Abstract
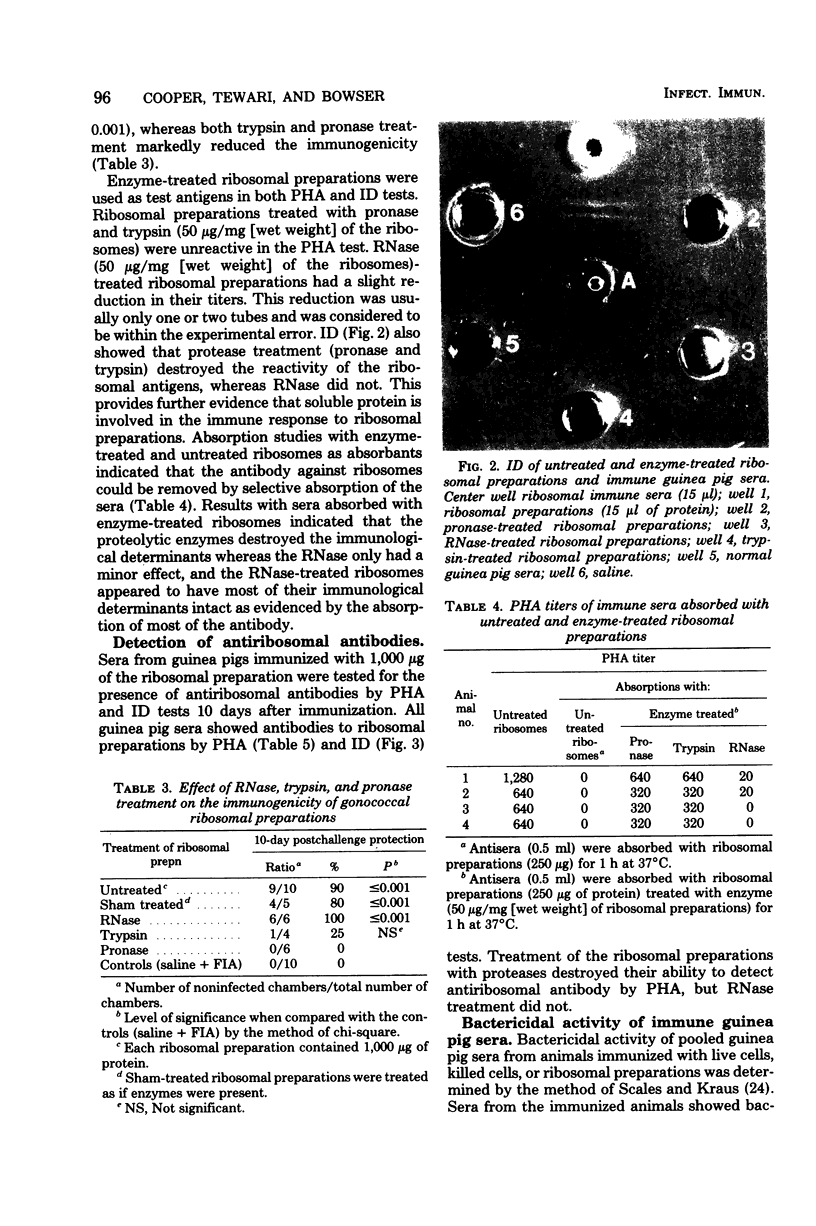
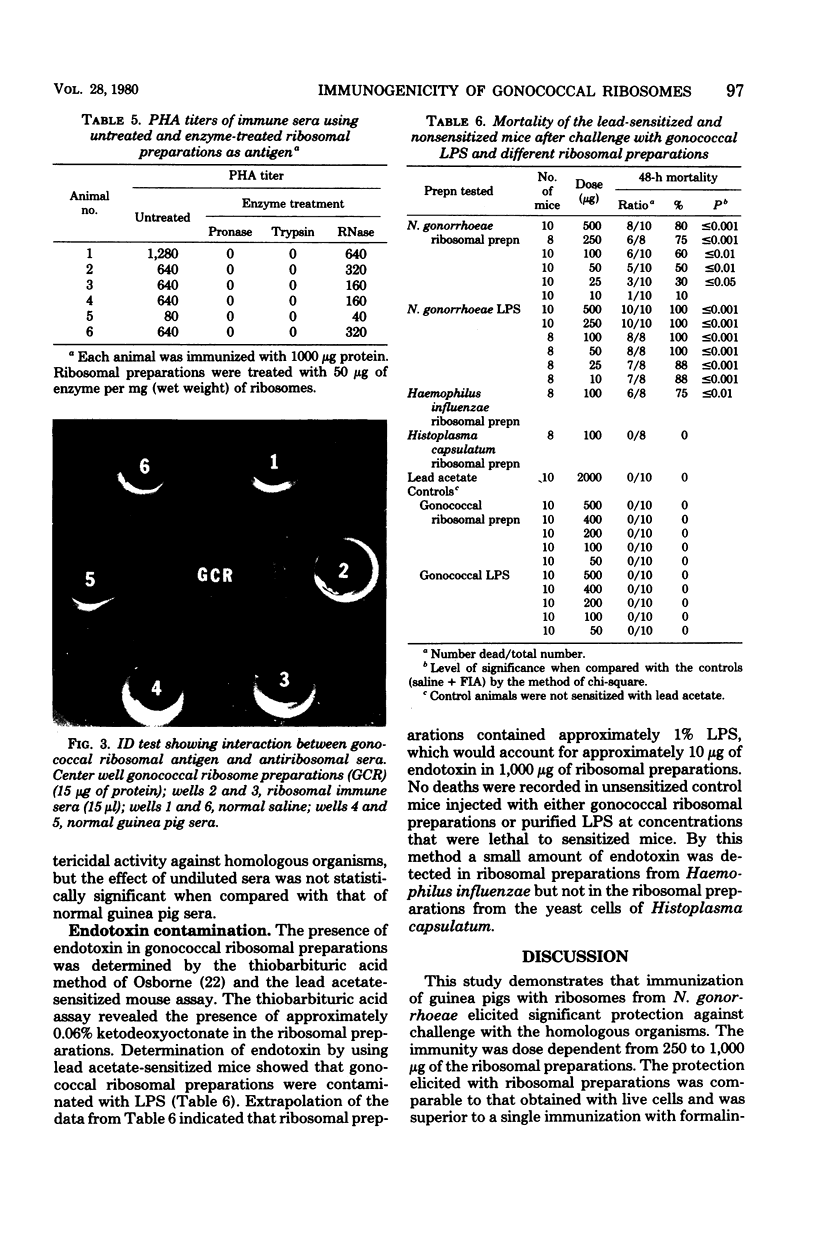
Protection against gonococcal infection was obtained by immunization with ribosomal preparations from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Ribosomes were isolated from disrupted cells by differential ultracentrifugation and treatment of the microsomal fraction with 0.25% sodium dodecyl sulfate. The isolated ribosomal preparations contained 55% ribonucleic acid, 39% protein, and 0.35% carbohydrate. The ribosomal preparations contained small amounts of endotoxin as determined by thiobarbituric acid- and lead acetate-sensitized mice assays. Guinea pigs immunized subcutaneously with ribosomal preparations were challenged intrachamberially with 10(7) colony-forming units of N. gonorrhoeae, and protection was assessed by clearance of the organism from subcutaneous chambers. The ribosomal preparations elicited significant protection, which was enhanced by incoporation of the immunogen into adjuvant. This protection was comparable to that obtained with whole cells. Treatment with proteolytic enzymes destroyed the protective effect of the ribosomal preparations, but ribonuclease had no measurable effect. Passive hemagglutination and immunodiffusion tests with sera from immunized animals demonstrated the presence of antibody to the ribosomal antigens. Results of adsorption of antiribosomal sera with enzyme-treated ribosomal preparations also indicated the protein nature of the immunogen. These results indicate that protein associated with the gonococcal ribosomal preparation is the major protective immunogen. The role of endotoxin contamination in the immunogenicity of gonococcal ribosomal preparations warrants further investigation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andron LA I. I., Eigelsbach H. T. Biochemical and immunological properties of ribonucleic acid-rich extracts from Francisella tularensis. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):137–142. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.137-142.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angerman C. R., Eisenstein T. K. Comparative efficacy and toxicity of a ribosomal vaccine, acetone-killed cells, lipopolysaccharide, and a live cell vaccine prepared from Salmonella typhhimurium. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):575–582. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.575-582.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arko R. J. An immunologic model in laboratory animals for the study of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Infect Dis. 1974 Apr;129(4):451–455. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.4.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arko R. J., Duncan W. P., Brown W. J., Peacock W. L., Tomizawa T. Immunity in infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae: duration and serological response in the chimpanzee. J Infect Dis. 1976 Apr;133(4):441–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arko R. J. Neisseria gonorrhoeae: experimental infection of laboratory animals. Science. 1972 Sep 29;177(4055):1200–1201. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4055.1200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M., Arko R. J. Immunity to gonococcal infection induced by vaccination with isolated outer membranes of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in guinea pigs. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jun;135(6):879–887. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.6.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Mechanisms in antimicrobial immunity. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1971 Jul;10(1):58–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein T. K., Angerman C. R. Immunity to experimental Salmonella infection: studies on the protective capacity and immunogenicity of lipopolysaccharide, acetone-killed cells, and ribosome-rich extracts of Salmonella typhimurium in C3H/HeJ and CD-1 mice. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1010–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein T. K. Evidence for O antigens as the antigenic determinants in "ribosomal" vaccines prepared from Salmonella. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):364–377. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.364-377.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feit C., Tewari R. P. Immunogenicity of Ribosomal Preparations from Yeast Cells of Histoplasma capsulatum. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1091–1097. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1091-1097.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoops P., Prather N. E., Berry J., Ravel J. M. Evidence for an extrinsic immunogen in effective ribosomal vaccines from Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1184–1192. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1184-1192.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R., Gregory B., Naylor J., Actor P. Isolation of protective somatic antigen from Vibrio cholerae (Ogawa) ribosomal preparations. Infect Immun. 1972 Aug;6(2):156–161. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.2.156-161.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. Ribosomal vaccines. I. Immunogenicity of ribosomal fractions isolated from Salmonella typhimurium and Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1972 Jun;5(6):947–952. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.6.947-952.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman M. M. Pseudomonas ribosomal vaccines: preparation, properties, and immunogenicity. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):76–86. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.76-86.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn M., Tewari R. P., Solotorovsky M. Immunoprotective activity of ribosomes from Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):453–460. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.453-460.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
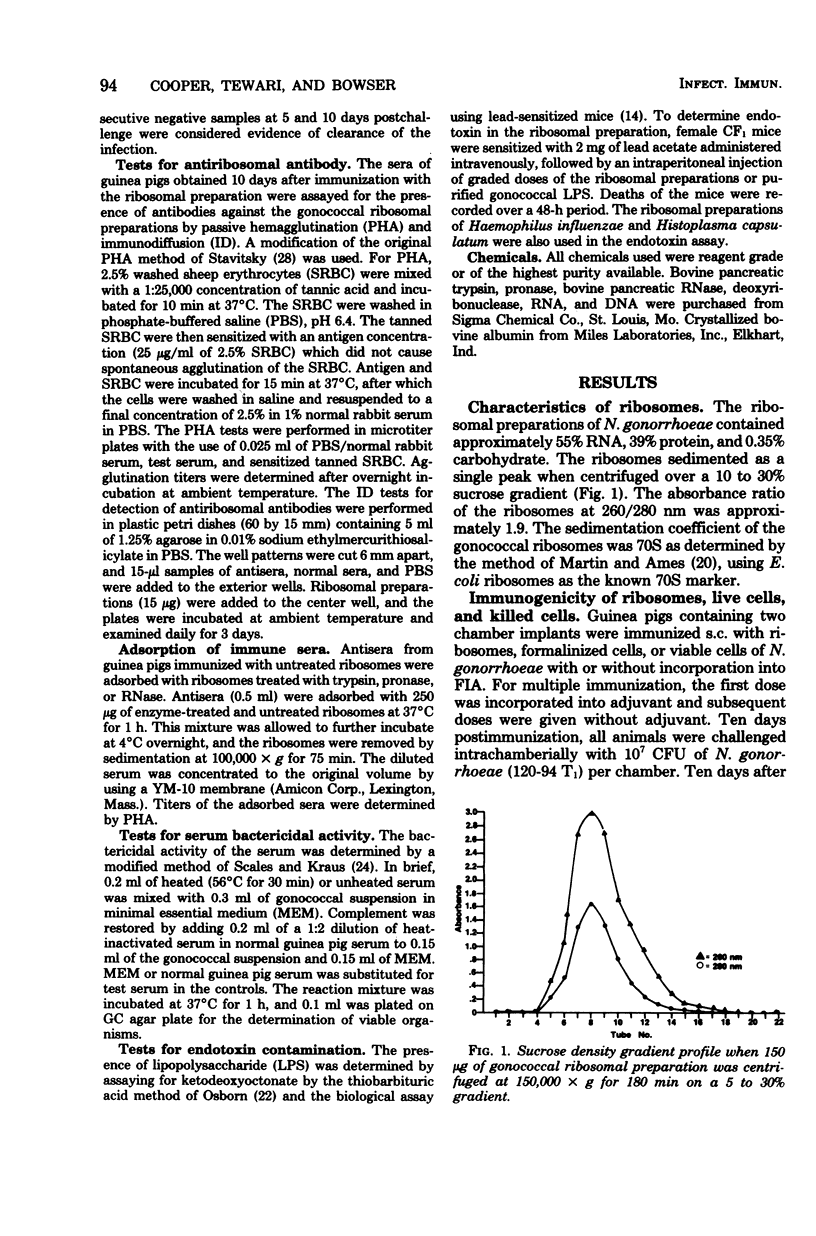
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M. B., Daoust V. The lipopolysaccharides of Neisseria gonorrhoeae colony types 1 and 4. Can J Biochem. 1975 May;53(5):623–629. doi: 10.1139/o75-084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAVITSKY A. B. Micromethods for the study of proteins and antibodies. I. Procedure and general applications of hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition reactions with tannic acid and protein-treated red blood cells. J Immunol. 1954 May;72(5):360–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scales R. W., Kraus S. J. Development and passive transfer of immunity to gonococcal infection in Guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1040–1043. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1040-1043.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalla W. O., Johnson W. Immunogenicity of ribosomal vaccines isolated from group A, type 14 Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1195–1202. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1195-1202.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stead A., Main J. S., Ward M. E., Watt P. J. Studies on lipopolysaccharides isolated from strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):123–131. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swendsen C. L., Johnson W. Humoral immunity to Streptococcus pneumoniae induced by a pneumococcal ribosomal protein fraction. Infect Immun. 1976 Aug;14(2):345–354. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.2.345-354.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUBER H., GARSON W. Isolation of lipopolysaccharide endotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1391–1393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari R. P., Lynn M., Birnbaum A. J., Solotorovsky M. Characterization of the immunoprotective antigen of ribosomal preparations from Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):58–65. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.58-65.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. W., Weiss E. Response of mice to injection of ribosomal fraction from group B Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):355–363. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.355-363.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson H. C., Snyder I. S. Protection against pneumococcal infection by a ribosomal preparation. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):16–23. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.16-23.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner W. H., Novotny P. The inability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae pili antibodies to confer immunity in subcutaneous guinea-pig chambers. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Jan;92(1):224–228. doi: 10.1099/00221287-92-1-224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veale D. R., Smith H., Witt K. A., Marshall R. B. Differential ability of colonial types of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to produce infection cutaneous perforated plastic chambers in guinea-pigs and rabbits. J Med Microbiol. 1975 May;8(2):325–335. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-2-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R., Bigley N. J., Berry L. J. Immunogenicity of Ribonucleic Acid Preparations Obtained from Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1970 Jun;1(6):574–582. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.6.574-582.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R., Bigley N. J. Isolation and partial characterization of an immunogenic moiety obtained from Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):140–148. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.140-148.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston S. H., Berry L. J. Antibacterial immunity induced by ribosomal vaccines. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1970 Jul;8(1):13–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston S., Berry L. J. Immunity induced by ribosomal extracts from Staphylococcus aureus. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1970 Jul;8(1):66–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman G. M., Caird J. D. Composition of the lipopolysaccharide of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):550–556. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.550-556.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUMANS A. S., YOUMANS G. P. IMMUNOGENIC ACTIVITY OF A RIBOSOMAL FRACTION OBTAINED FROM MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1291–1298. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1291-1298.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Factors affecting immunogenic activity of mycobacterial ribosomal and ribonucleic acid preparations. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):42–50. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.42-50.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Immunogenic mycobacterial ribosomal and ribonucleic Acid preparations: chemical and physical characteristics. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):659–668. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.659-668.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Preparation and effect of different adjuvants on the immunogenic activity of mycobacterial ribosomal fraction. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):836–843. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.836-843.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]