Abstract
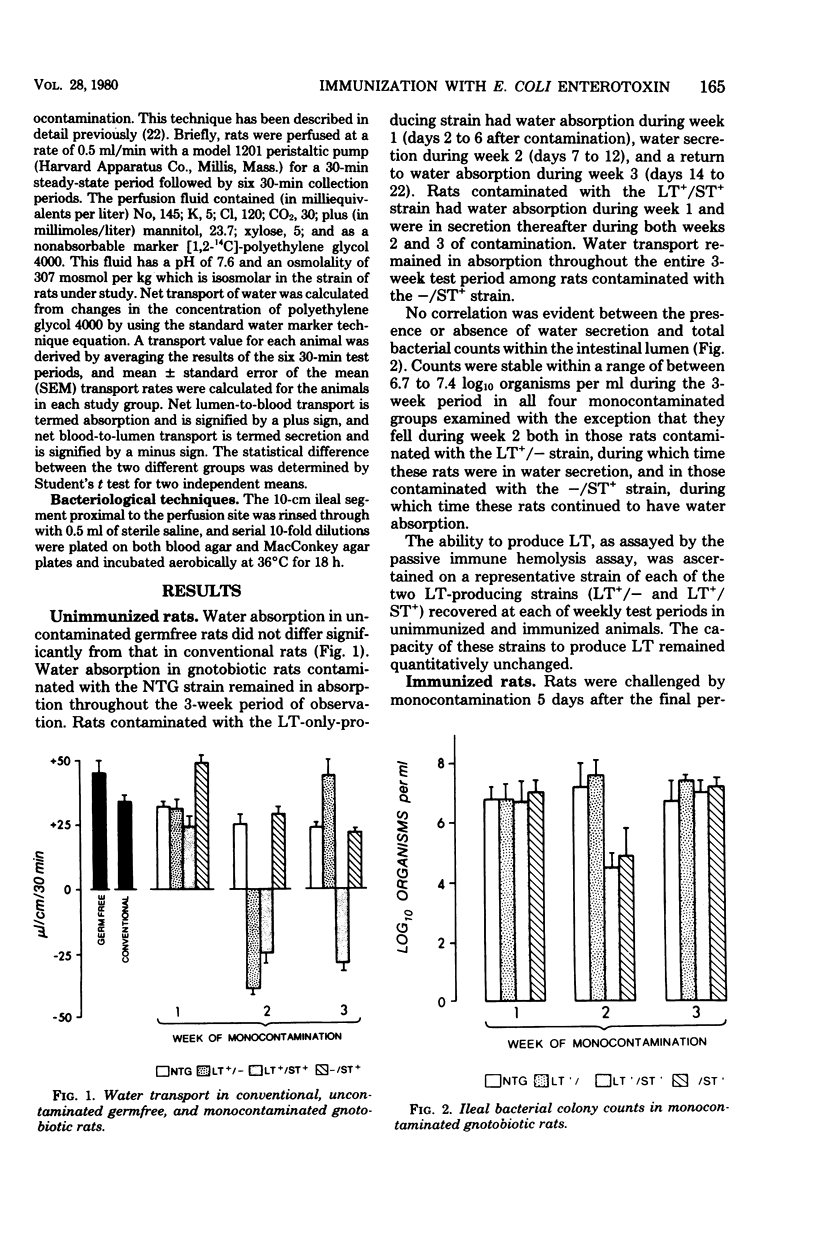
The protective effect of active immunization with a purified preparation of the polymyxin-release form of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin (LT), administered using a parenteral prime and peroral boosts given after ablation of gastric secretion by means of cimetidine, was assessed in gnotobiotic rats which were challenged by monocontamination with enterotoxigenic strains of E. coli. Water transport was evaluated by the in vivo marker perfusion technique at weekly intervals over a 3-week period after contamination. Water transport in unimmunized control rats was consistently in absorption in those contaminated by a nontoxigenic strain, in secretion during only week 2 in those contaminated by an LT+/− strain, in secretion during weeks 2 and 3 in those contaminated by an LT+/ST+ (heat-stable enterotoxin) strain, and consistently in absorption in those contaminated by an −/ST+ strain. Rats immunized with a booster dosage of 250 μg had a significant increase (P < 0.001) in net water absorption as compared to unimmunized rats, with values in the borderline range of absorption, when challenged with either the LT+/− or LT+/ST+ strains. Rats immunized with a 10-fold-higher boosting dosage had a significant increase (P < 0.001) in net water absorption as compared to those boosted at the lower dosage; water absorption was within the normal range. There was no difference between the ileal bacterial counts of unimmunized and immunized rats challenged by the various strains. These observations indicate that this immunization program provides complete protection in an animal model against challenge by intestinal contamination with enterotoxigenic strains of E. coli which produce LT, either alone or in combination with ST.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderete J. F., Robertson D. C. Purification and chemical characterization of the heat-stable enterotoxin produced by porcine strains of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1021–1030. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1021-1030.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimblecombe R. W., Duncan W. A., Durant G. J., Emmett J. C., Ganellin C. R., Leslie G. B., Parsons M. E. Characterization and development of cimetidine as a histamine H2-receptor antagonist. Gastroenterology. 1978 Feb;74(2 Pt 2):339–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Demonstration of shared and unique immunological determinants in enterotoxins from Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):709–713. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.709-713.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Immunological cross-reactivity between a heat-labile enterotoxin(s) of Escherichia coli and subunits of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):1036–1039. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.1036-1039.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Isolation and characterization of homogeneous heat-labile enterotoxins with high specific activity from Escherichia coli cultures. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):760–769. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.760-769.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr New surface-associated heat-labile colonization factor antigen (CFA/II) produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of serogroups O6 and O8. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):638–647. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.638-647.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Tjoa W. S., DuPont H. L. Detection and characterization of colonization factor of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from adults with diarrhea. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):727–736. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.727-736.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Satterwhite T. K., Evans D. J., Jr, DuPont H. L. Differences in serological responses and excretion patterns of volunteers challenged with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli with and without the colonization factor antigen. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):883–888. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.883-888.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Evans D. G., Gorbach S. L. Polymyxin B-Induced Release of Low-Molecular-Weight, Heat-Labile Enterotoxin from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1010–1017. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1010-1017.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G. Direct serological assay for the heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli, using passive immune hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):604–609. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.604-609.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Ruiz-Palacios G., Evans D. E., DuPont H. L., Pickering L. K., Olarte J. Humoral immune response to the heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli in naturally acquired diarrhea and antitoxin determination by passive immune hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):781–788. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.781-788.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Drake K. W. Effect of purified Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin on intestinal cyclic nucleotide metabolism and fluid secretion. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):19–23. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.19-23.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon H. A., Pesti L. The gnotobiotic animal as a tool in the study of host microbial relationships. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Dec;35(4):390–429. doi: 10.1128/br.35.4.390-429.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Söderlind O., Wadström T. Cross-reactivity between heat labile enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli in neutralization tests in rabbit ileum and skin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Dec;81(6):757–762. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer H. C., Atlas R., Moldan D., Kantor H. S. Inhibition of guanylate cyclase and cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase by cholera toxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 6;66(3):1017–1023. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90741-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Immunological interrelationships between cholera toxin and the heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins of coliform bacteria. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):110–117. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.110-117.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Immunological relationship of different preparations of coliform enterotoxins. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):771–778. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.771-778.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Influence of route of administration on immediate and extended protection in rats immunized with Escherichia coli heart-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):81–86. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.81-86.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Protective effect of active immunization with purified Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin in rats. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):592–599. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.592-599.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Goetsch C. A., Engert R. F., Short H. B., Schenk E. A. Effect of monocontamination of germfree rats by enterotoxigenic coliform bacteria. Gastroenterology. 1979 Feb;76(2):341–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler E. M., Cross R. F. Feeding bacteria-free whole cell lysates of Escherichia coli to gnotobiotic pigs and the effects of giving antiserums. Am J Vet Res. 1971 May;32(5):739–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler E. M. Neonatal enteric colibacillosis of pigs and current research on immunization. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Sep 1;173(5 Pt 2):588–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange S., Hansson H. A., Molin S. O., Nygren H. Local cholera immunity in mice: intestinal antitoxin-containing cells and their correlation with protective immunity. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):743–750. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.743-750.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange S., Holmgren J. Protective antitoxic cholera immunity in mice: influence of route and number of immunizations and mode of action of protective antibodies. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1978 Aug;86C(4):145–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1978.tb02572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Caplan E. S., Waterman D., Cash R. A., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J. Diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli that produce only heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):78–82. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.78-82.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
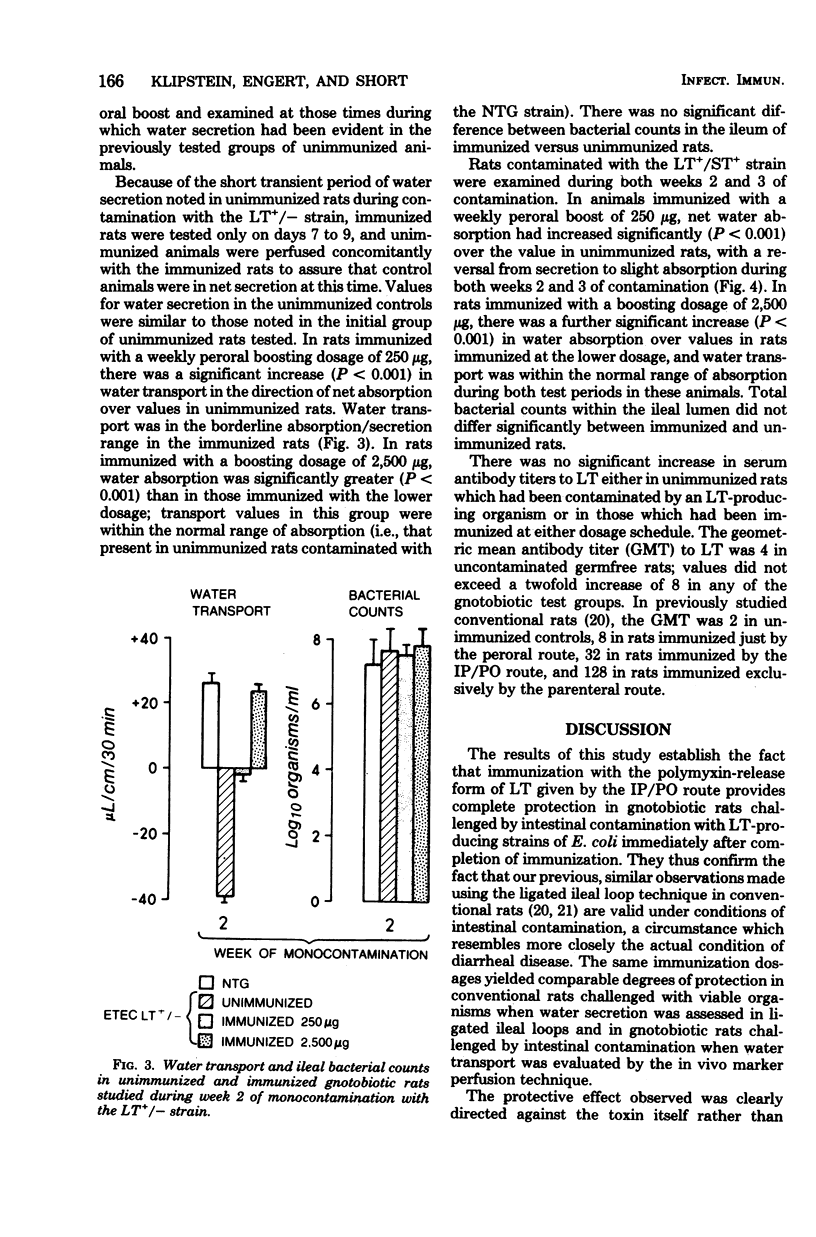
- Levine M. M., Nalin D. R., Hoover D. L., Bergquist E. J., Hornick R. B., Young C. R. Immunity to enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):729–736. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.729-736.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Rennels M. B. E. coli colonisation factor antigen in diarrhoea. Lancet. 1978 Sep 2;2(8088):534–534. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92268-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miniats O. P., Gyles C. L. The significance of proliferation and enterotoxin production by Escherichia coli in the intestine of gnotobiotic pigs. Can J Comp Med. 1972 Apr;36(2):150–159. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Sorensen D. K., Sautter J. H. Experimental enteric colibacillosis in piglets. Can J Comp Med. 1968 Jul;32(3):493–497. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan R. L., Isaacson R. E., Moon H. W., Brinton C. C., To C. C. Immunization of suckling pigs against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-induced diarrheal disease by vaccinating dams with purified 987 or K99 pili: protection correlates with pilus homology of vaccine and challenge. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):771–777. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.771-777.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy B., Moon H. W., Isaacson R. E., To C. C., Brinton C. C. Immunization of suckling pigs against enteric enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infection by vaccinating dams with purified pili. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):269–274. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.269-274.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Cray W. C., Jr, Sircar B. K. Induction of a mucosal antitoxin response and its role in immunity to experimental canine cholera. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):185–193. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.185-193.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
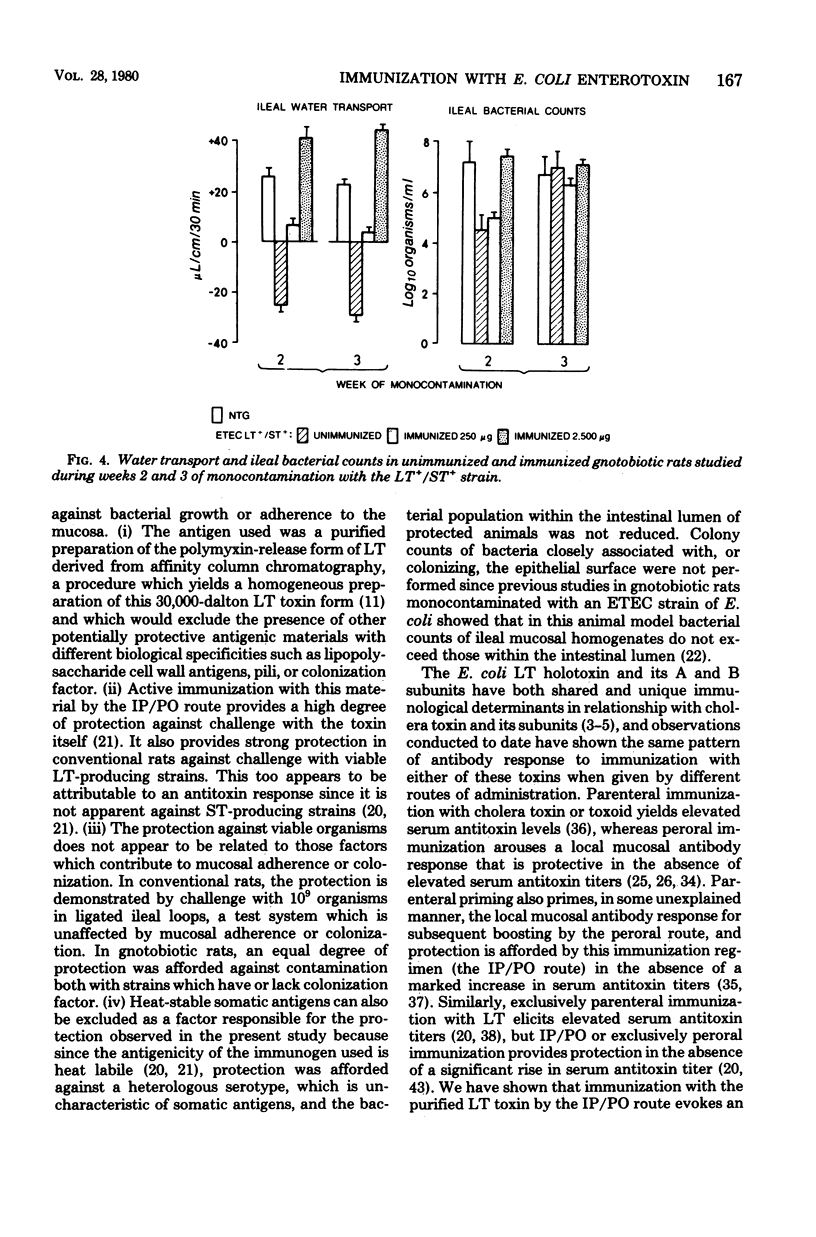
- Pierce N. F., Kaniecki E. A., Northrup R. S. Protection against experimental cholera by antitoxin. J Infect Dis. 1972 Dec;126(6):606–616. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.6.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Sack R. B., Sircar B. K. Immunity to experimental cholera. III. Enhanced duration of protection after sequential parenteral-oral administration of toxoid to dogs. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jun;135(6):888–896. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.6.888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F. The role of antigen form and function in the primary and secondary intestinal immune responses to cholera toxin and toxoid in rats. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):195–206. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Carpenter C. C. Experimental canine cholera. I. Development of the model. J Infect Dis. 1969 Feb;119(2):138–149. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.2.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Froehlich J. L. Antigenic similarity of heat-labile enterotoxins from diverse strains of Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jun;5(6):570–572. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.6.570-572.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Froehlich J. L., Zulich A. W., Hidi D. S., Kapikian A. Z., Orskov F., Orskov I., Greenberg H. B. Prophylactic doxycycline for travelers' diarrhea: results of a prospective double-blind study of Peace Corps volunteers in Morocco. Gastroenterology. 1979 Jun;76(6):1368–1373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Immunization with Escherichia coli enterotoxin protects against homologous enterotoxin challenge. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):641–644. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.641-644.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Johnson J., Pierce N. F., Keren D. F., Yardley J. H. Challenge of dogs with live enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and effects of repeated challenges on fluid secretion in jejunal Thiry-Vella loops. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jul;134(1):15–24. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W. The production of diarrhoea in baby rabbits by the oral administration of cell-free preparations of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae: the effect of antisera. J Med Microbiol. 1972 Aug;5(3):299–303. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-3-299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREXLER P. C., REYNOLDS L. I. Flexible film apparatus for the rearing and use of germfree animals. Appl Microbiol. 1957 Nov;5(6):406–412. doi: 10.1128/am.5.6.406-412.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipp S. C., Moon H. W., Lyon N. C. Heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin production in vivo. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):240–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.240-244.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


