Abstract
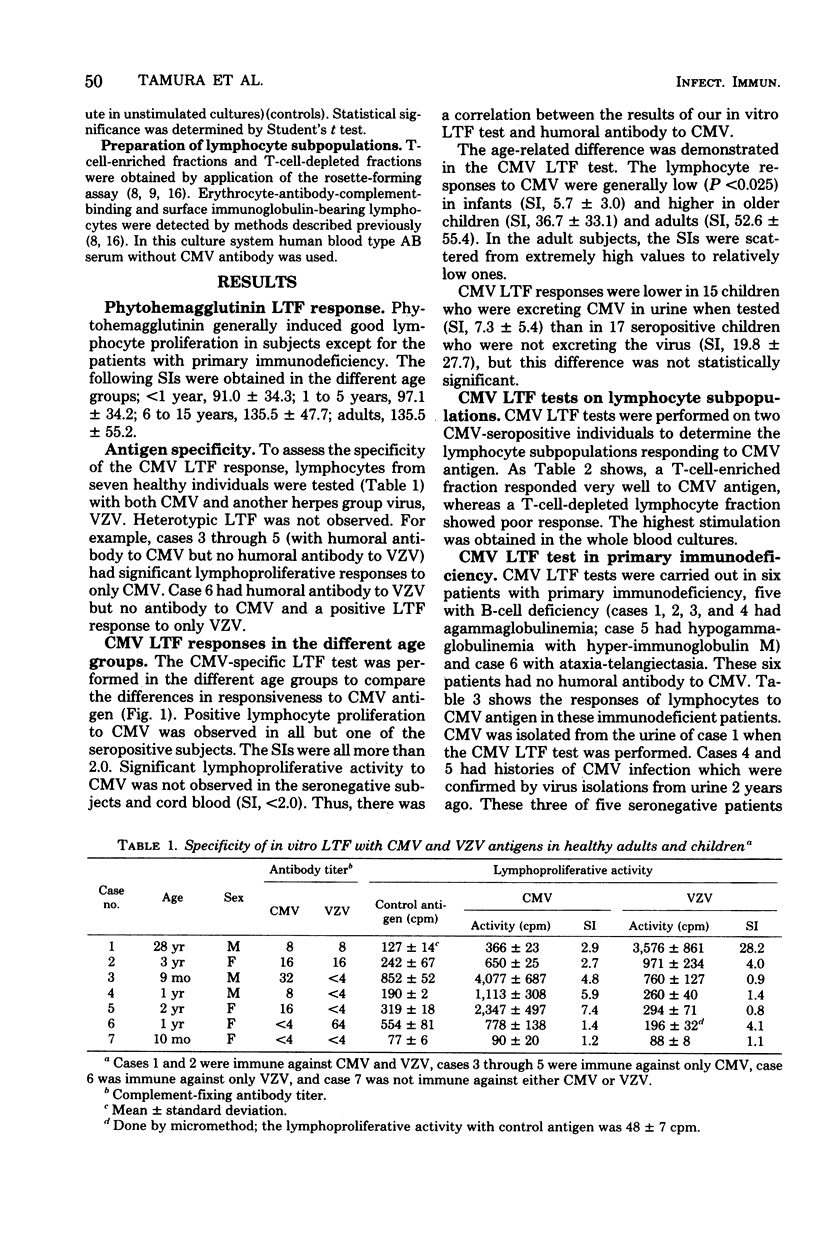
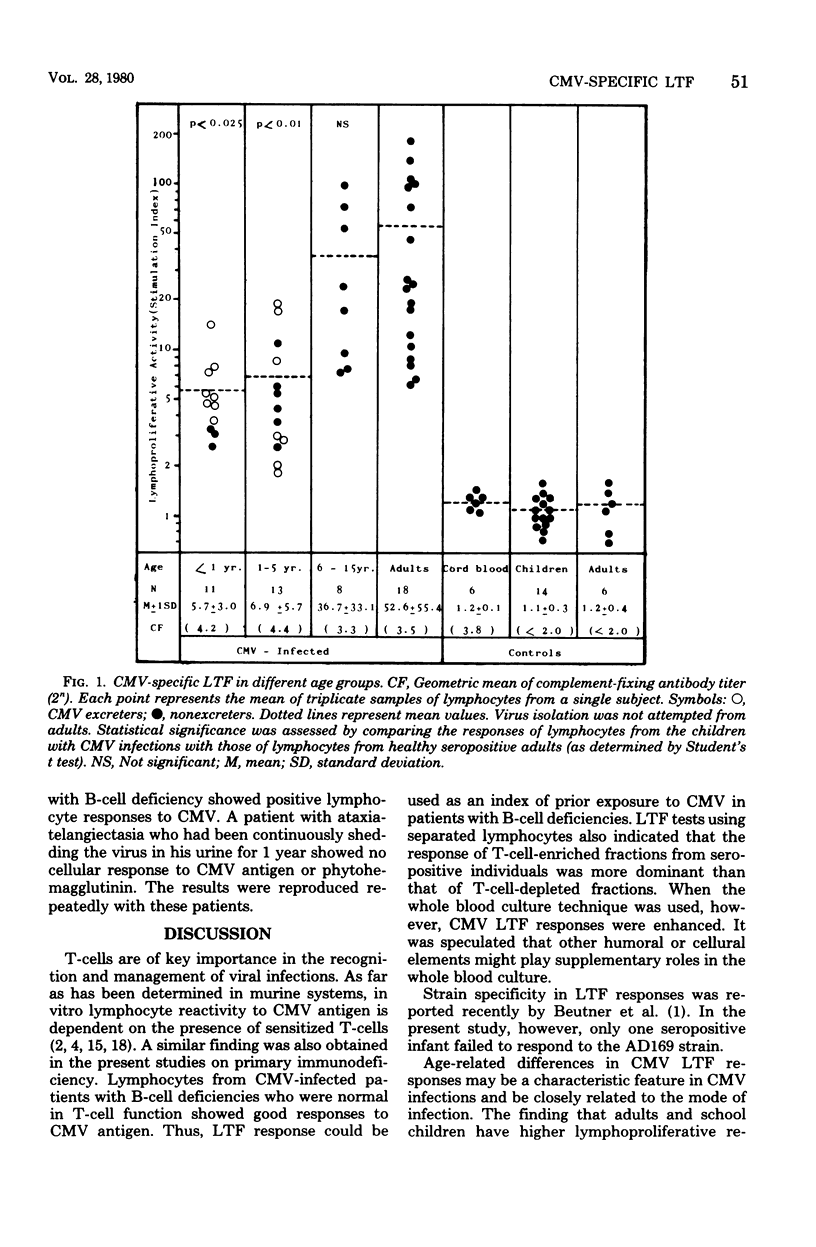
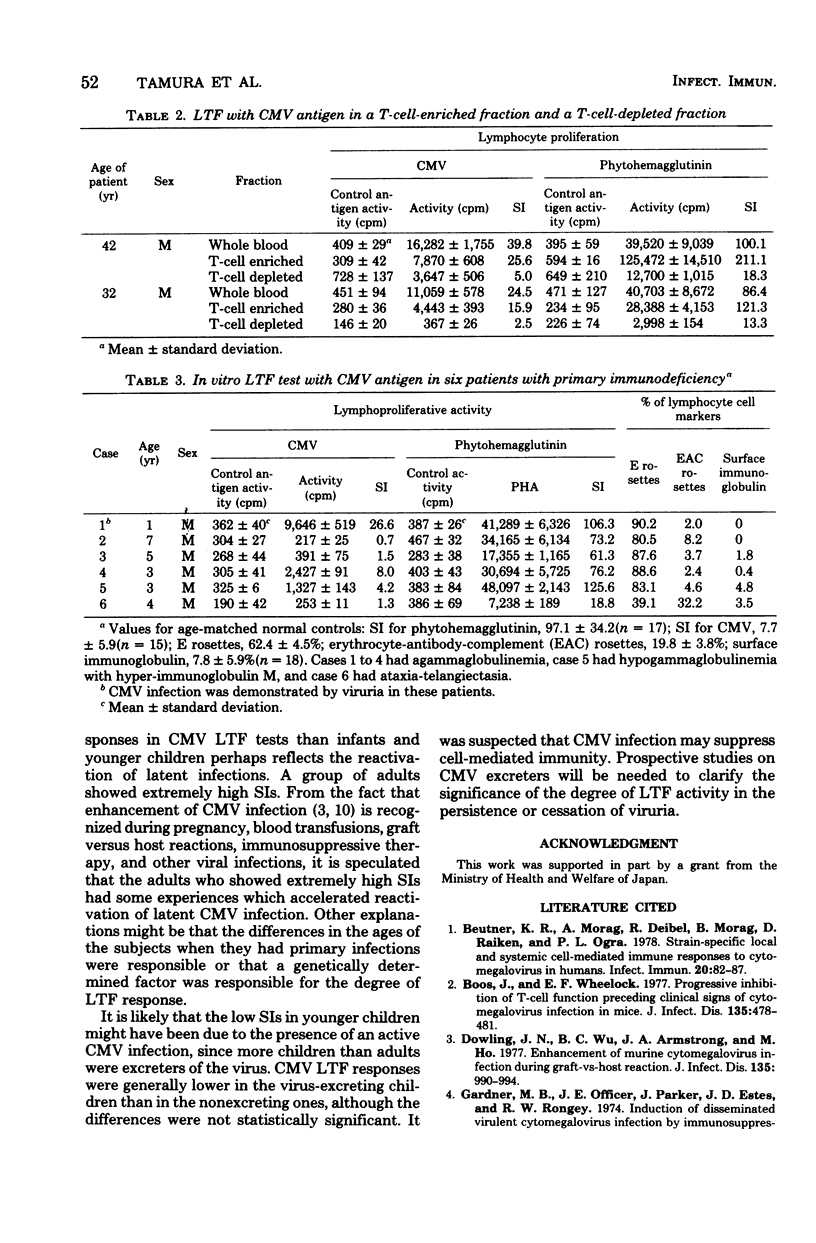
The role of specific cell-mediated immune responses in human cytomegalovirus (CMV) infections was studied by an in vitro lymphocyte transformation test, using a whole blood culture. CMV-induced in vitro lymphocyte proliferation was mainly dependent on the presence of sensitized T-cells. Three of five seronegative patients with B-cell deficiency showed positive lymphocyte responses to CMV antigen. In contrast, a patient with ataxia-telangiectasia who was shedding the virus in urine did not show a cellular response to either CMV or phytohemagglutinin. Age-related differences were found in the CMV lymphocyte transformation test. The responses were generally low (P less than 0.025) in infants and higher in older children and adults. CMV lymphocyte transformation responses were lower in 15 children who were excreting CMV in urine when tested than in 17 seropositive children who were not excreting the virus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutner K. R., Morag A., Deibel R., Morag B., Raiken D., Ogra P. L. Strain-specific local and systemic cell-mediated immune responses to cytomegalovirus in humans. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):82–87. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.82-87.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booss J., Wheelock E. F. Progressive inhibition of T-cell function preceding clinical signs of cytomegalovirus infection in mice. J Infect Dis. 1977 Mar;135(3):478–481. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.3.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling J. N., Wu B. C., Armstrong J. A., Ho M. Enhancement of murine cytomegalovirus infection during graft-vs.-host reaction. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jun;135(6):990–994. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.6.990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. B., Officer J. E., Parker J., Estes J. D., Rongey R. W. Induction of disseminated virulent cytomegalovirus infection by immunosuppression of naturally chronically infected wild mice. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):966–969. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.966-969.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehrz R. C., Marker S. C., Knorr S. O., Kalis J. M., Balfour H. H., Jr Specific cell-mediated immune defect in active cytomegalovirus infection of young children and their mothers. Lancet. 1977 Oct 22;2(8043):844–847. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90782-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLAUER C., KRONAUER G. EXTRACTION OF CELL-ASSOCIATED VIRUS WITHOUT DAMAGE OF THE CULTURE. (BRIEF REPORT). Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1965;15:433–440. doi: 10.1007/BF01241771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han T., Pauly J. Simplified whole blood method for evaluating in vitro lymphocyte reactivity of laboratory animals. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 May;11(1):137–142. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Holm G., Wigzell H. Surface markers on human T and B lymphocytes. I. A large population of lymphocytes forming nonimmune rosettes with sheep red blood cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):207–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiszkiss D. F., Sung Choi Y., Good R. A. Some characteristics of human rosette-forming cells. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1975;11(1):12–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovic R., Werch J., South M. A., Benyesh-Melnick M. Incidence of cytomegaloviremia in blood-bank donors and in infants with congenital cytomegalic inclusion disease. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):45–50. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.45-50.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moller-Larsen A., Andersen H. K., Heron I., Sarov I. In vitro stimulation of human lymphocytes by purified cytomegalovirus. Intervirology. 1975;6(4-5):249–257. doi: 10.1159/000149479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olding L. B., Jensen F. C., Oldstone M. B. Pathogenesis of of cytomegalovirus infection. I. Activation of virus from bone marrow-derived lymphocytes by in vitro allogenic reaction. J Exp Med. 1975 Mar 1;141(3):561–572. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauly J. L., Sokal J. E., Han T. Whole-blood culture technique for functional studies of lymphocyte reactivity to mitogens, antigens, and homologous lymphocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Sep;82(3):500–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rytel M. W., Aaberg T. M., Dee T. H., Heim L. H. Therapy of cytomegalovirus retinitis with transfer factor. Cell Immunol. 1975 Sep;19(1):8–21. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90287-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki M., Sekizawa T., Takahashi H., Abo T., Kumagai K. Heterogeneity of human T lymphocytes to bind sheep erythrocytes and mitogenic responses of their subpopulations. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1509–1514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkurt E. E. Induction of immune interferon by murine cytomegalovirus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Sep;155(4):611–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ten Napel C. H., The T. H., Bijker J., De Gast G. C., Langenhuysen M. M. Cytomegalovirus-directed lymphocyte reactivity in healthy adults tested by a CMV-induced lymphocyte transformation test. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Jul;29(1):52–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thong Y. H., Hensen S. A., Vincent M. M., Fuccillo D. A., Stiles W. A., Bellanti J. A. Use of cryopreserved virus-infected target cells in a lymphocytotoxicity 51Cr release microassay for cell-mediated immunity to cytomegalovirus. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):643–645. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.643-645.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



