Abstract
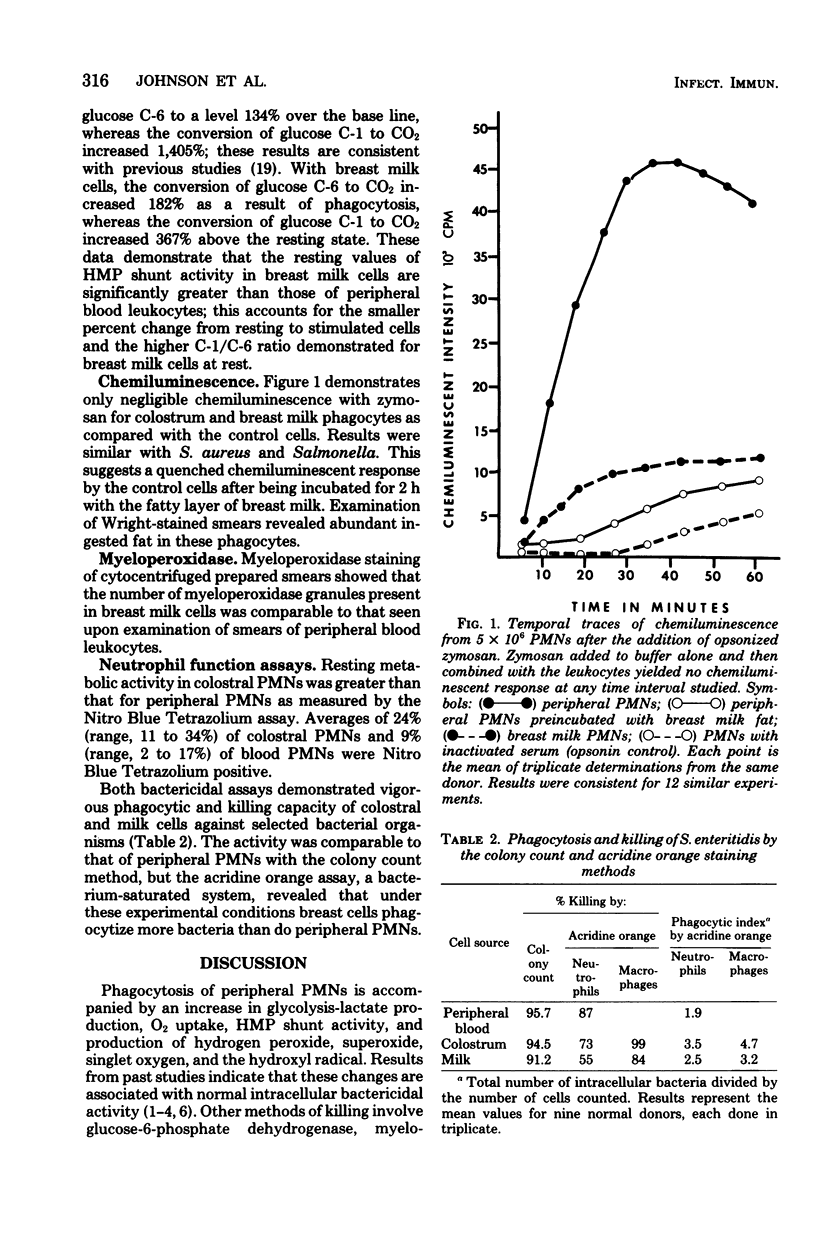
The functional capacity of human breast milk phagocytes was evaluated with both bactericidal and biochemical assays. Acridine orange was used as a vital stain for bacteria to directly visualize phagocytosis and killing. Bactericidal capabilities were further examined by colony count and chemiluminescent methods. Cytocentrifuged specimens stained for myeloperoxidase exhibited enzyme activity in breast milk leukocytes equal to that of peripheral neutrophils. A radioisotopic assay of hexose monophosphate shunt activity demonstrated metabolic activity in breast milk leukocytes greater than that in peripheral blood neutrophils. However, the chemiluminescent response of breast cells was negligible, apparently the result of quenching secondary to fat present in the milk; preincubation of human blood leukocytes with the fatty layer of breast milk produced similar inhibition in the chemiluminescence assay. By most parameters breast milk phagocytes are at least equal to blood neutrophils.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. C. Halide dependence of the myeloperoxidase-mediated antimicrobial system of the polymorphonuclear leukocyte in the phenomenon of electronic excitation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Apr 7;63(3):675–683. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80437-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. C., Stjernholm R. L., Steele R. H. Evidence for the generation of an electronic excitation state(s) in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and its participation in bactericidal activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 May 26;47(4):679–684. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90545-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. C. The role of PH in the chemiluminescent response of the myeloperoxidase-halide-HOOH antimicrobial system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Apr 7;63(3):684–691. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80438-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. C., Yevich S. J., Orth R. W., Steele R. H. The superoxide anion and singlet molecular oxygen: their role in the microbicidal activity of the polymorphonuclear leukocyte. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 8;60(3):909–917. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90401-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Nutrition Committee of the Canadian Paediatric Society and the Committee on Nutrition of the American Academy of Pediatrics. Breast-feeding. A commentary in celebration of the International Year of the Child, 1979. Pediatrics. 1978 Oct;62(4):591–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheson B. D., Christensen R. L., Sperling R., Kohler B. E., Babior B. M. The origin of the chemiluminescence of phagocytosing granulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):789–796. doi: 10.1172/JCI108530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham A. S. Morbidity in breast-fed and artificially fed infants. J Pediatr. 1977 May;90(5):726–729. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)81236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigin R. D., Shackelford P. G., Choi S. C., Flake K. K., Franklin F. A., Jr, Eisenberg C. S. Nitroblue tetrazolium dye test as an aid in the differential diagnosis of febrile disorders. J Pediatr. 1971 Feb;78(2):230–237. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- France G. L., Marmer D. J., Steele R. W. Breast-feeding and Salmonella infection. Am J Dis Child. 1980 Feb;134(2):147–152. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1980.02130140021007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho P. C., Lawton J. W. Human colostral cells: phagocytosis and killing of E. coli and C. albicans. J Pediatr. 1978 Dec;93(6):910–915. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)81210-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLOW L. S. SIMPLIFIED MYELOPEROXIDASE STAIN USING BENZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE. Blood. 1965 Aug;26:215–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ J., WOOD H. G. The use of glucose-C14 for the evaluation of the pathways of glucose metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1960 Aug;235:2165–2177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. A., Jr, Homer D. R. Relation of breast versus bottle feeding to hospitalization for gastroenteritis in a middle-class U.S. population. J Pediatr. 1978 Mar;92(3):417–418. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mata L. J., Urrutia J. J., Gordon J. E. Diarrhoeal disease in a cohort of Guatemalan village children observed from birth to age two years. Trop Geogr Med. 1967 Dec;19(4):247–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogra S. S., Ogra P. L. Immunologic aspects of human colostrum and milk. II. Characteristics of lymphocyte reactivity and distribution of E-rosette forming cells at different times after the onset of lactation. J Pediatr. 1978 Apr;92(4):550–555. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80286-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quie P. G., White J. G., Holmes B., Good R. A. In vitro bactericidal capacity of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: diminished activity in chronic granulomatous disease of childhood. J Clin Invest. 1967 Apr;46(4):668–679. doi: 10.1172/JCI105568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. E., Harvey B. A., Soothill J. F. Phagocytosis and killing of bacteria and yeast by human milk cells after opsonisation in aqueous phase of milk. Br Med J. 1978 Jun 3;1(6125):1443–1445. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6125.1443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. L., Rommel F. A rapid micro method for the simultaneous determination of phagocytic-microbiocidal activity of human peripheral blood leukocytes in vitro. J Immunol Methods. 1977;17(3-4):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90106-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


