Abstract
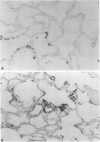
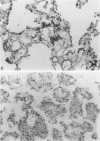
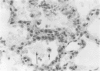
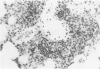
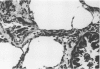
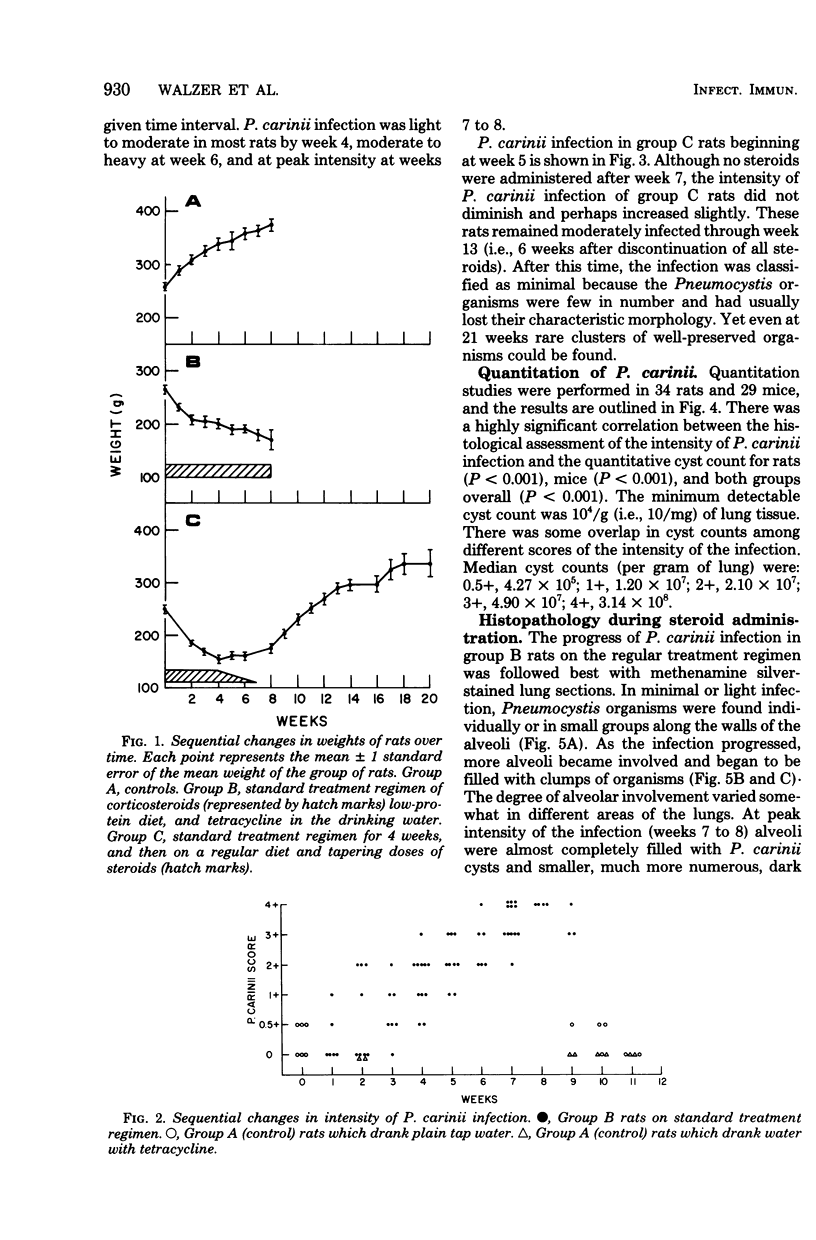
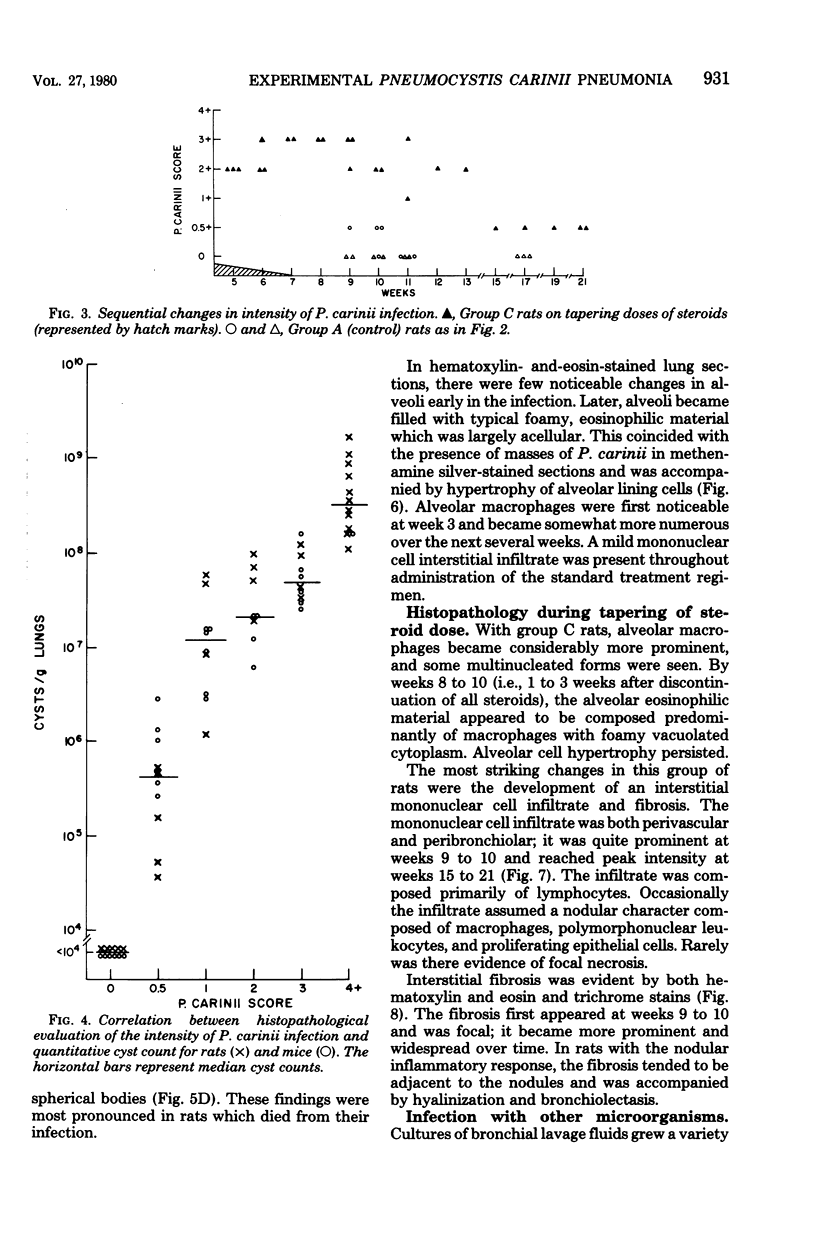
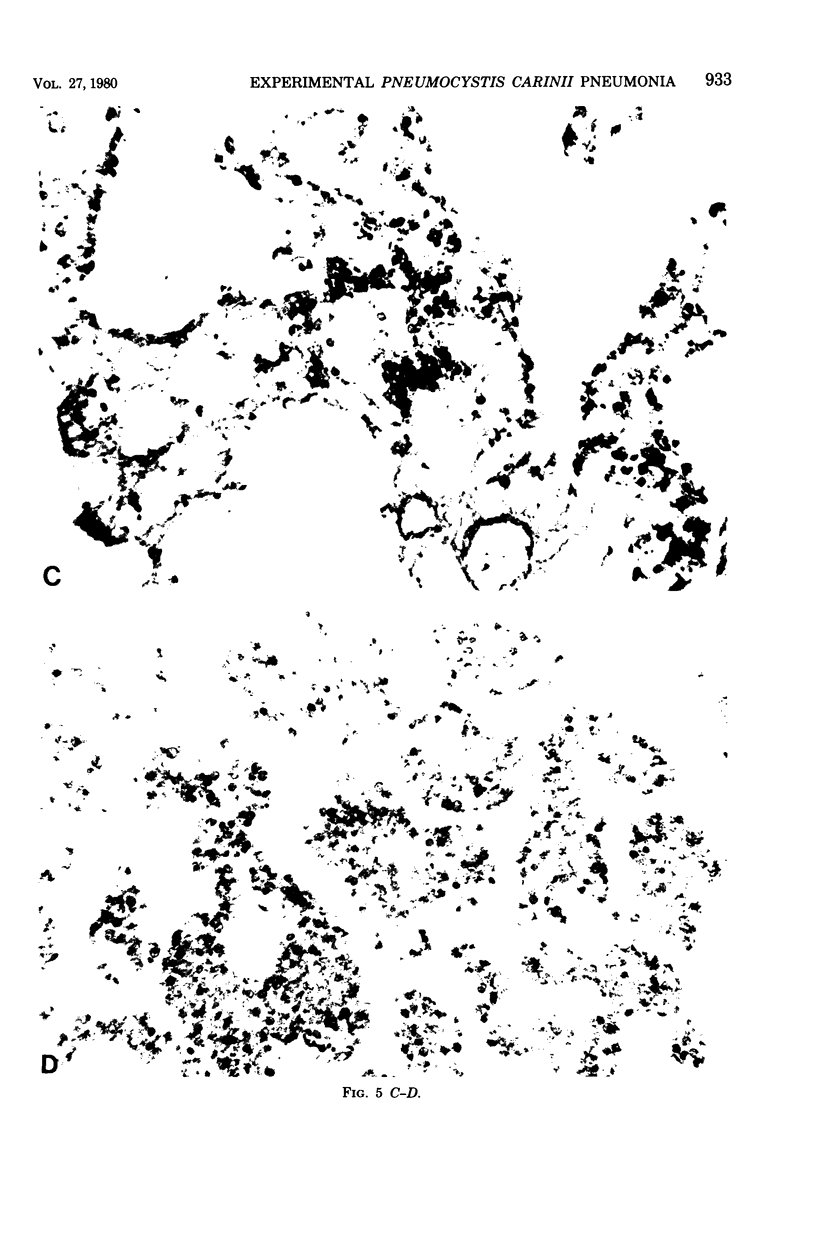
Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia was produced in two groups of rats by the administration of corticosteroids, a low-protein (8%) diet, and tetracycline in the drinking water. A third group not on corticosteroids or a low-protein diet served as controls. Members of the first group were sacrificed weekly for 8 weeks, and lungs were examined. A highly significant correlation was found between the histopathological assessment of the intensity of P. carinii infection and the number of cysts counted in enzyme-digested lungs. P. carinii progressively filled alveoli, and cyst counts increased from less than or equal to 10(4) to 10(9) cysts/g of lung at peak intensity of infection at 7 to 8 weeks. The second group of rats was placed on a regular diet and tapering doses of corticosteroids after week 4, and they were sacrificed at varying intervals for up to 21 weeks. P. carinii was not cleared from the lungs until after week 13 (more than 6 weeks after discontinuation of all steroids). Histologically, there was an increased prominence of alveolar macrophages and the progressive development of interstitial mononuclear cell infiltrate and fibrosis. Thus, P. carinii grows grows slowly in vivo and interacts with specific host cells. The resulting changes may be important in the pathogenesis of the infection and in the clearance of the organism from the lung after immunocompetence has been restored.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barton E. G., Jr, Campbell W. G., Jr Pneumocystis carinii in lungs of rats treated with cortisone acetate. Ultrastructural observations relating to the life cycle. Am J Pathol. 1969 Feb;54(2):209–236. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowling M. C., Smith I. M., Wescott S. L. A rapid staining procedure for Pneumocystis carinii. Am J Med Technol. 1973 Jul;39(7):267–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown I. N., Krenzien H. N. Systemic Mycobacterium lepraemurium infection in mice: differences in doubling time in liver, spleen, and bone marrow, and a method for measuring the proportion of viable organisms in an inoculum. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):480–486. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.480-486.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Good J. T., Shultz J. A. Latent Pneumocystis infection of rats, relapse, and chemotherapy. Lab Invest. 1966 Oct;15(10):1559–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschall J. L., Walzer P. D., Yoneda K. The morphologic changes of the rat type II pneumocytes induced by oxytetracycline. Lab Invest. 1979 Jul;41(1):5–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendley J. O., Weller T. H. Activation and transmission in rats of infection with Pneumocystis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Sep;137(4):1401–1404. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Kim H. K., Price R. A., Miller C. Attempts at prophylaxis for murine Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 1973 Aug;15(8):581–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., McNabb P. C., Makres T. D., Feldman S. Efficacy of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole in the prevention and treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):289–293. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Price R. A., Sisko F., Havron W. S., Kafatos A. G., Schonland M., Smythe P. M. Protein-calorie malnutrition. A host determinant for Pneumocystis carinii infection. Am J Dis Child. 1974 Jul;128(1):44–52. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1974.02110260046008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppert M., Sun S. H., Gleason-Jordon I., Vukovich K. R. Lung weight parallels disease severity in experimental coccidioidomycosis. Infect Immun. 1976 Dec;14(6):1356–1368. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.6.1356-1368.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. K., Hughes W. T., Feldman S. Studies of morphology and immunofluorescence of Pneumocystis carinii. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Oct;141(1):304–309. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluge R. M., Spaulding D. M., Spain A. J. Combination of pentamidine and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in therapy of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jun;13(6):975–978. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.6.975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre C. R., Sulzer A. J., Norman L. G. Serial propagation of Pneumocystis carinii in cell line cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1204–1206. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1204-1206.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim S. K., Eveland W. C., Porter R. J. Development and evaluation of a direct fluorescent antibody method for the diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii infections in experimental animals. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Nov;26(5):666–671. doi: 10.1128/am.26.5.666-671.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim S. K., Jones R. H., Eveland W. C. Fluorescent antibody studies on experimental pneumocytosis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Feb;136(2):675–679. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masur H., Jones T. C. The interaction in vitro of Pneumocystis carinii with macrophages and L-cells. J Exp Med. 1978 Jan 1;147(1):157–170. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer L. L., Hughes W. T., Murphy M. J., Jr Propagation of Pneumocystis carinii in vitro. Pediatr Res. 1977 Apr;11(4):305–316. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197704000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer L. L., Woods D., Hughes W. T. Propagation of Pneumocystis carinii in Vero cell culture. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):66–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.66-68.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
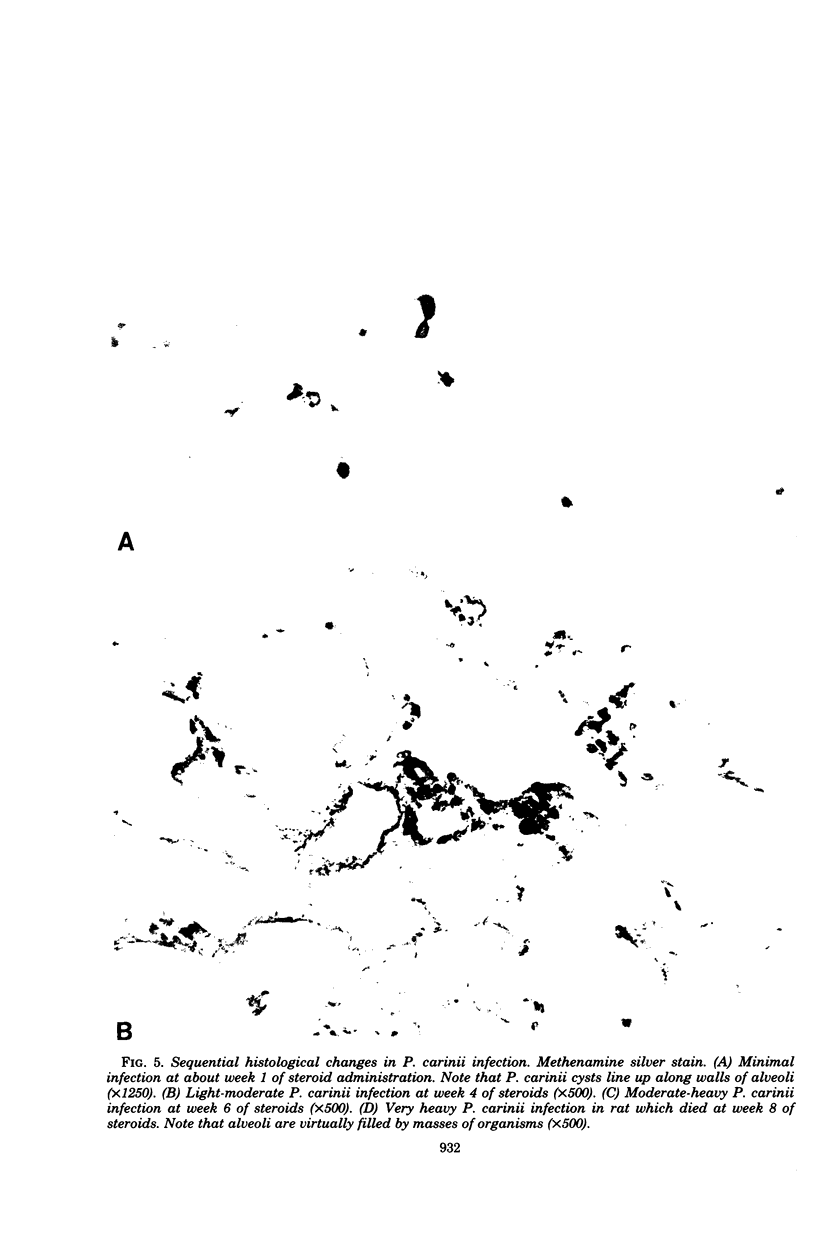
- Price R. A., Hughes W. T. Histopathology of Pneumocystis carinii infestation and infection in malignant disease in childhood. Hum Pathol. 1974 Nov;5(6):737–752. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(74)80043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen P., Armstrong D., Ramos C. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. A clinicopathologic study of twenty patients with neoplastic diseases. Am J Med. 1972 Oct;53(4):428–436. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHELDON W. H. Experimental pulmonary Pneumocystis carinii infection in rabbits. J Exp Med. 1959 Jul 1;110(1):147–160. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., Goto Y., Yamazaki S., Fujiwara K. Chronic fatal pneumocystosis in nude mice. Jpn J Exp Med. 1977 Dec;47(6):475–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vavra J., Kucera K. Pneumocystis carinii delanoë, its ultrastructure and ultrastructural affinities. J Protozool. 1970 Aug;17(3):463–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1970.tb04715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Behren L. A., Pesanti E. L. Uptake and degradation of Pneumocystis carinii by macrophages in vitro. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Dec;118(6):1051–1059. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.6.1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vossen M. E., Beckers P. J., Meuwissen J. H., Stadhouders A. M. Developmental biology of Pneumocystis carinii, and alternative view on the life cycle of the parasite. Z Parasitenkd. 1978 Apr 20;55(2):101–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00384826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELLER R. Weitere Untersuchungen über experimentelle Rattenpneumocytose im Hinblick auf die interstitielle Pneumonie der Frühgeborenen. Z Kinderheilkd. 1956;78(2):166–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELLER R. Zur Erzeugung von Pneumocystosen im Tierversuch. Z Kinderheilkd. 1955;76(4):366–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Perl D. P., Krogstad D. J., Rawson P. G., Schultz M. G. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the United States. Epidemiologic, diagnostic, and clinical features. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Jan;80(1):83–93. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Powell R. D., Jr, Yoneda K. Experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in different strains of cortisonized mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):939–947. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.939-947.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Rutledge M. E., Yoneda K., Stahr B. J. Pneumocystis carinii: new separation method from lung tissue. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Jun;47(3):356–368. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90088-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Schnelle V., Armstrong D., Rosen P. P. Nude mouse: a new experimental model for Pneumocystis carinii infection. Science. 1977 Jul 8;197(4299):177–179. doi: 10.1126/science.301657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber W. R., Askin F. B., Dehner L. P. Lung biopsy in Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: a histopathologic study of typical and atypical features. Am J Clin Pathol. 1977 Jan;67(1):11–19. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/67.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Western K. A., Norman L., Kaufmann A. G. Failure of pentamidine isethionate to provide chemoprophylaxis against Pneumocytis carinii infection in rats. J Infect Dis. 1975 Mar;131(3):273–276. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.3.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitcomb M. E., Schwarz M. I., Charles M. A., Larson P. H. Interstitial fibrosis after Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Nov;73(5):761–765. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-5-761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]