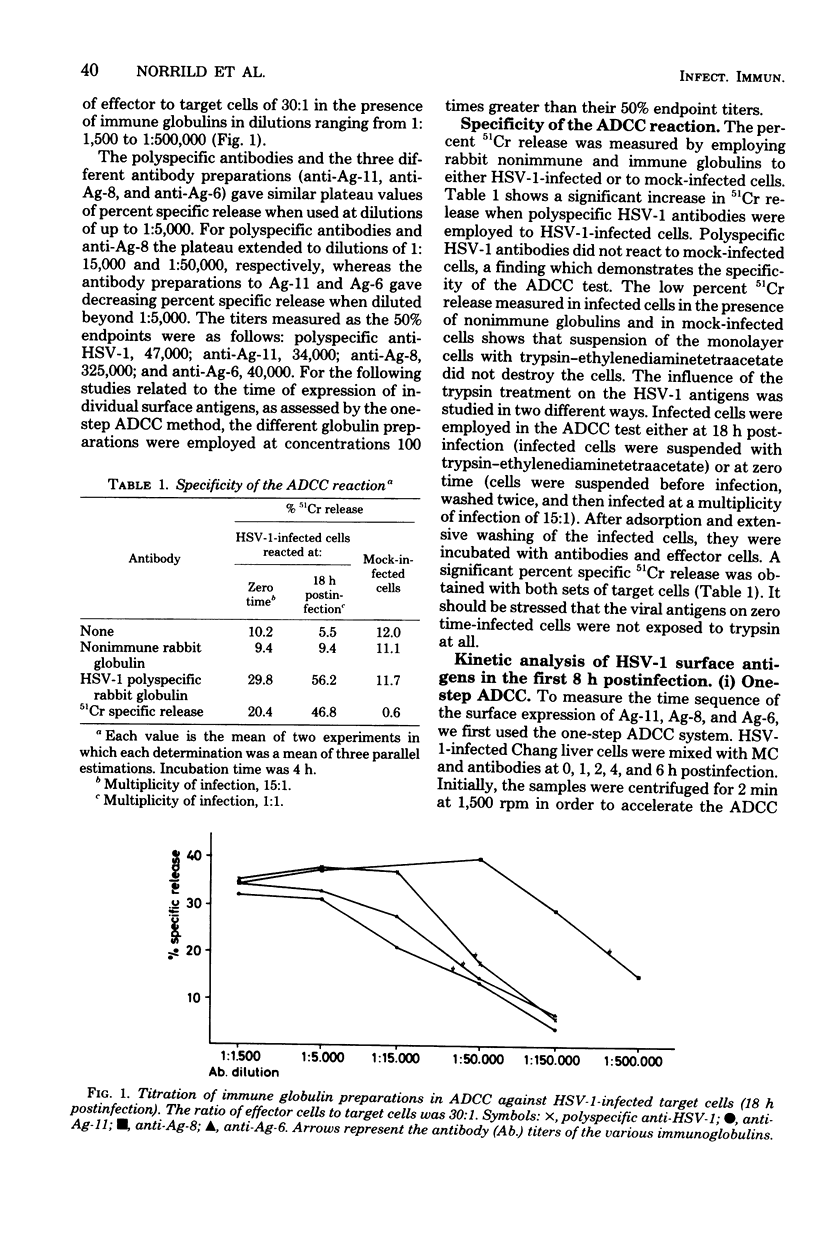
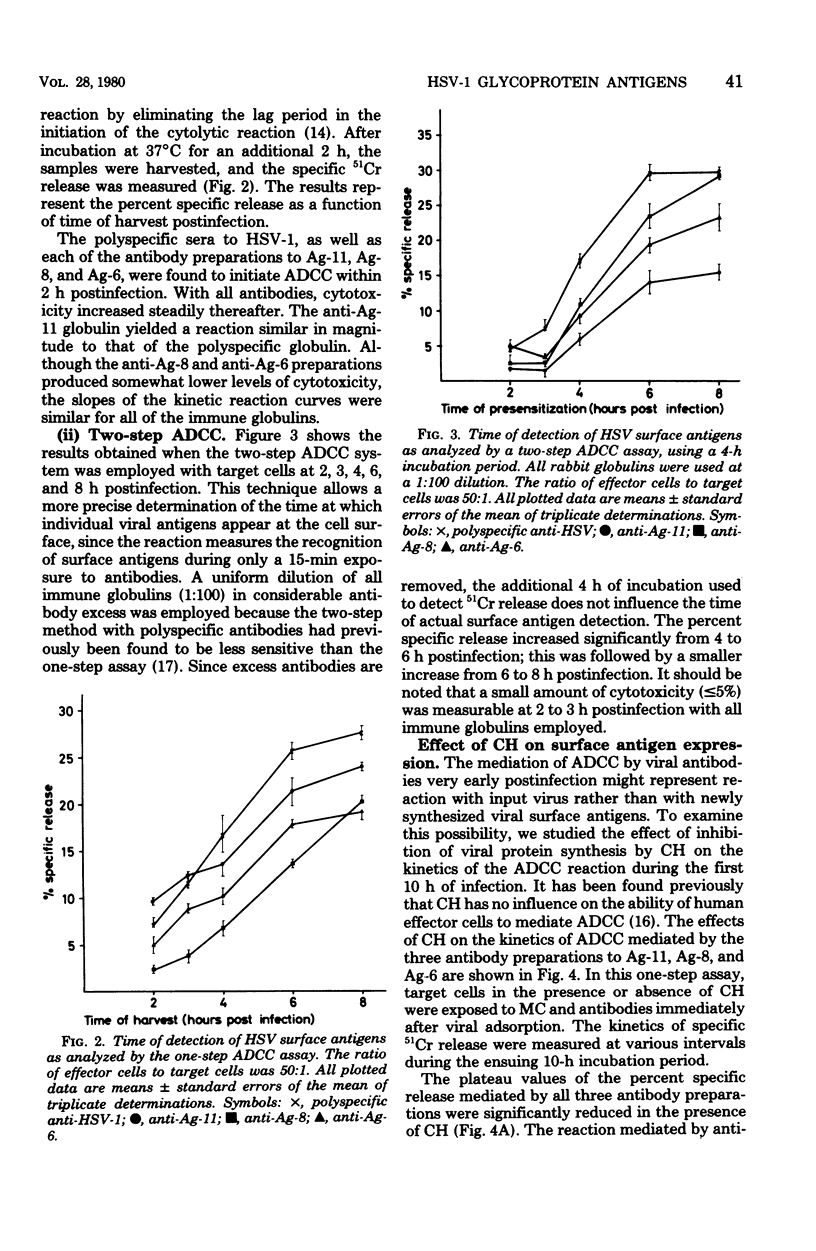
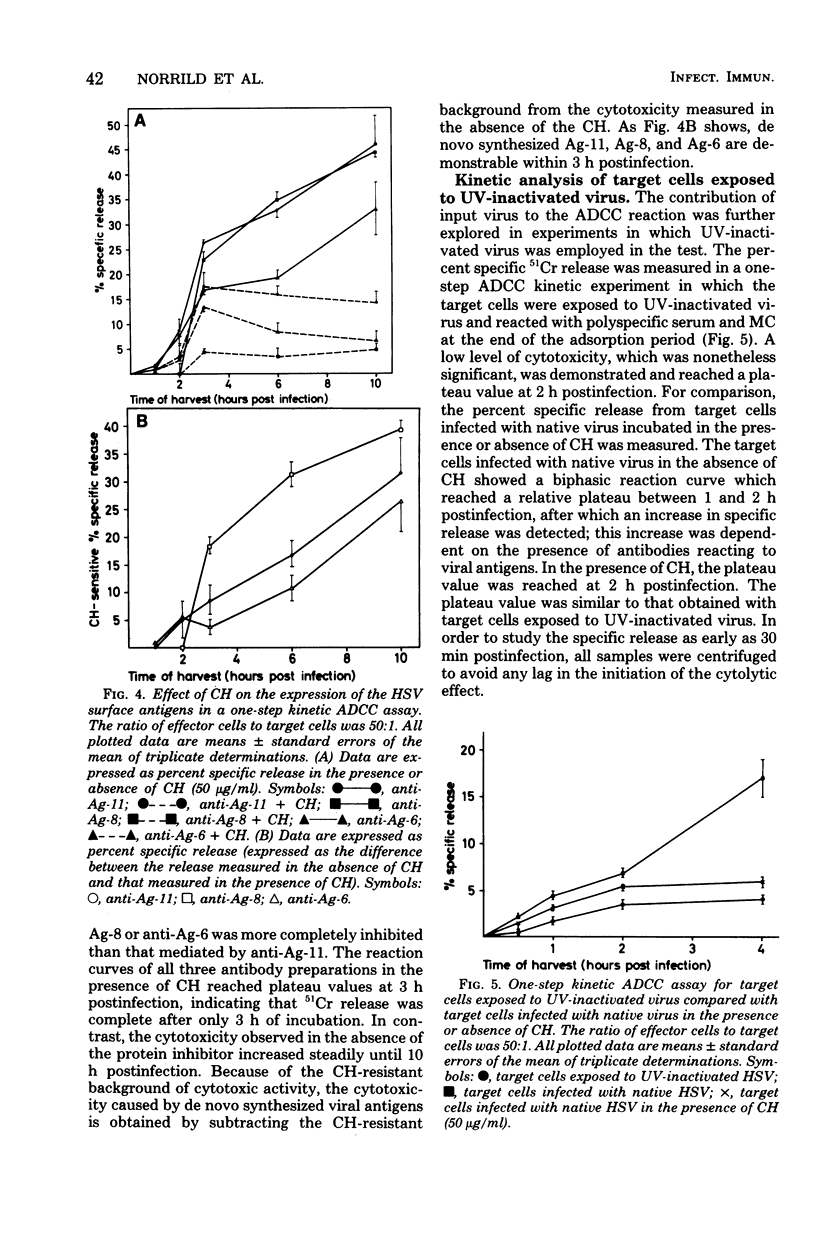
Abstract
Tissue culture cells infected with herpes simplex virus type 1 synthesize three major glycoprotein antigens (Ag-11, Ag-8, and Ag-6), which have been characterized by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. The three viral antigens have been identified as a mixture of gA and gB (Ag-11), gD (Ag-8), and gC (Ag-6). Recent findings have shown that antibodies directed to each of the three antigens individually are able to mediate antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity when tissue culture cells late in the infectious cycle (18 h postinfection) are used. In this work, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity was applied to study the time postinfection at which the individual viral antigens first made their appearance at the cell surface. All three viral antigens (Ag-11, Ag-8, and Ag-6) could be demonstrated as newly synthesized from 3 to 4 h postinfection, and the quantities of the antigens at the surfaces of the infected cells increased with time postinfection. The use of cycloheximide and ultraviolet-inactivated virus demonstrated that input virus could be detected by antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity during the first 2 h postinfection, but the cytotoxicity caused by input virus remained constant with time postinfection. In conclusion, these observations demonstrate the participation of individual herpes simplex virus surface antigens in antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity attack on cells early in infection.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Glorioso J. C., Smith J. W. Immune interactions with cells infected with herpes simplex virus: antibodies to radioiodinated surface antigens. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):114–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe N., Ingild A. Immunization, isolation of immunoglobulins, estimation of antibody titre. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:161–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R., Ukaejiofo E. O. Rapid preparation of lymphocytes for tissue-typing. Lancet. 1969 Aug 9;2(7615):327–327. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90096-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Spear P. G., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. VI. Viral proteins in the plasma membrane. J Virol. 1972 Mar;9(3):431–439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.3.431-439.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Starr S. E., oleske J. M., Shore S. L., Ashman R. B., Nahmias A. J. Human monocyte-macrophage-mediated antibody-dependent cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus-infected cells. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):729–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias A. J., Chiang W. T., Del Buono I., Duffey A. Typing of Herpesvirus hominis strains by a direct immunofluorescent technique. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Oct;132(1):386–390. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrild B., Bjerrum O. J., Ludwig H., Vestergaard B. F. Analysis of herpes simplex virus type 1 antigens exposed on the surface of infected tissue culture cells. Virology. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):307–316. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrild B., Ludwig H., Rott R. Identification of a common antigen of herpes simplex virus bovine herpes mammillitis virus, and B virus. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):712–717. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.712-717.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrild B., Shore S. L., Nahmias A. J. Herpes simplex virus glycoproteins: participation of individual herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein antigens in immunocytolysis and their correlation with previously identified glycopolypeptides. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):741–748. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.741-748.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleske J. M., Ashman R. B., Kohl S., Shore S. L., Starr S. E., Wood P., Nahmias A. J. Human polymorphonuclear leucocytes as mediators of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus-infected cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Mar;27(3):446–453. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauli G., Ludwig H. Immunoprecipitation of herpes simplex virus type 1 antigens with different antisera and human cerebrospinal fluids. Arch Virol. 1977;53(1-2):139–155. doi: 10.1007/BF01314855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano T. J., Shore S. L. Lysis of virus-infected target cells by antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. I. General requirements of the reaction and temporal relationship between lethal hits and cytolysis. Cell Immunol. 1977 Apr;30(1):66–81. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore S. L., Black C. M., Melewicz F. M., Wood P. A., Nahmias A. J. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity to target cells infected with type 1 and type 2 herpes simplex virus. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):194–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore S. L., Cromeans T. L., Norrild B. Early damage of herpes-infected cells by antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity: relative roles of virus-specified cell-surface antigens and input virus. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2239–2244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore S. L., Cromeans T. L., Romano T. J. Immune destruction of virus-infected cells early in the infectious cycle. Nature. 1976 Aug 19;262(5570):695–696. doi: 10.1038/262695a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. I. Identification of four glycoprotein precursors and their products in type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):991–1008. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.991-1008.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian T., Rawls W. E. Comparison of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and complement-dependent antibody lysis of herpes simplex virus-infected cells as methods of detecting antiviral antibodies in human sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jun;5(6):551–558. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.6.551-558.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vestergaard B. F., Bjerrum O. J., Norrild B., Grauballe P. C. Crossed immunoelectrophoretic studies of the solubility immunogenicity of herpes simplex virus antigens. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):82–90. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.82-90.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vestergaard B. F., Norrild B. Crossed immunoelectrophoresis of a herpes simplex virus type 1-specific antigen: immunological and biochemical characterization. J Infect Dis. 1978 Nov;138(5):639–643. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.5.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


