Abstract
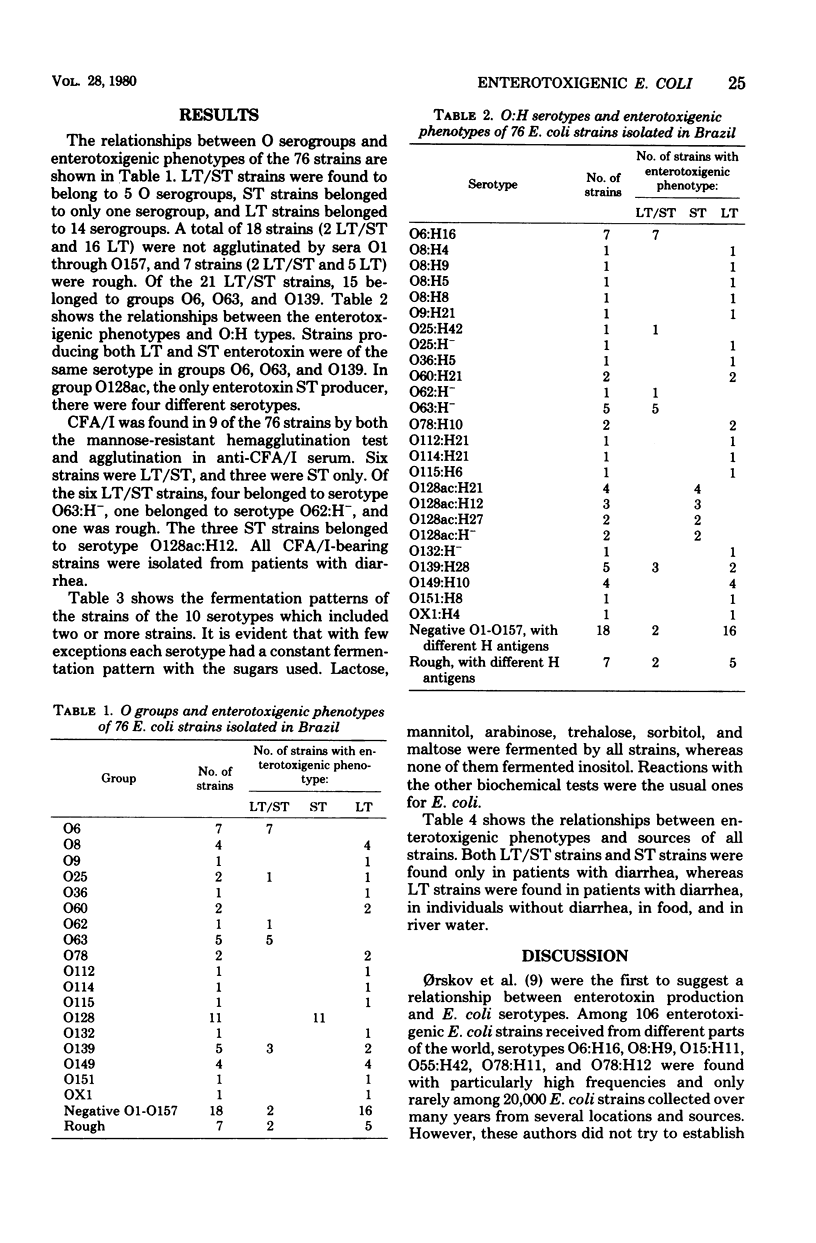
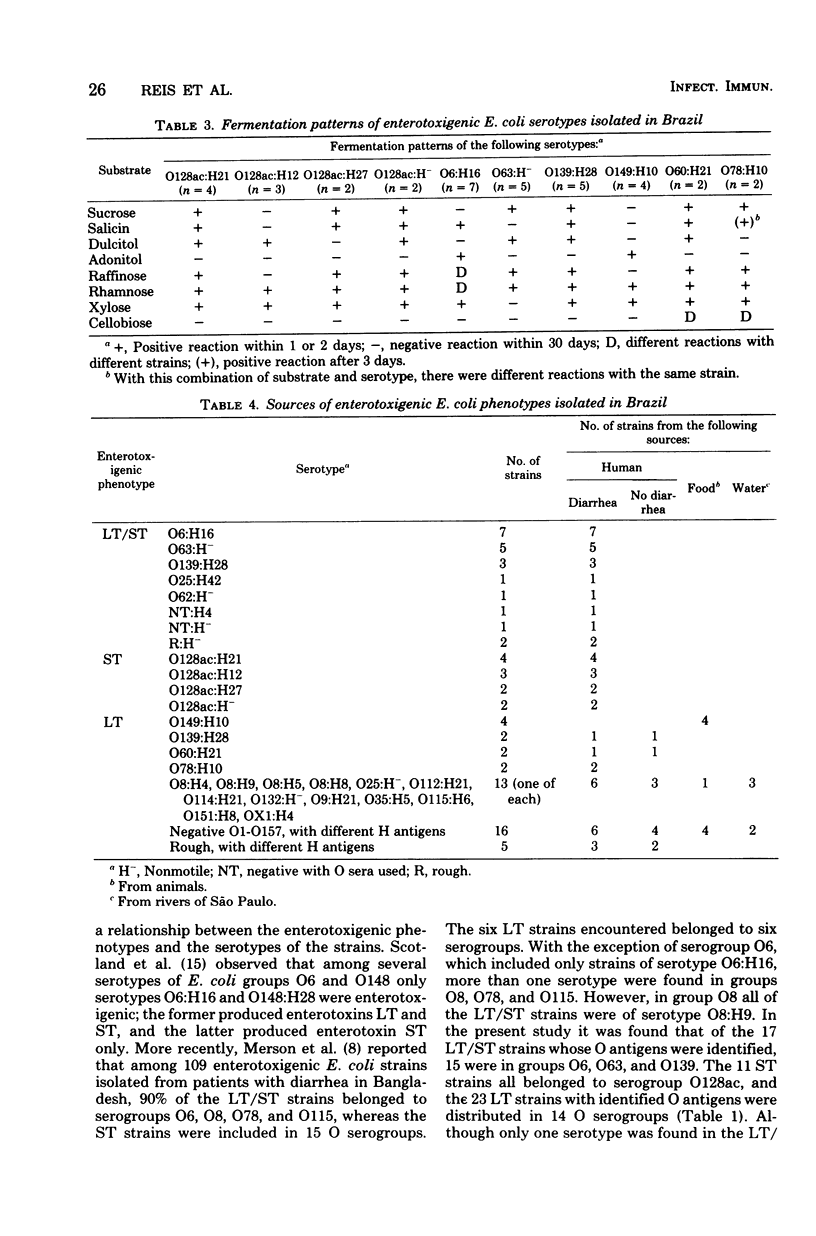
The relationship among O groups, O:H serotypes and enterotoxigenic phenotypes was examined in 76 Escherichia coli strains isolated in Brazil from different sources. Of the 17 heat-labile and -stable enterotoxin (LT/ST)-producing strains whose O antigens were identified, 15 belonged to serotypes O6:H16 (7 strains), O63:H- (5 strains), and O139:H28 (3 strains). All 11 ST strains were in group OO128PAC, which was represented by four O:H serotypes. The 23 LT strains with the O antigen identified were distributed among serotypes of 14 O groups. Colonization factor CFA/I was not found in any of the LT strains, but it was found in six LT/ST and three ST strains. On the whole, each E. coli O:H serotype had a particular fermentation pattern. LT/ST as well as ST strains were all isolated from patients with diarrhea, whereas LT strains were isolated from patients with diarrhea, normal children, food, and river water.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C. Detection of heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin with the use of adrenal cells in tissue culture. Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):334–336. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr New surface-associated heat-labile colonization factor antigen (CFA/II) produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of serogroups O6 and O8. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):638–647. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.638-647.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merson M. H., Orskov F., Orskov I., Sack R. B., Huq I., Koster F. T. Relationship between enterotoxin production and serotype in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):325–329. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.325-329.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F., Orskov I., Evans D. J., Jr, Sack R. B., Sack D. A., Wadström T. Special Escherichia coli serotypes among enterotoxigenic strains from diarrhoea in adults and children. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1976 Jun 1;162(2):73–80. doi: 10.1007/BF02121318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F. Special O:K:H serotypes among enterotoxigenic E. coli strains from diarrhea in adults and children. Occurrence of the CF (colonization factor) antigen and of hemagglutinating abilities. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1977 Jul 18;163(2):99–110. doi: 10.1007/BF02121825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering L. K., Evans D. J., Jr, Muñoz O., DuPont H. L., Coello-Ramírez P., Vollet J. J., Conklin R. H., Olarte J., Kohl S. Prospective study of enteropathogens in children with diarrhea in Houston and Mexico. J Pediatr. 1978 Sep;93(3):383–388. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)81142-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis M. H., Castro A. F., Toledo M. R., Trabulsi L. R. Production of heat-stable enterotoxin by the O128 serogroup of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):289–290. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.289-290.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Gorbach S. L., Banwell J. G., Jacobs B., Chatterjee B. D., Mitra R. C. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from patients with severe cholera-like disease. J Infect Dis. 1971 Apr;123(4):378–385. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.4.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotland S. M., Gross R. J., Rowe B. Serotype-related enterotoxigenicity in Escherichia coli O6.H16 and O148.H28. J Hyg (Lond) 1977 Dec;79(3):395–403. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400053249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafim M. B., de Castro A. F., Rangel H. A., Neto L. P. Isolation of heat-stable enterotoxin-producing strains of Escherichia coli isolated from cases of diarrhea in Campinas, SP, Brazil. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1977 May-Jun;19(3):144–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsmuth I. K., Falkow S., Ryder R. W. Plasmid-mediated properties of a heat-stable enterotoxin-producing Escherichia coli associated with infantile diarrhea. Infect Immun. 1976 Aug;14(2):403–407. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.2.403-407.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsmuth K., Wells J., Shipley P., Ryder R. Heat-labile enterotoxin production in isolates from a shipboard outbreak of human diarrheal illness. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):793–797. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.793-797.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



