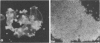
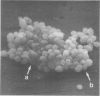
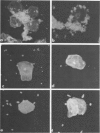
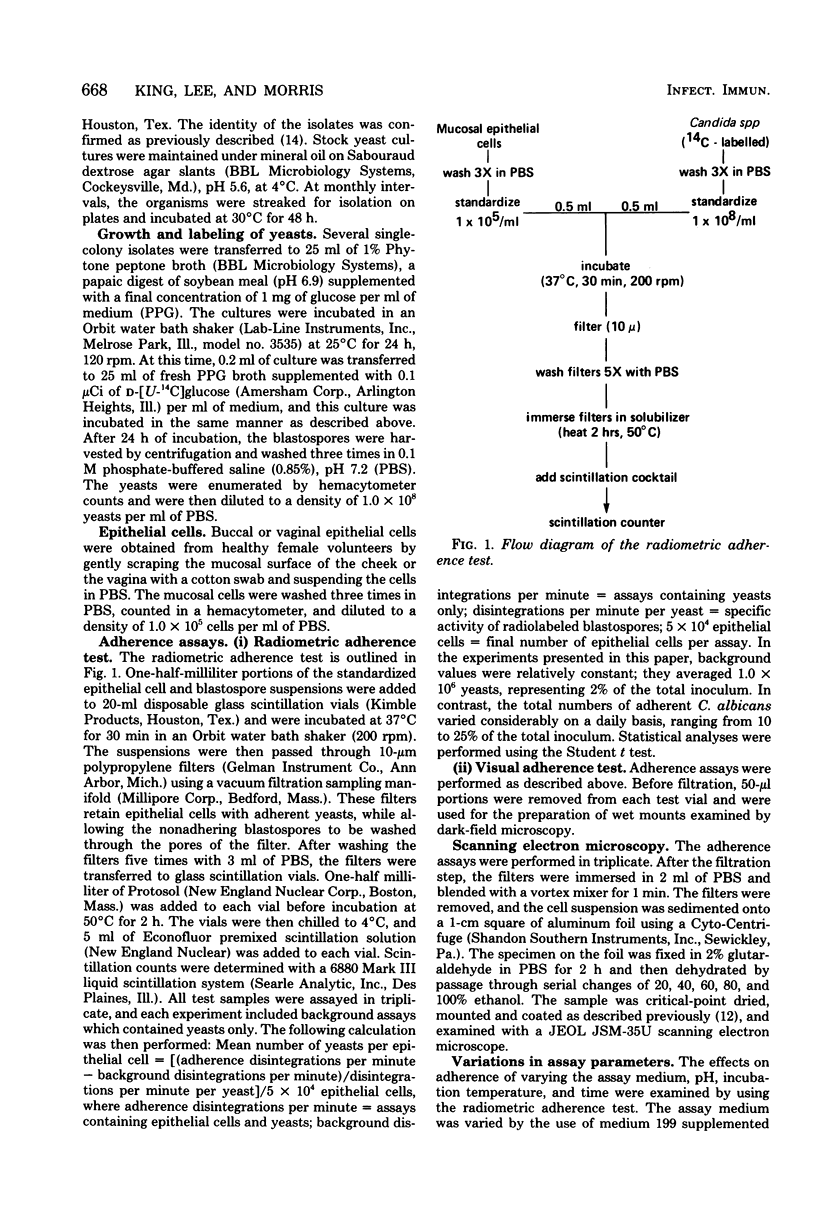
Abstract
To study the possible involvement of candidal adherence in mucosal colonization, we examined the in vitro adherence capabilities of seven Candida species. Adherence was evaluated by direct microscopic examination and by a quantitative radiometric adherence test. The results indicate that C. albicans adheres to vaginal and buccal epithelial cells to a significantly greater degree (P less than 0.01) than the other species tested. C. tropicalis and C. stellatoidea demonstrated moderate adherence capabilities, while C. parapsilosis adhered only to a slight degree. Other species failed to interact with isolated mucosal cells. These findings suggest that there is a relationship between the adherence capabilities of the Candida species and their abilities to colonize mucosal surfaces, since those species which adhere are those which most frequently colonize mucosal surfaces. C. albicans was found to be adherent under a variety of environmental conditions. Stationary-phase blastospores of C. albicans were found to be more adherent than logarithmic-phase yeasts, and larger blastospore cell-to-epithelial cell ratios resulted in greater adherence values. The actual number of adherent yeasts varied considerably when epithelial cells were obtained from different donors.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahearn D. G. Medically important yeasts. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:59–68. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.000423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow A. J., Chattaway F. W. Observations on the carriage of Candida albicans in man. Br J Dermatol. 1969 Feb;81(2):103–106. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1969.tb15988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botta G. A. Hormonal and type-dependent adhesion of group B streptococci to human vaginal cells. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):1084–1086. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.1084-1086.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton Y. M., Noble W. C. Observations on the epidemiology of Candida albicans. J Clin Pathol. 1966 Jan;19(1):76–78. doi: 10.1136/jcp.19.1.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Houte J. V. Bacterial adherence in oral microbial ecology. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:19–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura L. H., Pearsall N. N. Adherence of Candida albicans to human buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):64–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.64-68.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed W. P., Williams R. C., Jr Bacterial adherence: first step in pathogenesis of certain infections. J Chronic Dis. 1978 Feb;31(2):67–72. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(78)90091-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford B. A., Smith N., Shelokov A., Ramsay M. A. Adherence of group B streptococci and human erythrocytes to influenza A virus-infected MDCK cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Feb;160(2):226–232. doi: 10.3181/00379727-160-40424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASCHDJIAN C. L., KOZINN P. J. Laboratory and clinical studies on candidiasis in the newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1957 Apr;50(4):426–433. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(57)80252-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wain W. H., Price M. F., Cawson R. A. Factors affecting plaque formation by Candida albicans infecting the chick chorio-allantoic membrane. Sabouraudia. 1976 Jul;14(2):149–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]