Abstract
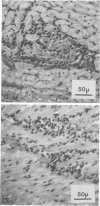
Two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis, indirect immunofluorescence, and radioimmunoassay were used to demonstrate that antisera from rabbits immunized with some strains of Streptococcus mutans contain antibodies that cross-react with human cardiac tissue. These rabbits were sensitized to a shocking dose of human heart antigen, and anaphylactic deaths were sometimes produced. Myocarditis was also a result of the immunization procedure. Data obtained with all five techniques were comparable. Cross-reactivity could be associated with three antigens designated ID, IF, and HL. Antigens ID and IF were major immunogens of S. mutans Ingbritt, but HL antibodies were produced only after hyperimmunization. Corss-reactivity was of an immunological nature and not the result of nonspecific factors such as bacterial Fc reactive components or antibody elicited to growth medium constituents. These findings support the hypothesis that immunization with S. mutans can induce autoimmune reactions and indicate that antigens must be selected with caution before formulating any dental caries vaccine.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axén R., Porath J., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of peptides and proteins to polysaccharides by means of cyanogen halides. Nature. 1967 Jun 24;214(5095):1302–1304. doi: 10.1038/2141302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen W. H. A vaccine against dental caries. A pilot experiment in monkeys (Macaca irus). Br Dent J. 1969 Feb 18;126(4):159–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B., Colman G., Russell R. R. Immunisation against dental caries: further studies. Br Dent J. 1979 Jul 3;147(1):9–14. doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.4804266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood D. C., Hunter J. R., Longyear V. M. Growth of Streptococcus mutans in a chemostat. Arch Oral Biol. 1974 Aug;19(8):659–664. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(74)90134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. T., Emmings F. G., Genco R. J. Prevention of Streptococcus mutans infection of tooth surfaces by salivary antibody in Irus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis). Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):293–302. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.293-302.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gambrell S. C., Jr, Allen J. M., Jr Stress concentrations at the apex of pinned, implanted teeth. J Dent Res. 1976 Jan-Feb;55(1):59–65. doi: 10.1177/00220345760550012501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes M., Thomson R. O., Knight P., Stephen J. The immunopurification of tetanus toxoid. J Appl Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;37(4):603–621. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1974.tb00485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN M. H. IMMUNOLOGIC RELATION OF STREPTOCOCCAL AND TISSUE ANTIGENS. I. PROPERTIES OF AN ANTIGEN IN CERTAIN STRAINS OF GROUP A STREPTOCOCCI EXHIBITING AN IMMUNOLOGIC CROSS-REACTION WITH HUMAN HEART TISSUE. J Immunol. 1963 Apr;90:595–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN M. H. Immunologic studies of heart tissue. I. Production in rabbits of antibodies reactive with an autologous myocardial antigen following immunization with heterologous heart tissue. J Immunol. 1958 Apr;80(4):254–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN M. H. Immunologic studies of heart tissue. II. Differentiation of a myocardial sarcoplasmic antigen and cardiolopin. J Immunol. 1958 Apr;80(4):268–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. H., Frengley J. D. Autoimmunity to the heart in cardiac disease. Current concepts of the relation of autoimmunity to rheumatic fever, postcardiotomyand postinfarction syndromes and cardiomyopathies. Am J Cardiol. 1969 Oct;24(4):459–473. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(69)90489-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. A surface component in group A, C, and G streptococci with non-immune reactivity for immunoglobulin G. J Immunol. 1973 Nov;111(5):1401–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Holmberg O., Ripa T. Protein A in Staphylococcus aureus strains of human and bovine origin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(5):735–742. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Challacombe S. J., Caldwell J. An immunological investigation into the prevention of caries in deciduous teeth of rhesus monkeys. Arch Oral Biol. 1975 May-Jun;20(5-6):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(75)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J., Rowan J., Straffon L. H., Loos P. J. Association of Streptococcus mutants with human dental decay. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1252–1260. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1252-1260.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee, Michalek S. M., Webb J., Navia J. M., Rahman A. F., Legler D. W. Effective immunity to dental caries: protection of gnotobiotic rats by local immunization with Streptococcus mutans. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):300–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson G. A. Dextran receptors as immunogens in caries prophylaxis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;107:771–781. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3369-2_87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onică D., Mihalcu F., Lenkei R., Gherman M., Tudor M. Autoantibodies detected in rabbits hyperimmunized with group A, C, and G streptococcal vaccines. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):624–628. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.624-628.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER R. R. The hydrolysis of rabbit y-globulin and antibodies with crystalline papain. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:119–126. doi: 10.1042/bj0730119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Wall-associated protein antigens of Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Sep;114(1):109–115. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-1-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J., Friedman-Kien A. E., Salton M. R. Antigenic analysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1273–1288. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1273-1288.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbman M. A., Smith D. J. Effects of local immunization with Streptococcus mutans on induction of salivary immunoglobulin A antibody and experimental dental caries in rats. Infect Immun. 1974 Jun;9(6):1079–1091. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.6.1079-1091.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taubman M. A., Smith D. J. Effects of local immunization with glucosyltransferase fractions from Streptococcus mutans on dental caries in rats and hamsters. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):710–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Rijn I., Bleiweis A. S. Antigens of Streptococcus mutans. I. Characterization of a serotype-specific determinant from Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1973 May;7(5):795–804. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.5.795-804.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B. Crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:47–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabriskie J. B., Freimer E. H. An immunological relationship between the group. A streptococcus and mammalian muscle. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):661–678. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]