Abstract
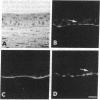
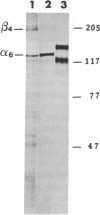
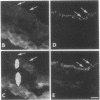
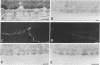
Antisera that recognize the alpha 6 and beta 4 subunits of integrins were found by immunoelectron microscopy to localize to hemidesmosomes in the basal cells of mouse corneal epithelium. Immunoprecipitation experiments using extracts of metabolically labeled corneal epithelial cells indicate that the primary alpha 6-subunit-containing integrin heterodimer present is alpha 6 beta 4 and not alpha 6 beta 1. Here we extend previous studies to report that by immunofluorescence microscopy the alpha 6 integrin subunit colocalizes with bullous pemphigoid antigen and type VII collagen in newly forming hemidesmosomes in the developing 17-day fetal rabbit eye. Neither the composition of the anchoring filaments, which span the region between the hemidesmosomal plaque and the lamina densa of basement membrane where the globular domain of type VII collagen is located, nor the extracellular ligand of alpha 6 beta 4 is known. Once anchoring filament proteins are identified, it will be of interest to determine whether any bind to alpha 6 beta 4.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benian G. M., Kiff J. E., Neckelmann N., Moerman D. G., Waterston R. H. Sequence of an unusually large protein implicated in regulation of myosin activity in C. elegans. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):45–50. doi: 10.1038/342045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck C. A., Horwitz A. F. Cell surface receptors for extracellular matrix molecules. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:179–205. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedhar S., Gray V. Isolation of a novel integrin receptor mediating Arg-Gly-Asp-directed cell adhesion to fibronectin and type I collagen from human neuroblastoma cells. Association of a novel beta 1-related subunit with alpha v. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2185–2193. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar D., Timpl R., Thoenen H. The heparin-binding domain of laminin is responsible for its effects on neurite outgrowth and neuronal survival. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1463–1468. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcioni R., Kennel S. J., Giacomini P., Zupi G., Sacchi A. Expression of tumor antigen correlated with metastatic potential of Lewis lung carcinoma and B16 melanoma clones in mice. Cancer Res. 1986 Nov;46(11):5772–5778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcioni R., Perrotti N., Piaggio G., Kennel S. K., Sacchi A. Insulin-induced phosphorylation of the beta-4 integrin subunit expressed on murine metastatic carcinoma cells. Mol Carcinog. 1989;2(6):361–368. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940020611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gipson I. K., Anderson R. A. Effect of lectins on migration of the corneal epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1980 Apr;19(4):341–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gipson I. K., Grill S. M., Spurr S. J., Brennan S. J. Hemidesmosome formation in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):849–857. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gipson I. K., Spurr-Michaud S. J., Tisdale A. S. Hemidesmosomes and anchoring fibril collagen appear synchronously during development and wound healing. Dev Biol. 1988 Apr;126(2):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90136-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. L., Deutzmann R., von der Mark K. Two distinct cell-binding domains in laminin can independently promote nonneuronal cell adhesion and spreading. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):589–598. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall D. E., Reichardt L. F., Crowley E., Holley B., Moezzi H., Sonnenberg A., Damsky C. H. The alpha 1/beta 1 and alpha 6/beta 1 integrin heterodimers mediate cell attachment to distinct sites on laminin. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2175–2184. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E., Crouse C., Sonnenberg A. Association of the VLA alpha 6 subunit with a novel protein. A possible alternative to the common VLA beta 1 subunit on certain cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6529–6535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E., Crouse C., Takada Y., Sonnenberg A. Multiple very late antigen (VLA) heterodimers on platelets. Evidence for distinct VLA-2, VLA-5 (fibronectin receptor), and VLA-6 structures. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7660–7665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogervorst F., Kuikman I., von dem Borne A. E., Sonnenberg A. Cloning and sequence analysis of beta-4 cDNA: an integrin subunit that contains a unique 118 kd cytoplasmic domain. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):765–770. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08171.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzmann B., Weissman I. L. Peyer's patch-specific lymphocyte homing receptors consist of a VLA-4-like alpha chain associated with either of two integrin beta chains, one of which is novel. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1735–1741. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03566.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Marcantonio E. E., Stepp M. A., Urry L. A., Yee G. H. Integrin heterodimer and receptor complexity in avian and mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):409–420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. C., Yokoo K. M., Goldman R. D. Further analysis of pemphigus autoantibodies and their use in studies on the heterogeneity, structure, and function of desmosomes. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):1109–1117. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene D. R., Sakai L. Y., Lunstrum G. P., Morris N. P., Burgeson R. E. Type VII collagen forms an extended network of anchoring fibrils. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):611–621. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatte D. H., Kurpakus M. A., Grelling K. A., Jones J. C. Immunochemical characterization of three components of the hemidesmosome and their expression in cultured epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3377–3390. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawczyk W. S., Wilgram G. F. Hemidesmosome and desmosome morphogenesis during epidermal wound healing. J Ultrastruct Res. 1973 Oct;45(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(73)90035-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunstrum G. P., Sakai L. Y., Keene D. R., Morris N. P., Burgeson R. E. Large complex globular domains of type VII procollagen contribute to the structure of anchoring fibrils. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):9042–9048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcantonio E. E., Hynes R. O. Antibodies to the conserved cytoplasmic domain of the integrin beta 1 subunit react with proteins in vertebrates, invertebrates, and fungi. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1765–1772. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltonen J., Larjava H., Jaakkola S., Gralnick H., Akiyama S. K., Yamada S. S., Yamada K. M., Uitto J. Localization of integrin receptors for fibronectin, collagen, and laminin in human skin. Variable expression in basal and squamous cell carcinomas. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):1916–1923. doi: 10.1172/JCI114379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):491–497. doi: 10.1126/science.2821619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacchi A., Falcioni R., Piaggio G., Gianfelice M. A., Perrotti N., Kennel S. J. Ligand-induced phosphorylation of a murine tumor surface protein (TSP-180) associated with metastatic phenotype. Cancer Res. 1989 May 15;49(10):2615–2620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacchi A., Piaggio G., Rizzo M. A., Falcioni R., Kennel S. J. Stimulation of tumor cell growth in vitro by a monoclonal antibody to a tumor specific protein (TSP-180) present on the cell surface of 3LL cells. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1989 Jan-Feb;7(1):41–54. doi: 10.1007/BF02057180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai L. Y., Keene D. R., Morris N. P., Burgeson R. E. Type VII collagen is a major structural component of anchoring fibrils. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1577–1586. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schermer A., Galvin S., Sun T. T. Differentiation-related expression of a major 64K corneal keratin in vivo and in culture suggests limbal location of corneal epithelial stem cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):49–62. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw L. M., Messier J. M., Mercurio A. M. The activation dependent adhesion of macrophages to laminin involves cytoskeletal anchoring and phosphorylation of the alpha 6 beta 1 integrin. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2167–2174. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., Janssen H., Hogervorst F., Calafat J., Hilgers J. A complex of platelet glycoproteins Ic and IIa identified by a rat monoclonal antibody. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10376–10383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., Linders C. J., Modderman P. W., Damsky C. H., Aumailley M., Timpl R. Integrin recognition of different cell-binding fragments of laminin (P1, E3, E8) and evidence that alpha 6 beta 1 but not alpha 6 beta 4 functions as a major receptor for fragment E8. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2145–2155. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr S. J., Gipson I. K. Isolation of corneal epithelium with Dispase II or EDTA. Effects on the basement membrane zone. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1985 Jun;26(6):818–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R. A specific antigen-antibody interaction triggers the cellular pathophysiology of bullous pemphigoid. Br J Dermatol. 1985 Jul;113 (Suppl 28):67–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1985.tb15628.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R., Woodley D. T., Katz S. I. Identification and partial characterization of pemphigoid antigen extracted from normal human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Jan;82(1):108–111. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12259224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susi F. R., Belt W. D., Kelly J. W. Fine structure of fibrillar complexes associated with the basement membrane in human oral mucosa. J Cell Biol. 1967 Aug;34(2):686–690. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.2.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Naitoh Y. Amino acid sequence of a novel integrin beta 4 subunit and primary expression of the mRNA in epithelial cells. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):757–763. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08170.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinkaus-Randall V., Gipson I. K. Role of calcium and calmodulin in hemidesmosome formation in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1565–1571. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieske J. D., Bukusoglu G., Gipson I. K. Enhancement of vinculin synthesis by migrating stratified squamous epithelium. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):571–576. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieske J. D., Gipson I. K. Protein synthesis during corneal epithelial wound healing. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1986 Jan;27(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]