Abstract
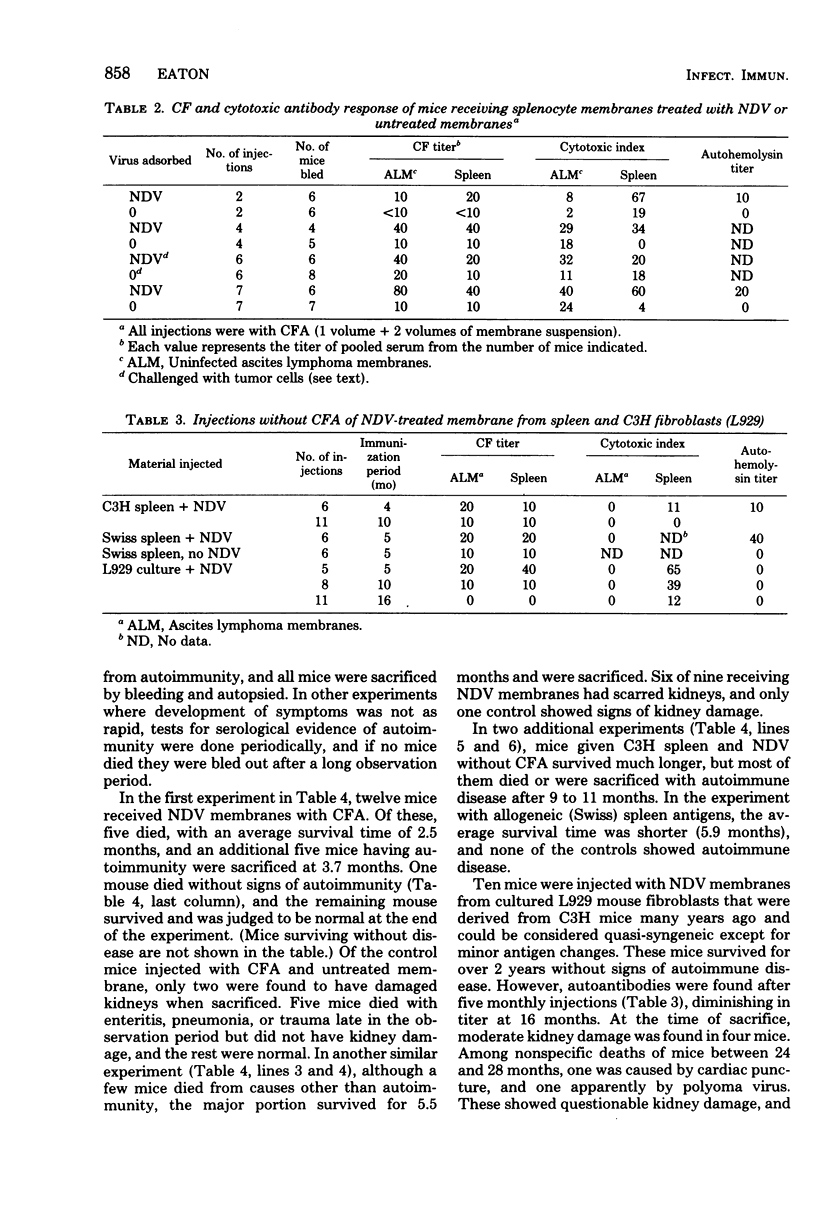
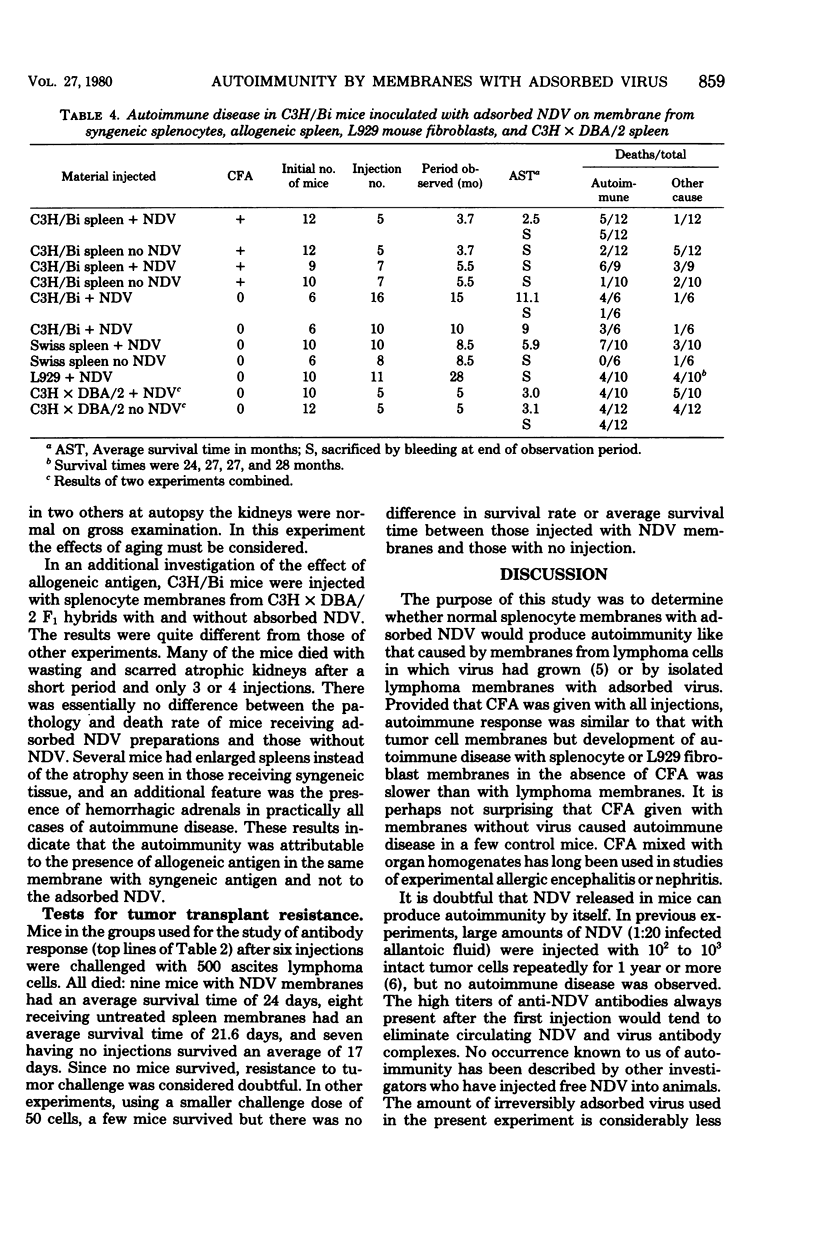
Newcastle disease virus was adsorbed to a membrane fraction prepared from splenocytes, and the resulting preparation was injected into syngeneic C3H mice. Complement fixing and cytotoxic antibodies reactive with syngeneic tissue and intact cells developed, and some mice died with autoimmune disease characterized by wasting, severe kidney damage, and loss of lymphoid tissue as described previously for animals receiving the membrane fraction of a syngeneic lymphoma in which Newcastle disease virus had grown. Similar experiments were done with L929 mouse fibroblasts and allogeneic spleen membrane fractions. With syngeneic spleen tissue and L929 fibroblasts, serological evidence of autoimmunity appeared after several injections, but deaths from autoimmunity were considerably delayed unless Freund's complete adjuvant was given with the antigen. The results suggest that antigen modification occurs after adsorption of the paramyxovirus to normal tissue as well as lymphoma cell membranes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURNET F. M. The haemolytic action of Newcastle disease virus. I. The two types of interaction between virus and red cell. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1950 May;28(3):299–309. doi: 10.1038/icb.1950.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baechtel F. S., Prager M. D. Anti-thymocyte autoimmunity in BALB/C mice accompanying immunization to a syngeneic lymphoma. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):175–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeHeer D. H., Linder E. J., Edgington T. S. Delineation of spontaneous erythrocyte autoantibody responses of NZB and other strains of mice. J Immunol. 1978 Mar;120(3):825–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton M. D., Almquist S. J. Autoimmunity induced by injection of virus-modified cell membrane antigens in syngeneic mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):322–328. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.322-328.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton M. D., Levinthal J. D., Scala A. R. Contribution of antiviral immunity to oncolysis by Newcastle disease virus in a murine lymphoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1967 Dec;39(6):1089–1097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton M. D. Role of envelope proteins of paramyxoviruses in the modification of cell membrane antigens. Arch Virol. 1979;61(4):327–336. doi: 10.1007/BF01315020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton M. D., Scala A. R. Species source of complement in viral-immune and other cytolytic reactions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Feb;133(2):615–619. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahimi A., Carruthers M. M., Wolf P., Lerner A. M. Congenital infections with reovirus. J Exp Med. 1966 Jul 1;124(1):33–46. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isacson P. Myxoviruses and autoimmunity. Prog Allergy. 1967;10:256–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano K., Fjelde A., Milgrom F. Paul-Bunnell antigen in lymphoma and leukemia spleens. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):945–949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuzumaki N., Moriuchi T., Kodama T., Kobayashi H. Xenogenization of rat erythroid cells by lymphatic leukemia virus: its role in induction of autoimmune hemolytic anemia. J Immunol. 1976 Oct;117(4):1250–1255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson L., Ebbesen P. Immunoadjuvant treatment of primary grafted and spontaneous AKR-leukemia. II. In vitro cytotoxicity of lymphoid cells against normal and malignant syngeneic cells and against normal allogeneic cells. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):781–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salaman M. H., Turk J. L., Wedderburn N. Foreign antigenicity in tissues of mice infected with a lymphomagenic virus. I. Antigenicity of spleen cells. Transplantation. 1973 Dec;16(6):583–590. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197312000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staab H. J., Anderer F. A. Chemical modification and immunogenicity of membrane fractions from mouse tumour cells. Br J Cancer. 1978 Oct;38(4):496–502. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1978.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeichi N., Kuzumaki N., Kodama T., Sendo F., Hosokawa M. Runting syndrome in rats inoculated with Friend virus. Cancer Res. 1972 Mar;32(3):445–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N., Steinberg A. D. The pathogenesis of autoimmunity in New Zealand black mice. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1974;64(0):79–103. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65848-8_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonietti G., Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J. The effect of induced chronic viral infections on the immunologic diseases of New Zealand mice. J Exp Med. 1970 Jul 1;132(1):89–109. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandeputte M., De Somer P. Runting syndrome in mice inoculated with polyoma virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1965 Aug;35(2):237–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Jr, Zinkernagel R. M., Hallenbeck L. A. Cytotoxic cells induced during lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection of mice. II. "Specificities" of the natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1979 Feb;122(2):475–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



