are influenced strongly by age, gender, functional capacity and chronic comorbidities. Whilst all studies estimated severity of illness, the most frequently employed—Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE-II)—are limited in capturing information about chronic comorbid disease that are over-represented in the critical care medicine population. For example, diabetes mellitus, a common condition associated with cardiac autonomic neuropathy, is not captured by this type of assessment [60]. Typically, chronic conditions at the severe end of the disease spectrum are included (e.g. APACHE-II score only includes severe heart failure (≥NYHA class 3). However, HRV parameters have been found to be abnormal in early cases of chronic disease, including preserved ejection fraction, coronary artery disease, chronic kidney disease and hypertension [60–63]. Although some studies have considered these factors, serial measures or dynamic autonomic challenges offer a potentially more insightful and individualised approach to assessing HRV. Novel HRV parameters that can be captured within the first few minutes of critical illness, such as deceleration capacity of heart rate [71], may mitigate the need for refining the use of more traditional time and frequency domain measures. For mechanistic studies investigating whether changes in autonomic parameters correlate with, or precede, pathologic events, targeting clinical scenarios where multiple, complementary baseline autonomic measures [72, 73] can be made before critical illness develops may be optimal [74]. Studies where basal autonomic function can be captured, including elective surgery [73–76] and oncologic sepsis [48, 49], may provide particularly powerful mechanistic insights since autonomic changes can be individualised and referenced to pre-insult normal, or pre-existing, dysfunction. Several studies have highlighted that HRV values in critical care medicine are similar to those found in common cardiovascular pathologic conditions [74, 75, 77]; this highlights the need for individualised patient data in order to rule out that autonomic dysfunction is not a precursor of critical illness, rather than merely a biomarker.
Commonly used anti-arrhythmic drugs, anti-hypertensive drugs, statins, metformin and inhaled bronchodilators have all been associated with changes in HRV parameters [60–63]. However, the lack of reporting on medications that critically ill patients received reduces the mechanistic insight afforded by this approach, particularly given the strong correlation between HRV and morbidity/mortality appears to be largely attributable to incident heart rate. Similarly, the majority of studies in this review failed to consistently report on the use of common critical care interventions. This may explain why conflicting conclusions over how variety of features of critical illness may affect HRV. Continuous enteral or parenteral nutrition are both associated with a reduction in time domain HRV measures indicative of parasympathetic cardiac modulation [67]. However, we did not find any studies that reported on the feeding or fasting status of patients. Although a significant limitation of our study was the lack of primary source data, in any event, we could not identify a single common HRV parameter measured in all studies that enabled comparison. A further limitation is that we did not consider newer nonlinear and multiscale approaches, since very few studies incorporating these analyses have been undertaken. These approaches are also likely to be affected by the same factors that influence traditional HRV parameters [78]. Thus, in a clinical setting, further work is required to establish whether these newer approaches reduce the impact of several confounding factors we have identified in this review.
Conclusions
Heart rate and derived heart rate variability offers a non-invasive, inexpensive tool that may add mechanistic insights to our understanding of critical illness and also assist clinical care. However, the current interpretation of generalizable and clinically relevant values to aid clinical decisions/research is hampered by a non-standardised methodologic approach and lack of adjustment for important confounding factors. For critical care medicine to exploit recent advances in translational autonomic physiology, further high-quality prospective HRV studies underpinned by the development of consensus reporting standards relevant for critical care medicine are needed.
Acknowledgements
n/a
Funding
GLA is supported by a British Journal of Anaesthesia and Royal College of Anaesthetists Basic Science fellowship, British Oxygen Company grant from the Royal College of Anaesthetists and British Heart Foundation programme grant (RG/14/4/30736). Funding bodies played no role in the design of the study and collection, analysis and interpretation of data or in writing the manuscript should be declared.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- HRV
Heart rate variability
- APACHE-II
Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II
- NYHA
New York Heart Association
- ECG
Electrocardiogram
- MODS
Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
Additional file
Clinical confounding factors. (DOCX 34 kb)
Authors’ contributions
GLA devised hypothesis/study plan. SK and AS sourced the primary material. SMM independently verified quality of studies. GLA and SK wrote the first draft of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the final revised draft. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
GLA is a member of the Associate editorial board of Intensive Care Medicine Experimental. GLA has received consultancy fees from Glaxo Smith Kline for unrelated purposes. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Footnotes
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s40635-017-0146-1) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
References
- 1.Lahiri MK, Kannankeril PJ, Goldberger JJ. Assessment of autonomic function in cardiovascular disease: physiological basis and prognostic implications. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;51:1725–1733. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.01.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Akselrod S, Gordon D, Ubel FA, Shannon DC, Berger AC, Cohen RJ. Power spectrum analysis of heart rate fluctuation: a quantitative probe of beat-to-beat cardiovascular control. Science. 1981;213:220–222. doi: 10.1126/science.6166045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Buccelletti E, Gilardi E, Scaini E, Galiuto L, Persiani R, Biondi A, Basile F, Silveri NG. Heart rate variability and myocardial infarction: systematic literature review and metanalysis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2009;13:299–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nolan J, Batin PD, Andrews R, Lindsay SJ, Brooksby P, Mullen M, Baig W, Flapan AD, Cowley A, Prescott RJ, Neilson JM, Fox KA. Prospective study of heart rate variability and mortality in chronic heart failure: results of the United Kingdom heart failure evaluation and assessment of risk trial (UK-heart) Circulation. 1998;98:1510–1516. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.98.15.1510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bilchick KC, Fetics B, Djoukeng R, Fisher SG, Fletcher RD, Singh SN, Nevo E, Berger RD. Prognostic value of heart rate variability in chronic congestive heart failure (Veterans Affairs’ Survival Trial of Antiarrhythmic Therapy in Congestive Heart Failure) Am J Cardiol. 2002;90:24–28. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9149(02)02380-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Stuckey MI, Petrella RJ. Heart rate variability in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2013;41:137–147. doi: 10.1615/CritRevBiomedEng.2013008103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Singh JP, Larson MG, Tsuji H, Evans JC, O'Donnell CJ, Levy D. Reduced heart rate variability and new-onset hypertension: insights into pathogenesis of hypertension: the Framingham Heart Study. Hypertension. 1998;32:293–297. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.32.2.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ahmad S, Tejuja A, Newman KD, Zarychanski R, Seely AJ. Clinical review: a review and analysis of heart rate variability and the diagnosis and prognosis of infection. Crit Care. 2009;13:232. doi: 10.1186/cc8132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Stein PK. Challenges of heart rate variability research in the ICU. Crit Care Med. 2013;41:666–667. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e318270e6f0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nunan D, Sandercock GR, Brodie DA. A quantitative systematic review of normal values for short-term heart rate variability in healthy adults. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2010;33:1407–1417. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.2010.02841.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mazzeo AT, La Monaca E, Di Leo R, Vita G, Santamaria LB. Heart rate variability: a diagnostic and prognostic tool in anesthesia and intensive care. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2011;55:797–811. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2011.02466.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Monfredi O, Lyashkov AE, Johnsen AB, Inada S, Schneider H, Wang R, Nirmalan M, Wisloff U, Maltsev VA, Lakatta EG, Zhang H, Boyett MR. Biophysical characterization of the underappreciated and important relationship between heart rate variability and heart rate. Hypertension. 2014;64:1334–1343. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.03782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Martelli D, Silvani A, McAllen RM, May CN, Ramchandra R. The low frequency power of heart rate variability is neither a measure of cardiac sympathetic tone nor of baroreflex sensitivity. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014;307:H1005–1012. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00361.2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bauer A, Malik M, Schmidt G, Barthel P, Bonnemeier H, Cygankiewicz I, Guzik P, Lombardi F, Muller A, Oto A, Schneider R, Watanabe M, Wichterle D, Zareba W. Heart rate turbulence: standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use: International Society for Holter and Noninvasive Electrophysiology Consensus. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52:1353–1365. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.07.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.(1996) Heart rate variability: standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Circulation 93: 1043-1065 [PubMed]
- 16.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62:1006–1012. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2009.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sassi R, Cerutti S, Lombardi F, Malik M, Huikuri HV, Peng CK, Schmidt G, Yamamoto Y. Advances in heart rate variability signal analysis: joint position statement by the e-Cardiology ESC Working Group and the European Heart Rhythm Association co-endorsed by the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society. Europace. 2015;17:1341–1353. doi: 10.1093/europace/euv015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Downs SH, Black N. The feasibility of creating a checklist for the assessment of the methodological quality both of randomised and non-randomised studies of health care interventions. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1998;52:377–384. doi: 10.1136/jech.52.6.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Higgins JPT, Green S, (2011) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. www.handbook.cochrane.org Version 5.1.0
- 20.Annane D, Trabold F, Sharshar T, Jarrin I, Blanc AS, Raphael JC, Gajdos P. Inappropriate sympathetic activation at onset of septic shock: a spectral analysis approach. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;160:458–465. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.160.2.9810073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Korach M, Sharshar T, Jarrin I, Fouillot JP, Raphaël JC, Gajdos P, Annane D. Cardiac variability in critically ill adults: influence of sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:1380–1385. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200107000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Barnaby D, Ferrick K, Kaplan DT, Shah S, Bijur P, Gallagher EJ. Heart rate variability in emergency department patients with sepsis. Acad Emerg Med. 2002;9:661–670. doi: 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2002.tb02143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Pontet J, Contreras P, Curbelo A, Medina J, Noveri S, Bentancourt S, Migliaro ER. Heart rate variability as early marker of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in septic patients. J Crit Care. 2003;18:156–163. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2003.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Shen HN, Lin LY, Chen KY, Kuo PH, Yu CJ, Wu HD, Yang PC. Changes of heart rate variability during ventilator weaning. Chest. 2003;123:1222–1228. doi: 10.1378/chest.123.4.1222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Schmidt H, Muller-Werdan U, Hoffmann T, Francis DP, Piepoli MF, Rauchhaus M, Prondzinsky R, Loppnow H, Buerke M, Hoyer D, Werdan K. Autonomic dysfunction predicts mortality in patients with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome of different age groups. Crit Care Med. 2005;33:1994–2002. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000178181.91250.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Papaioannou VE, Maglaveras N, Houvarda I, Antoniadou E, Vretzakis G. Investigation of altered heart rate variability, nonlinear properties of heart rate signals, and organ dysfunction longitudinally over time in intensive care unit patients. J Crit Care. 2006;21:95–103. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2005.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Nogueira AC, Kawabata V, Biselli P, Lins MH, Valeri C, Seckler M, Hoshino W, Júnior LG, Bernik MM, de Andrade Machado JB, Martinez MB, Lotufo PA, Caldini EG, Martins E, Curi R, Soriano FG. Changes in plasma free fatty acid levels in septic patients are associated with cardiac damage and reduction in heart rate variability. Shock. 2008;29:342–348. doi: 10.1097/shk.0b013e31815abbc6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Papaioannou VE, Dragoumanis C, Theodorou V, Gargaretas C, Pneumatikos I. Relation of heart rate variability to serum levels of C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, and 10 in patients with sepsis and septic shock. J Crit Care. 2009;24:625.e621–627. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2008.11.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Schmidt H, Hoyer D, Rauchhaus M, Prondzinsky R, Hennen R, Schlitt A, Carter J, Hottenrott K, Muller-Werdan U, Werdan K, Buerke M. ACE-inhibitor therapy and survival among patients with multiorgan dysfunction syndrome (MODS) of cardiac and non-cardiac origin. Int J Cardiol. 2010;140:296–303. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2008.11.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kasaoka S, Nakahara T, Kawamura Y, Tsuruta R, Maekawa T. Real-time monitoring of heart rate variability in critically ill patients. J Crit Care. 2010;25:313–316. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2009.06.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Chen WL, Shen YS, Huang CC, Chen JH, Kuo CD. Postresuscitation autonomic nervous modulation after cardiac arrest resembles that of severe sepsis. Am J Emerg Med. 2012;30:143–150. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2010.11.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Gomez Duque M, Enciso Olivera C, Peña Torres E, Segura Durán OD, Nieto Estrada VH. ECAIS study: inadvertent cardiovascular adverse events in sepsis. Med Intensiva. 2012;36:343–350. doi: 10.1016/j.medin.2011.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Brown SM, Tate Q, Jones JP, Knox DB, Kuttler KG, Lanspa M, Rondina MT, Grissom CK, Behera S, Mathews VJ, Morris A. Initial fractal exponent of heart rate variability is associated with success of early resuscitation in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock: a prospective cohort study. J Crit Care. 2013;28:959–963. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2013.07.050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Green GC, Bradley B, Bravi A, Seely AJ. Continuous multiorgan variability analysis to track severity of organ failure in critically ill patients. J Crit Care. 2013;28:879.e871–811. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2013.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wieske L, Chan Pin Yin DR, Verhamme C, Schultz MJ, van Schaik IN, Horn J. Autonomic dysfunction in ICU-acquired weakness: a prospective observational pilot study. Intensive Care Med. 2013;39:1610–1617. doi: 10.1007/s00134-013-2991-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wieske L, Kiszer ER, Schultz MJ, Verhamme C, van Schaik IN, Horn J. Examination of cardiovascular and peripheral autonomic function in the ICU: a pilot study. J Neurol. 2013;260:1511–1517. doi: 10.1007/s00415-012-6818-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Bradley BD, Green G, Ramsay T, Seely AJ. Impact of sedation and organ failure on continuous heart and respiratory rate variability monitoring in critically ill patients: a pilot study. Crit Care Med. 2013;41:433–444. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31826a47de. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Huang CT, Tsai YJ, Lin JW, Ruan SY, Wu HD, Yu CJ. Application of heart-rate variability in patients undergoing weaning from mechanical ventilation. Crit Care. 2014;18:R21. doi: 10.1186/cc13705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zhang L, Zhou J, Ke L, Nie Y, Tong Z, Li W, Li J. Role of heart rate variability in predicting the severity of severe acute pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2014;59:2557–2564. doi: 10.1007/s10620-014-3192-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Schmidt H, Lotze U, Ghanem A, Anker SD, Said SM, Braun-Dullaeus R, Oltmanns G, Rose S, Buerke M, Müller-Werdan U, Werdan K, Rauchhaus M. Relation of impaired interorgan communication and parasympathetic activity in chronic heart failure and multiple-organ dysfunction syndrome. J Crit Care. 2014;29:367–373. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2013.12.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Zaal IJ, van der Kooi AW, van Schelven LJ, Oey PL, Slooter AJ. Heart rate variability in intensive care unit patients with delirium. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2015;27:e112–116. doi: 10.1176/appi.neuropsych.13090213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hammash MH, Moser DK, Frazier SK, Lennie TA, Hardin-Pierce M. Heart rate variability as a predictor of cardiac dysrhythmias during weaning from mechanical ventilation. Am J Crit Care. 2015;24:118–127. doi: 10.4037/ajcc2015318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Bradley B, Green GC, Batkin I, Seely AJ (2011) Feasibility of continuous multiorgan variability analysis in the intensive care unit. J Crit Care 27:218.e9–20 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 44.Bourgault AM, Brown CA, Hains SM, Parlow JL. Effects of endotracheal tube suctioning on arterial oxygen tension and heart rate variability. Biol Res Nurs. 2006;7:268–278. doi: 10.1177/1099800405285258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Chen WL, Kuo CD. Characteristics of heart rate variability can predict impending septic shock in emergency department patients with sepsis. Acad Emerg Med. 2007;14:392–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2007.tb01796.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Chen WL, Chen JH, Huang CC, Kuo CD, Huang CI, Lee LS. Heart rate variability measures as predictors of in-hospital mortality in ED patients with sepsis. Am J Emerg Med. 2008;26:395–401. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2007.06.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Aboab J, Polito A, Orlikowski D, Sharshar T, Castel M, Annane D. Hydrocortisone effects on cardiovascular variability in septic shock: a spectral analysis approach. Critical Care Med. 2008;36:1481–1486. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31816f48f2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Ahmad S, Ramsay T, Huebsch L, Flanagan S, McDiarmid S, Batkin I, McIntyre L, Sundaresan SR, Maziak DE, Shamji FM, Hebert P, Fergusson D, Tinmouth A, Seely AJ. Continuous multi-parameter heart rate variability analysis heralds onset of sepsis in adults. PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e6642. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bravi A, Green G, Longtin A, Seely AJ. Monitoring and identification of sepsis development through a composite measure of heart rate variability. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e45666. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Passariello G, Peluso A, Moniello G, Maio A, Mazo S, Boccia G, Passariello N, Lettieri B, Chiefari M. Effect of autonomic nervous system dysfunction on sudden death in ischemic patients with anginal syndrome died during electrocardiographic monitoring in Intensive Care Unit. Minerva Anestesiol. 2007;73:207–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Tiainen M, Parikka HJ, Mäkijärvi MA, Takkunen OS, Sarna SJ, Roine RO. Arrhythmias and heart rate variability during and after therapeutic hypothermia for cardiac arrest. Crit Care Med. 2009;37:403–409. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31819572c4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Tang SC, Jen HI, Lin YH, Hung CS, Jou WJ, Huang PW, Shieh JS, Ho YL, Lai DM, Wu AY, Jeng JS, Chen MF. Complexity of heart rate variability predicts outcome in intensive care unit admitted patients with acute stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2015;86:95–100. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2014-308389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Nagaraj SB, McClain LM, Zhou DW, Biswal S, Rosenthal ES, Purdon PL, Westover MB. Automatic classification of sedation levels in ICU patients using heart rate variability. Crit Care Med. 2016;44:e782–789. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000001708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.McKinley PS, Shapiro PA, Bagiella E, Myers MM, De Meersman RE, Grant I, Sloan RP. Deriving heart period variability from blood pressure waveforms. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2003;95:1431–1438. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01110.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Carrasco S, Gonzalez R, Jimenez J, Roman R, Medina V, Azpiroz J. Comparison of the heart rate variability parameters obtained from the electrocardiogram and the blood pressure wave. J Med Eng Technol. 1998;22:195–205. doi: 10.3109/03091909809032542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Montano N, Ruscone TG, Porta A, Lombardi F, Pagani M, Malliani A. Power spectrum analysis of heart rate variability to assess the changes in sympathovagal balance during graded orthostatic tilt. Circulation. 1994;90:1826–1831. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.90.4.1826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Peltola MA. Role of editing of R-R intervals in the analysis of heart rate variability. Front Physiol. 2012;3:148. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Brown TE, Beightol LA, Koh J, Eckberg DL. Important influence of respiration on human R-R interval power spectra is largely ignored. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1993;75:2310–2317. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1993.75.5.2310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Antelmi I, de Paula RS, Shinzato AR, Peres CA, Mansur AJ, Grupi CJ. Influence of age, gender, body mass index, and functional capacity on heart rate variability in a cohort of subjects without heart disease. Am J Cardiol. 2004;93:381–385. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2003.09.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.França da Silva AK, Penachini da Costa de Rezende Barbosa M, Marques Vanderlei F, Destro Christofaro DG, Marques Vanderlei LC (2016) Application of heart rate variability in diagnosis and prognosis of individuals with diabetes mellitus: systematic review. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol 21:223–235 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 61.Patel H, Ozdemir BA, Patel M, Xiao HB, Poole-Wilson PA, Rosen SD (2010) Impairment of autonomic reactivity is a feature of heart failure whether or not the left ventricular ejection fraction is normal. IntJ Cardiol 151(1):34–9. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2010.04.054. Epub 2010 May 18 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 62.Drawz PE, Babineau DC, Brecklin C, He J, Kallem RR, Soliman EZ, Xie D, Appleby D, Anderson AH, Rahman M, Investigators CS. Heart rate variability is a predictor of mortality in chronic kidney disease: a report from the CRIC Study. Am J Nephrol. 2013;38:517–528. doi: 10.1159/000357200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Pagani M, Lucini D. Autonomic dysregulation in essential hypertension: insight from heart rate and arterial pressure variability. Auton Neurosci. 2001;90:76–82. doi: 10.1016/S1566-0702(01)00270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Cekici L, Valipour A, Kohansal R, Burghuber OC. Short-term effects of inhaled salbutamol on autonomic cardiovascular control in healthy subjects: a placebo-controlled study. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009;67:394–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2009.03377.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Vrtovec B, Okrajsek R, Golicnik A, Ferjan M, Starc V, Radovancevic B. Atorvastatin therapy increases heart rate variability, decreases QT variability, and shortens QTc interval duration in patients with advanced chronic heart failure. J Card Fail. 2005;11:684–690. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2005.06.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Manzella D, Grella R, Esposito K, Giugliano D, Barbagallo M, Paolisso G. Blood pressure and cardiac autonomic nervous system in obese type 2 diabetic patients: effect of metformin administration. Am J Hypertens. 2004;17:223–227. doi: 10.1016/j.amjhyper.2003.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Gale SC, Shanker BA, Coyle SM, Macor MA, Choi CW, Calvano SE, Corbett SA, Lowry SF. Continuous enteral and parenteral feeding each reduces heart rate variability but differentially influences monocyte gene expression in humans. Shock. 2012;38:255–261. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e31826171b9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Roque AL, Valenti VE, Massetti T, da Silva TD, Monteiro CB, Oliveira FR, de Almeida JÁ, Lacerda SN, Pinasco GC, Nascimento VG, Granja Filho LG, de Abreu LC, Garner DM, Ferreira C. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and heart rate variability: a literature update. Int Arch Med. 2014;7:43. doi: 10.1186/1755-7682-7-43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Pinna GD, Maestri R, Torunski A, Danilowicz-Szymanowicz L, Szwoch M, La Rovere MT, Raczak G. Heart rate variability measures: a fresh look at reliability. Clin Sci (Lond) 2007;113:131–140. doi: 10.1042/CS20070055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Sandercock GR, Bromley PD, Brodie DA. The reliability of short-term measurements of heart rate variability. Int J Cardiol. 2005;103:238–247. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2004.09.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Eick C, Rizas KD, Meyer-Zurn CS, Groga-Bada P, Hamm W, Kreth F, Overkamp D, Weyrich P, Gawaz M, Bauer A. Autonomic nervous system activity as risk predictor in the medical emergency department: a prospective cohort study. Crit Care Med. 2015;43:1079–1086. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Sykora M, Czosnyka M, Liu X, Donnelly J, Nasr N, Diedler J, Okoroafor F, Hutchinson P, Menon D, Smielewski P. Autonomic impairment in severe traumatic brain injury: a multimodal neuromonitoring study. Crit Care Med. 2016;44:1173–1181. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000001624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Ackland GL, Iqbal S, Paredes LG, Toner A, Lyness C, Jenkins N, Bodger P, Karmali S, Whittle J, Reyes A, Singer M, Hamilton M, Cecconi M, Pearse RM, Mallett SV, Omar RZ. Individualised oxygen delivery targeted haemodynamic therapy in high-risk surgical patients: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, controlled, mechanistic trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2015;3:33–41. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70205-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Ackland GL, Whittle J, Toner A, Machhada A, Del Arroyo AG, Sciuso A, Jenkins N, Dyson A, Struthers R, Sneyd JR, Minto G, Singer M, Shah AM, Gourine AV. Molecular mechanisms linking autonomic dysfunction and impaired cardiac contractility in critical illness. Crit Care Med. 2016;44:e614–624. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000001606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Stein PK, Schmieg RE, Jr, El-Fouly A, Domitrovich PP, Buchman TG. Association between heart rate variability recorded on postoperative day 1 and length of stay in abdominal aortic surgery patients. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:1738–1743. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200109000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Karmali S, Jenkins N, Sciusco A, John J, Haddad F, Ackland GL, Investigators P-XS. Randomized controlled trial of vagal modulation by sham feeding in elective non-gastrointestinal (orthopaedic) surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2015;115:727–735. doi: 10.1093/bja/aev283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Bauer A, Kantelhardt JW, Barthel P, Schneider R, Makikallio T, Ulm K, Hnatkova K, Schomig A, Huikuri H, Bunde A, Malik M, Schmidt G. Deceleration capacity of heart rate as a predictor of mortality after myocardial infarction: cohort study. Lancet. 2006;367:1674–1681. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)68735-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Thuraisingham RA, Gottwald GA. On multiscale entropy analysis for physiological data. Phys A Stat Mech Appl. 2006;366:323–332. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2005.10.008. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.


