Abstract
The virulence of Yersinia enterocolitica, biotype 2, serotype O:8, in mice is related to its ability to produce plague V and W antigens. V and W antigens in Y. enterocolitica are shown to be immunologically identical to the previously described V and W antigens of Yersinia pestis and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis.
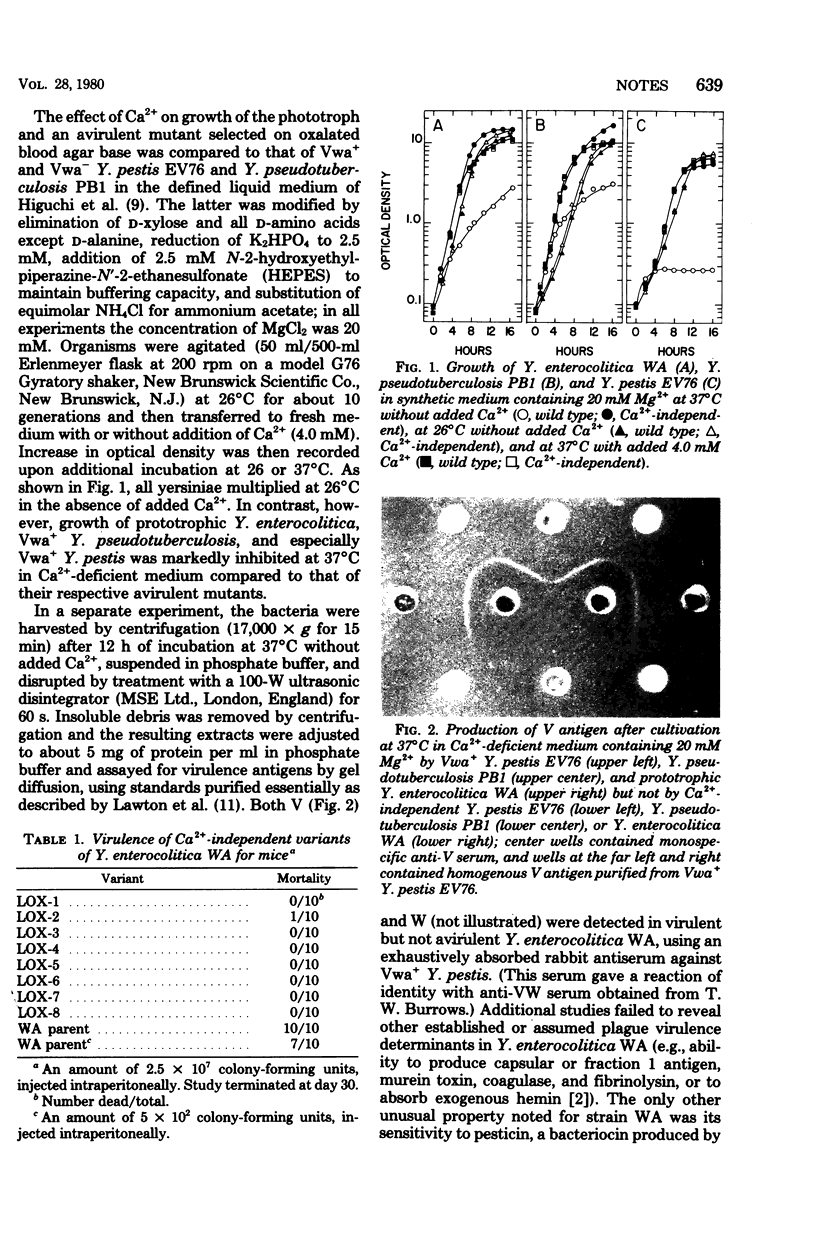
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURROWS T. W. An antigen determining virulence in Pasteurella pestis. Nature. 1956 Mar 3;177(4505):426–427. doi: 10.1038/177426b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., BACON G. A. The effects of loss of different virulence determinants on the virulence and immunogenicity of strains of Pasteurella pestis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1958 Jun;39(3):278–291. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W. VIRULENCE OF PASTEURELLA PESTIS AND IMMUNITY TO PLAGUE. Ergeb Mikrobiol Immunitatsforsch Exp Ther. 1963;37:59–113. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-36742-1_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R. The genus Yersinia: biochemistry and genetics of virulence. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1972;57:111–158. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65297-4_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. B., Collins F. M. Experimental Yersinia enterocolitica infection in mice: kinetics of growth. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):851–857. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.851-857.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. B. Pathogenecity of Yersinia enterocolitica for mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):164–170. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.164-170.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T. Plasmid associated with pathogenicity and calcium dependency of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):682–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.682-685.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGUCHI K., KUPFERBERG L. L., SMITH J. L. Studies on the nutrition and physiology of Pasteurella pestis. III. Effects of calcium ions on the growth of virulent and avirulent strains of Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1959 Mar;77(3):317–321. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.3.317-321.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp W., Lysy J., Knapp C., Stille W., Goll U. Enterale Infektionen beim Menschen durch Yersinia enterocolitica und ihre Diagnose. Infection. 1973;1(2):113–125. doi: 10.1007/BF01638486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWTON W. D., ERDMAN R. L., SURGALLA M. J. BIOSYNTHESIS AND PURIFICATION OF V AND W ANTIGEN IN PASTEURELLA PESTIS. J Immunol. 1963 Aug;91:179–184. doi: 10.21236/ad0299868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollaret H. H., Guillon J. C. Contribution à l'étude d'un nouveau groupe de germes (Yersinia enterocolitica) proches du bacille de Malassez et Vignal. II. Pouvoir pathogène expérimental. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 Oct;109(4):608–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]