Abstract
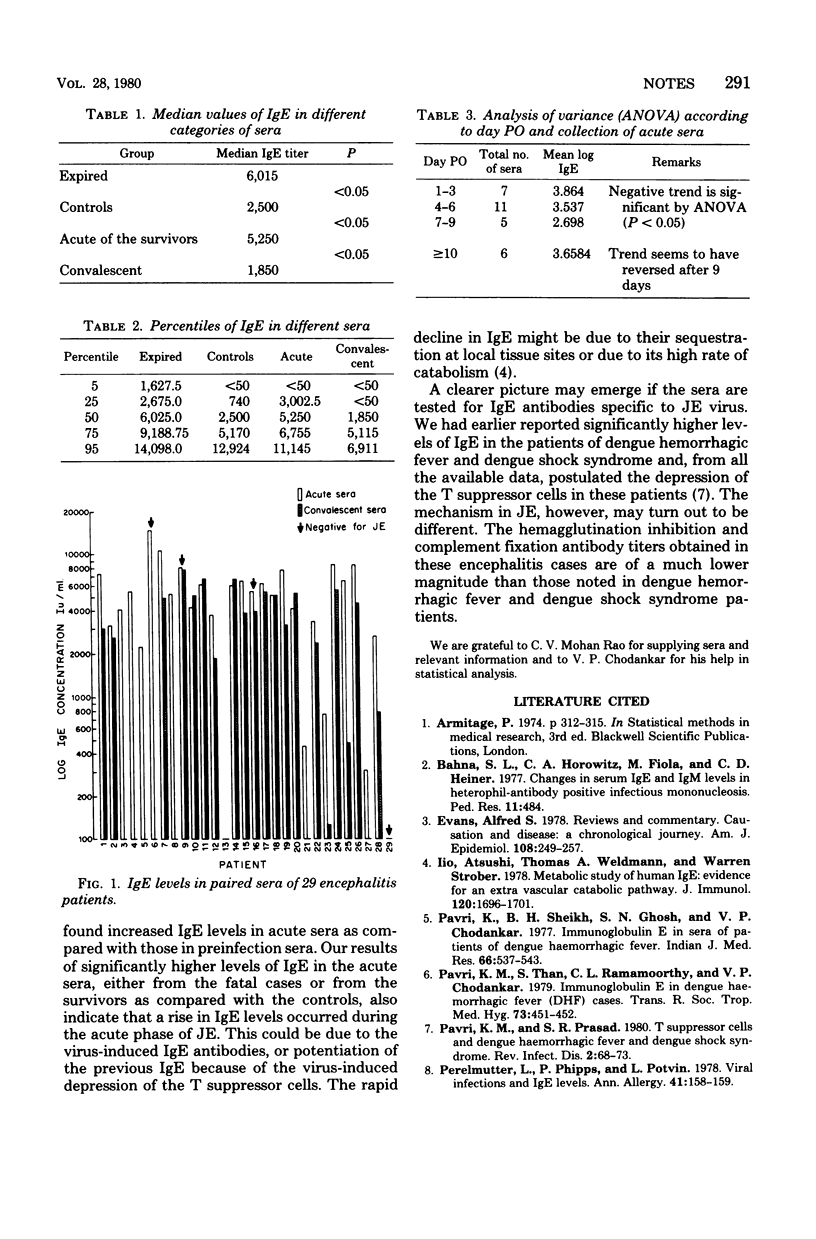
Significantly high levels of immunoglobulin E in the acute sera of encephalitis cases (suspected or confirmed as Japanese encephalitis) declined sharply during early convalescence.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Evans A. S. Causation and disease: a chronological journey. The Thomas Parran Lecture. Am J Epidemiol. 1978 Oct;108(4):249–258. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iio A., Waldmann T. A., Strober W. Metabolic study of human IgE: evidence for an extravascular catabolic pathway. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1696–1701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavri K. M., Sheikh B. H., Ghosh S. N., Chodankar V. P. Immunoglobulin E in sera of patients of dengue haemorrhagic fever. Indian J Med Res. 1977 Oct;66(4):537–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavri K., Swe T., Ramamoorthy C. L., Chodankar V. P. Immunoglobulin E in dengue haemorrhagic fever (DHF) cases. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1979;73(4):451–452. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(79)90174-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perelmutter L., Phipps P., Potvin L. Viral infections and IgE levels. Ann Allergy. 1978 Sep;41(3):158–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


