Abstract
The effects of tolerance to Escherichia coli endotoxin on the phagocytic and bactericidal activity of the hepatic reticuloendothelial system against viable E. coli were examined using ex vivo perfused rat livers. Livers were isolated from control and endotoxin-tolerant rats and perfused with a medium containing 5% homologous serum from either control or tolerant rats. After the addition of the E. coli (2 × 107 cells per ml) to the perfusate, the hepatic clearance of the bacteria was followed for 30 min. The highest activation of the hepatic reticuloendothelial system was observed when serum from tolerant animals was added to the perfusate. Under these conditions phagocytosis was 47% (12% in controls), and 37 to 38% of the bacteria were killed (5% in controls). This activation was less when livers obtained from tolerant rats were perfused with serum from controls or with saline only. The data suggests that, during endotoxin tolerance, humoral factors play an important role in the activation of the hepatic reticulendothelial system, although a direct stimulation of Kupffer cells also occurs. The enhancement of phagocytosis by tolerant serum did not require the presence of homologous antibodies and involved the activation of the alternative complement pathway, since it was lost after removal of factor B activity. On the other hand, stimulation of intracellular killing required both complement and specific antibodies. The data suggest a role of endotoxin in the activation of humoral and cellular mechanisms involved in the host resistance to gram-negative bacterial infection.
Full text
PDF

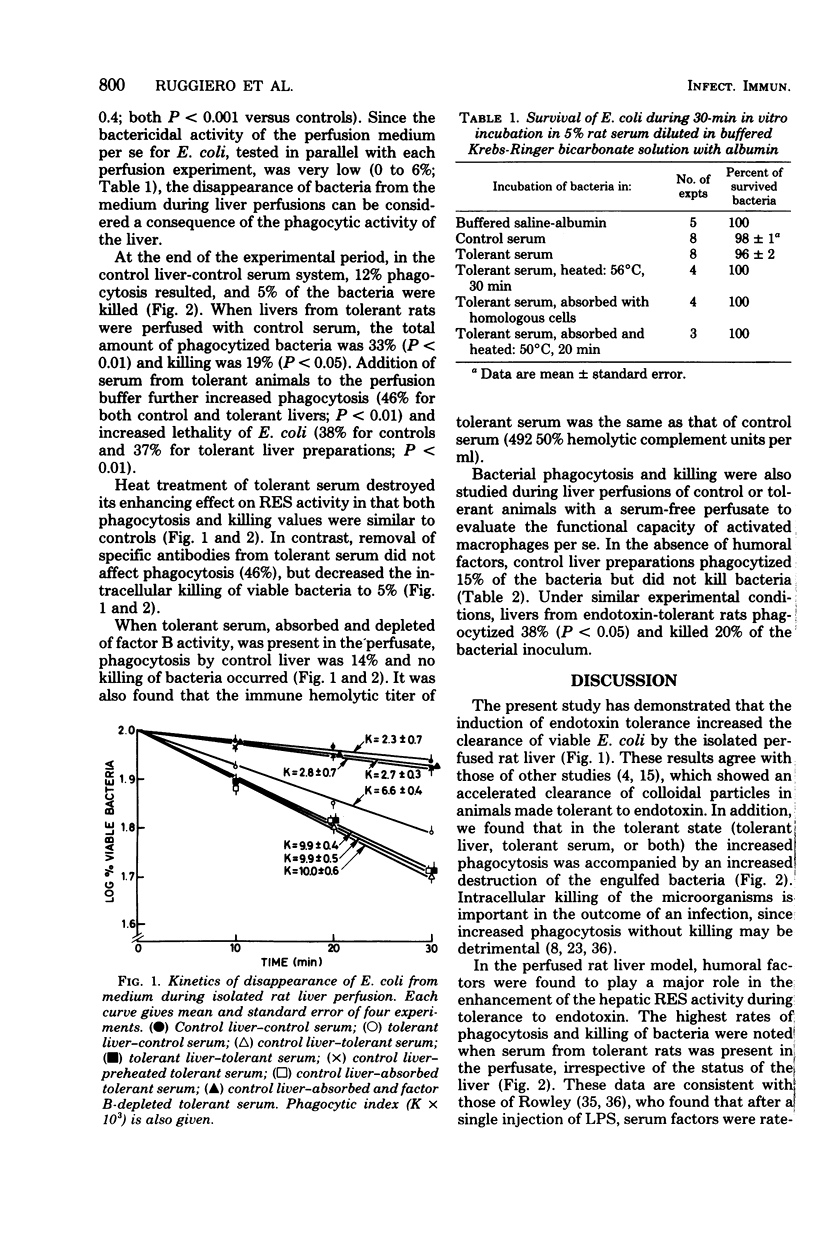
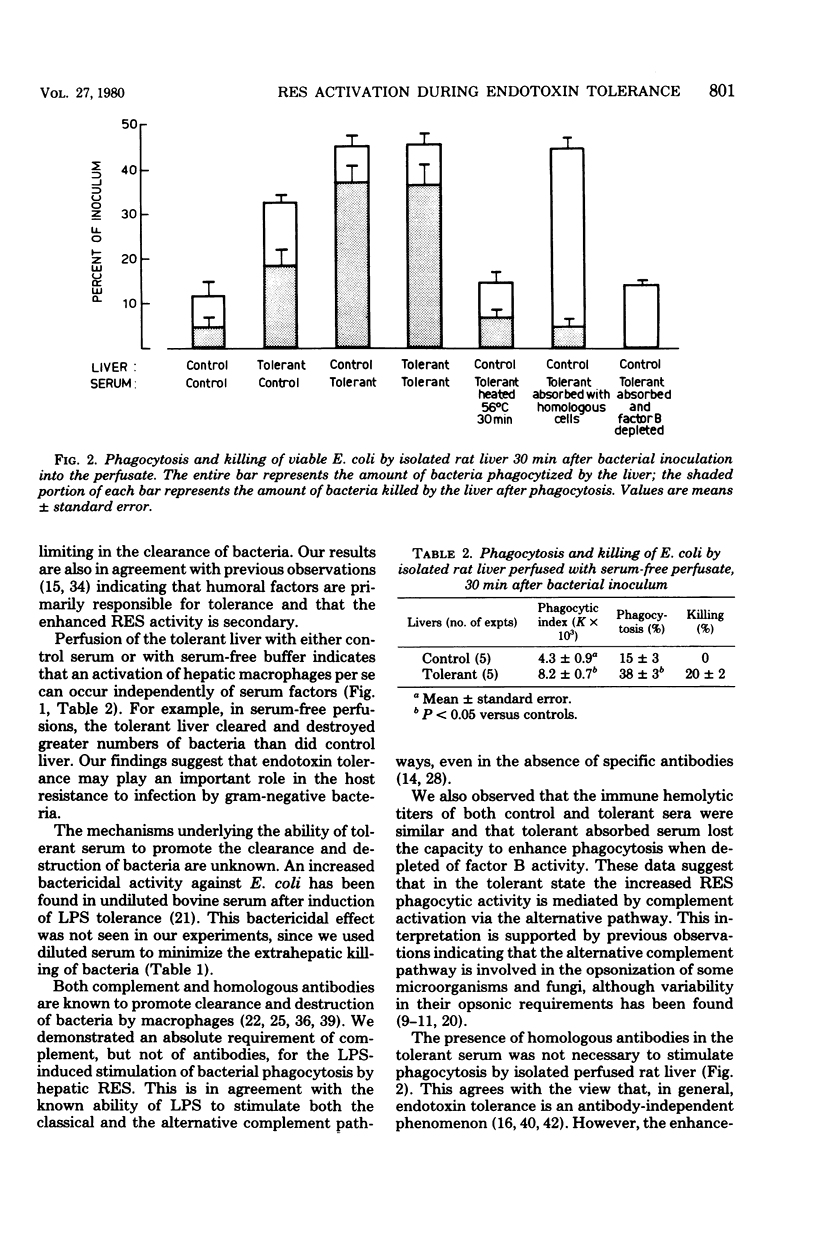


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABERNATHY R. S., SPINK W. W. Studies with Brucella endotoxin in humans: the significance of susceptibility to endotoxin in the pathogenesis of brucellosis. J Clin Invest. 1958 Feb;37(2):219–231. doi: 10.1172/JCI103601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENACERRAF B., SEBESTYEN M. M., SCHLOSSMAN S. A quantitative study of the kinetics of blood clearance of P32-labelled Escherichia coli and Staphylococci by the reticuloendothelial system. J Exp Med. 1959 Jul 1;110(1):27–48. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIOZZI G., BENACERRAF B., HALPERN B. N. The effect of Salm. typhi and its endotoxin on the phagocytic activity of the reticuloendothelial system in mice. Br J Exp Pathol. 1955 Jun;36(3):226–235. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Oxman E. Phagocytosis and intracellular disposition of viable bacteria by the isolated perfused rat liver. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1965 Nov;2(4):313–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braude A. I., Ziegler E. J., McCutchan J. A. Antiserum treatment of gram-negative bacteremia. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1978 Dec 2;108(48):1872–1876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruins S. C., Stumacher R., Johns M. A., McCabe W. R. Immunization with R mutants of Salmonella minnesota. II. Comparison of the protective effect of immunization with lipid A and the Re mutant. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):16–20. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.16-20.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cluff L. E. Effects of endotoxins on susceptibility to infections. J Infect Dis. 1970 Sep;122(3):205–215. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.3.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEDMAN H. H. Passive transfer of tolerance to pyrogenicity of bacterial endotoxin. J Exp Med. 1960 Apr 1;111:453–463. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.4.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Thong Y. H. Activation of the alternative complement pathway by Torulopsis glabrata. Scand J Infect Dis. 1979;11(1):77–79. doi: 10.3109/inf.1979.11.issue-1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Quie P. G. Opsonic activity in human serum chelated with ethylene glycoltetra-acetic acid. Immunology. 1974 Jun;26(6):1251–1256. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank M. M. The complement system in host defense and inflammation. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 May-Jun;1(3):483–501. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.3.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREISMAN S. E., CAROZZA F. A., Jr, HILLS J. D. Mechanisms of endotoxin tolerance. I. Relationship between tolerance and reticuloendothelial system phagocytic activity in the rabbit. J Exp Med. 1963 Apr 1;117:663–674. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.4.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREISMAN S. E., HORNICK R. B., CAROZZA F. A., Jr, WOODWARD T. E. The role of endotoxin during typhoid fever and tularemia in man. I. Acquisition of tolerance to endotoxin. J Clin Invest. 1963 Jul;42:1064–1075. doi: 10.1172/JCI104792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREISMAN S. E., HORNICK R. B., WOODWARD T. E. THE ROLE OF ENDOTOXIN DURING TYPHOID FEVER AND TULAREMIA IN MAN. 3. HYPERREACTIVITY TO ENDOTOXIN DURING INFECTION. J Clin Invest. 1964 Sep;43:1747–1757. doi: 10.1172/JCI105049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREISMAN S. E., WAGNER H. N., IIO M., HORNICK R. B. MECHANISMS OF ENDOTOXIN TOLERANCE. II. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN ENDOTOXIN TOLERANCE AND RETICULOENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM PHAGOCYTIC ACTIVITY IN MAN. J Exp Med. 1964 Feb 1;119:241–264. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.2.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guckian J. C., Christensen W. D., Fine D. P. Evidence for quantitative variability of bacterial opsonic requirements. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):822–826. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.822-826.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD J. G., WARDLAW A. C. The opsonic effect of normal serum on the uptake of bacteria by the reticulo-endothelial system; perfusion studies with isolated rat liver. Immunology. 1958 Oct;1(4):338–352. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. W., Shears A. L., Hibbitt K. G. Increased antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli in bovine serum after the induction of endotoxin tolerance. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):257–265. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.257-265.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKIN C., BENACERRAF B. In vitro studies on the interaction between mouse peritoneal macrophages and strains of Salmonella and Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1960 Aug 1;112:403–417. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIM Y. B., WATSON D. W. MODIFICATION OF HOST RESPONSES TO BACTERIAL ENDOTOXINS. II. PASSIVE TRANSFER OF IMMUNIY TO BACTERIAL ENDOTOXIN WITH FRACTIONS CONTAINING 19S ANTIBODIES. J Exp Med. 1965 May 1;121:751–759. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.5.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijh P. C., van den Barselaar M. T., van Zwet T. L., Daha M. R., van Furth R. Requirement of extracellular complement and immunoglobulin for intracellular killing of micro-organisms by human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):772–784. doi: 10.1172/JCI109362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER L. L., BLY C. G., WATSON M. L., BALE W. F. The dominant role of the liver in plasma protein synthesis; a direct study of the isolated perfused rat liver with the aid of lysine-epsilon-C14. J Exp Med. 1951 Nov;94(5):431–453. doi: 10.1084/jem.94.5.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe W. R. ENDOTOXIN TOLERANCE. II. ITS OCCURRENCE IN PATIENTS WITH PYELONEPHRITIS. J Clin Invest. 1963 May;42(5):618–625. doi: 10.1172/JCI104752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Kline L. F. Activation of the classical and properdin pathways of complement by bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS). J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):362–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEVA F. A., MORGAN H. R. Tolerance to the action of endotoxins of enteric bacilli in patients convalescent from typhoid and paratyphoid fevers. J Lab Clin Med. 1950 Jun;35(6):911–922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newborg M. F., North R. J. Suppressive effect of bacterial endotoxin on the expression of cell-mediated anti-Listeria immunity. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):667–672. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.667-672.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan J. P., Ali M. V. Endotoxin and the liver. II. Effect of tolerance on carbon tetrachloride-induced injury. J Med. 1973;4(1):28–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWLEY D. The role of opsonins in non-specific immunity. J Exp Med. 1960 Jan 1;111:137–144. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBENSTEIN M., MULHOLLAND J. H., JEFFERY G. M., WOLFF S. M. MALARIA INDUCED ENDOTOXIN TOLERANCE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Jan;118:283–287. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggiero G., Utili R., Andreana A. Clearance of viable Salmonella strains by the isolated, perfused rat liver: a study of serum and cellular factors involved and of the effect of treatments with carbon tetrachloride or Salmonella enteritidis lipopolysaccharide. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1977 Feb;21(2):79–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. How do phagocytes eat? Ann Intern Med. 1978 Sep;89(3):398–402. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-3-398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utili R., Abernathy C. O., Zimmerman H. J. Endotoxin effects on the liver. Life Sci. 1977 Feb 15;20(4):553–568. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90458-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFF S. M., MULHOLLAND J. H., WARD S. B., RUBENSTEIN M., MOTT P. D. EFFECT OF 6-MERCAPTOPURINE ON ENDOTOXIN TOLERANCE. J Clin Invest. 1965 Aug;44:1402–1409. doi: 10.1172/JCI105245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaldivar N. M., Scher I. Endotoxin lethality and tolerance in mice: analysis with the B-lymphocyte-defective CBA/N strain. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):127–131. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.127-131.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


