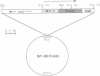
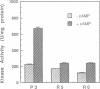
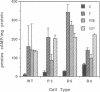
Abstract
Cl- channels in the apical membranes of salt-secreting epithelia are activated by both cAMP and Ca2+ second-messenger systems, and dysfunctions in their hormonal regulation have been demonstrated in patients with cystic fibrosis. We have transfected the epithelial cell line T84 with an expression vector containing a mutant form of the regulatory subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Stable transformants that express this construct have reduced basal cAMP-dependent protein kinase activity and do not increase kinase activity beyond the basal level of control cells in response to cAMP. Forskolin, vasoactive intestinal peptide, and prostaglandin E2 each stimulate intracellular cAMP accumulation in both mutant and control clones; however, the activation of Cl- channels in response to elevated cAMP is blocked in mutant clones, indicating direct involvement of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. In contrast, Ca2+ ionophores retain their ability to activate the Cl- channel in T84 cells expressing the mutant regulatory subunit, suggesting that activation of the channel by means of Ca2+ does not require the participation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase activity. These clones will be useful for further studies of the interactions between the cAMP- and Ca2(+)-dependent regulatory pathways in salt-secreting epithelial cells. They can also be used to identify the mediators of Ca2(+)-dependent Cl- channel activation in isolation from interactions with the cAMP second-messenger pathway.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bringhurst F. R., Zajac J. D., Daggett A. S., Skurat R. N., Kronenberg H. M. Inhibition of parathyroid hormone responsiveness in clonal osteoblastic cells expressing a mutant form of 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Jan;3(1):60–67. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-1-60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brum G., Flockerzi V., Hofmann F., Osterrieder W., Trautwein W. Injection of catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase into isolated cardiac myocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Jul;398(2):147–154. doi: 10.1007/BF00581064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., McRoberts J. A., Mandel K. G., Dharmsathaphorn K. Synergistic action of cyclic adenosine monophosphate- and calcium-mediated chloride secretion in a colonic epithelial cell line. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1837–1842. doi: 10.1172/JCI112176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg C. H., Cadd G. G., McKnight G. S. Genetic characterization of a brain-specific form of the type I regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3703–3707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg C. H., Correll L. A., Cadd G. G., McKnight G. S. Inhibition of intracellular cAMP-dependent protein kinase using mutant genes of the regulatory type I subunit. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):13111–13119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cliff W. H., Frizzell R. A. Separate Cl- conductances activated by cAMP and Ca2+ in Cl(-)-secreting epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):4956–4960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.4956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. M., Catterall W. A. Phosphorylation of the calcium antagonist receptor of the voltage-sensitive calcium channel by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2528–2532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., Mandel K. G., Masui H., McRoberts J. A. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-induced chloride secretion by a colonic epithelial cell line. Direct participation of a basolaterally localized Na+,K+,Cl- cotransport system. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):462–471. doi: 10.1172/JCI111721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., McRoberts J. A., Mandel K. G., Tisdale L. D., Masui H. A human colonic tumor cell line that maintains vectorial electrolyte transport. Am J Physiol. 1984 Feb;246(2 Pt 1):G204–G208. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.246.2.G204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fesenko E. E., Kolesnikov S. S., Lyubarsky A. L. Induction by cyclic GMP of cationic conductance in plasma membrane of retinal rod outer segment. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):310–313. doi: 10.1038/313310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell R. A., Rechkemmer G., Shoemaker R. L. Altered regulation of airway epithelial cell chloride channels in cystic fibrosis. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):558–560. doi: 10.1126/science.2425436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraldez F., Murray K. J., Sepúlveda F. V., Sheppard D. N. Characterization of a phosphorylation-activated Cl-selective channel in isolated Necturus enterocytes. J Physiol. 1989 Sep;416:517–537. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. A., Harris A., Coleman L., Greenwell J. R., Argent B. E. Two types of chloride channel on duct cells cultured from human fetal pancreas. Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 1):C240–C251. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.2.C240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halm D. R., Rechkemmer G. R., Schoumacher R. A., Frizzell R. A. Apical membrane chloride channels in a colonic cell line activated by secretory agonists. Am J Physiol. 1988 Apr;254(4 Pt 1):C505–C511. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.254.4.C505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahnsen T., Hedin L., Kidd V. J., Beattie W. G., Lohmann S. M., Walter U., Durica J., Schulz T. Z., Schiltz E., Browner M. Molecular cloning, cDNA structure, and regulation of the regulatory subunit of type II cAMP-dependent protein kinase from rat ovarian granulosa cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12352–12361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. C., Carmichael D. F., Krebs E. G., McKnight G. S. Isolation of a cDNA clone for the type I regulatory subunit of bovine cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3608–3612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitan I. B. Phosphorylation of ion channels. J Membr Biol. 1985;87(3):177–190. doi: 10.1007/BF01871217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M., McCann J. D., Liedtke C. M., Nairn A. C., Greengard P., Welsh M. J. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase opens chloride channels in normal but not cystic fibrosis airway epithelium. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):358–360. doi: 10.1038/331358a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light D. B., Corbin J. D., Stanton B. A. Dual ion-channel regulation by cyclic GMP and cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase. Nature. 1990 Mar 22;344(6264):336–339. doi: 10.1038/344336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Stafford J., Dharmsathaphorn K., Carlson S. Structural analysis of a human intestinal epithelial cell line. Gastroenterology. 1987 May;92(5 Pt 1):1133–1145. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(87)91069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Uhler M. D., Clegg C. H., Correll L. A., Cadd G. G. Application of molecular genetic techniques to the cAMP-dependent protein kinase system. Methods Enzymol. 1988;159:299–311. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)59030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRoberts J. A., Beuerlein G., Dharmsathaphorn K. Cyclic AMP and Ca2+-activated K+ transport in a human colonic epithelial cell line. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14163–14172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P. L., Clegg C. H., Correll L. A., McKnight G. S. Regulation of transcription by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4887–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Sevarino K. A., Wagner J. A., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Identification of a cyclic-AMP-responsive element within the rat somatostatin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6682–6686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Gold G. H. A cyclic nucleotide-gated conductance in olfactory receptor cilia. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):442–444. doi: 10.1038/325442a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunoki K., Florio V., Catterall W. A. Activation of purified calcium channels by stoichiometric protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6816–6820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickles R. J., Darrow A. L., Strickland S. Differentiation-responsive elements in the 5' region of the mouse tissue plasminogen activator gene confer two-stage regulation by retinoic acid and cyclic AMP in teratocarcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1691–1704. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R., Rommens J. M., Kerem B., Alon N., Rozmahel R., Grzelczak Z., Zielenski J., Lok S., Plavsic N., Chou J. L. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1066–1073. doi: 10.1126/science.2475911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommens J. M., Iannuzzi M. C., Kerem B., Drumm M. L., Melmer G., Dean M., Rozmahel R., Cole J. L., Kennedy D., Hidaka N. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: chromosome walking and jumping. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1059–1065. doi: 10.1126/science.2772657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roskoski R., Jr Assays of protein kinase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:3–6. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99034-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougon G., Barbet J., Reisine T. Protein phosphorylation induced by phorbol esters and cyclic AMP in anterior pituitary cells: possible role in adrenocorticotropin release and synthesis. J Neurochem. 1989 Apr;52(4):1270–1278. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb01875.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoppa N., Shorofsky S. R., Jow F., Nelson D. J. Voltage-gated chloride currents in cultured canine tracheal epithelial cells. J Membr Biol. 1989 Apr;108(1):73–90. doi: 10.1007/BF01870427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoumacher R. A., Shoemaker R. L., Halm D. R., Tallant E. A., Wallace R. W., Frizzell R. A. Phosphorylation fails to activate chloride channels from cystic fibrosis airway cells. Nature. 1987 Dec 24;330(6150):752–754. doi: 10.1038/330752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuster M. J., Camardo J. S., Siegelbaum S. A., Kandel E. R. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase closes the serotonin-sensitive K+ channels of Aplysia sensory neurones in cell-free membrane patches. 1985 Jan 31-Feb 6Nature. 313(6001):392–395. doi: 10.1038/313392a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelbaum S. A., Camardo J. S., Kandel E. R. Serotonin and cyclic AMP close single K+ channels in Aplysia sensory neurones. Nature. 1982 Sep 30;299(5882):413–417. doi: 10.1038/299413a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. N., Driscoll D., Mutzel R., Part D., Williams J., Véron M. Overproduction of the regulatory subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase blocks the differentiation of Dictyostelium discoideum. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2039–2043. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03612.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. L., McCabe R. D. A23187-induced changes in colonic K and Cl transport are mediated by separate mechanisms. Am J Physiol. 1984 Dec;247(6 Pt 1):G695–G702. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.247.6.G695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A., O'Farrell P. H., Friedrich U., Coffino P. Mutations causing charge alterations in regulatory subunits of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase of cultured S49 lymphoma cells. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90025-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Seagar M. J., Jones J. F., Reber B. F., Catterall W. A. Subunit structure of dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels from skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5478–5482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhler M. D., Chrivia J. C., McKnight G. S. Evidence for a second isoform of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15360–15363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venglarik C. J., Bridges R. J., Frizzell R. A. A simple assay for agonist-regulated Cl and K conductances in salt-secreting epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Aug;259(2 Pt 1):C358–C364. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.2.C358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. Y., Ascoli M. Reduced gonadotropin responses in a novel clonal strain of Leydig tumor cells established by transfection of MA-10 cells with a mutant gene of the type I regulatory subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Jan;4(1):80–90. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-1-80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J., Liedtke C. M. Chloride and potassium channels in cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):467–470. doi: 10.1038/322467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weymer A., Huott P., Liu W., McRoberts J. A., Dharmsathaphorn K. Chloride secretory mechanism induced by prostaglandin E1 in a colonic epithelial cell line. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1828–1836. doi: 10.1172/JCI112175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]