Abstract
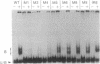
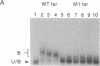
Bacterially expressed Tat protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 binds selectively to short RNA transcripts containing the viral transactivation-responsive element (TAR). Sequences sufficient for Tat interaction map to the distal portion of the TAR stem-loop. We show that critical sequences for Tat binding are located in the single-stranded "bulge," but no requirement for specific "loop" sequences could be demonstrated. TAR RNA competed for complex formation, and TAR mutants exhibited up to 10-fold reduced affinity for Tat. Synthetic peptides containing the basic region of Tat bound selectively to TAR RNA and exhibited the same sequence requirements and similar relative affinities for mutant TAR RNA as the intact protein. These results suggest that Tat contains a small RNA-binding domain capable of recognizing TAR and implicate functional relevance for direct Tat-TAR interaction in transactivation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkhout B., Jeang K. T. trans activation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 is sequence specific for both the single-stranded bulge and loop of the trans-acting-responsive hairpin: a quantitative analysis. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5501–5504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5501-5504.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., Register R. B., Callahan P. L., Garsky V. M., Colonno R. J. Cleavage of small peptides in vitro by human rhinovirus 14 3C protease expressed in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5037–5045. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5037-5045.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Heaphy S., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A., Valerio R. Human immunodeficiency virus 1 tat protein binds trans-activation-responsive region (TAR) RNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6925–6929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng S., Holland E. C. HIV-1 tat trans-activation requires the loop sequence within tar. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):165–167. doi: 10.1038/334165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Bredt D. S., Pabo C. O. Tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus forms a metal-linked dimer. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):70–73. doi: 10.1126/science.2832944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Pabo C. O. Cellular uptake of the tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1189–1193. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. A., Harrich D., Pearson L., Mitsuyasu R., Gaynor R. B. Functional domains required for tat-induced transcriptional activation of the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3143–3147. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03181.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatignol A., Kumar A., Rabson A., Jeang K. T. Identification of cellular proteins that bind to the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 trans-activation-responsive TAR element RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7828–7832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor R., Soultanakis E., Kuwabara M., Garcia J., Sigman D. S. Specific binding of a HeLa cell nuclear protein to RNA sequences in the human immunodeficiency virus transactivating region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4858–4862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauber J., Malim M. H., Cullen B. R. Mutational analysis of the conserved basic domain of human immunodeficiency virus tat protein. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1181–1187. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1181-1187.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuppuswamy M., Subramanian T., Srinivasan A., Chinnadurai G. Multiple functional domains of Tat, the trans-activator of HIV-1, defined by mutational analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3551–3561. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazinski D., Grzadzielska E., Das A. Sequence-specific recognition of RNA hairpins by bacteriophage antiterminators requires a conserved arginine-rich motif. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90882-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak R. A., Garcia-Blanco M. A., Sharp P. A. Identification and characterization of a HeLa nuclear protein that specifically binds to the trans-activation-response (TAR) element of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3624–3628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport J., Lee S. J., Khalili K., Wong-Staal F. The acidic amino-terminal region of the HIV-1 Tat protein constitutes an essential activating domain. New Biol. 1989 Oct;1(1):101–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Pavlakis G. N. Tat and Rev: positive regulators of HIV gene expression. AIDS. 1990 Jun;4(6):499–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouault T. A., Hentze M. W., Haile D. J., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. The iron-responsive element binding protein: a method for the affinity purification of a regulatory RNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5768–5772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Parkin N. T., Rosen C., Itovitch J., Sonenberg N. Structural requirements for trans activation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat-directed gene expression by tat: importance of base pairing, loop sequence, and bulges in the tat-responsive sequence. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1402–1406. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1402-1406.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S., Perkins A., Purcell R., Joung K., Sia R., Burghoff R., Haseltine W. A., Rosen C. A. Structural and functional characterization of human immunodeficiency virus tat protein. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.1-8.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby M. J., Bain E. S., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Structure, sequence, and position of the stem-loop in tar determine transcriptional elongation by tat through the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):547–558. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Marciniak R. A. HIV TAR: an RNA enhancer? Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):229–230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90279-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southgate C., Zapp M. L., Green M. R. Activation of transcription by HIV-1 Tat protein tethered to nascent RNA through another protein. Nature. 1990 Jun 14;345(6276):640–642. doi: 10.1038/345640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]