Erratum
Upon publication of the original article [1], it was noticed that Fig. 5 contained an error. The Fig. 5e (middle) for CD34 area fraction (%) data was erroneously included during the drafting of the manuscript. This has now been acknowledged and corrected in this erratum. The correct Fig. 5 is shown below.
Fig. 5.
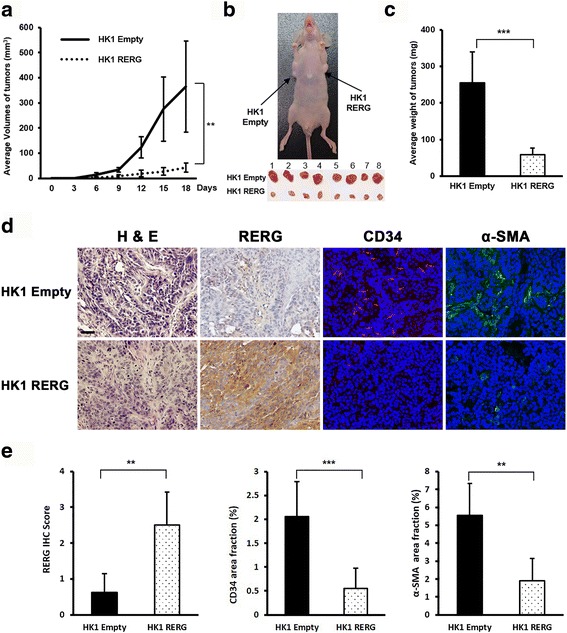
RERG inhibited the tumorigenesis and angiogenesis of NPC in vivo. Eight male BALB/c athymic nu/nu mice injected with 2 × 106 cells. a Growth curve of tumors in nude mice. Tumor volume was measured every 3 days after inoculation. b Image of nude mouse tumors derived from HK1 cells stably transfected with RERG or empty vector. Arrows indicate positions and locations of tumors. c The average weights of tumors in nude mice. d Representative photographs of H&E staining, IHC analyses of the expression of RERG and immunofluorescence analyses of the expression of CD34 (red), α-SMA (green) in tumors from nude mice. Nuclei were counterstained by DAPI (blue) in the merged pictures of immunofluorescence analyses. Original magnification is × 200. Bar represents 50 μm. e Left, IHC scores of RERG in tumors from nude mice. Middle and right, for immunofluorescence analyses, graphs represent average area fraction (%) ± SD of microvessels/field by CD34 and α-SMA area fraction (%) in tumors from nude mice analyzed by Image J. Data are shown as means ± SD. **: P < 0.01, ***: P < 0.001 by Mann-Whitney U test or Student’s t-test
Footnotes
The online version of the original article can be found under doi:10.1186/s13046-017-0554-9
Contributor Information
Mariko Murata, Email: mmurata@doc.medic.mie-u.ac.jp.
Kazuhiko Takeuchi, Email: kazuhiko@clin.medic.mie-u.ac.jp.
Reference
- 1.Zhao W, Ma N, Wang S, Mo Y, Zhang Z, Huang G, Midorikawa K, Hiraku Y, Oikawa S, Murata M, Takeuchi K. RERG suppresses cell proliferation, migration and angiogenesis through ERK/NF-κB signaling pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017;36(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0554-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


