Abstract
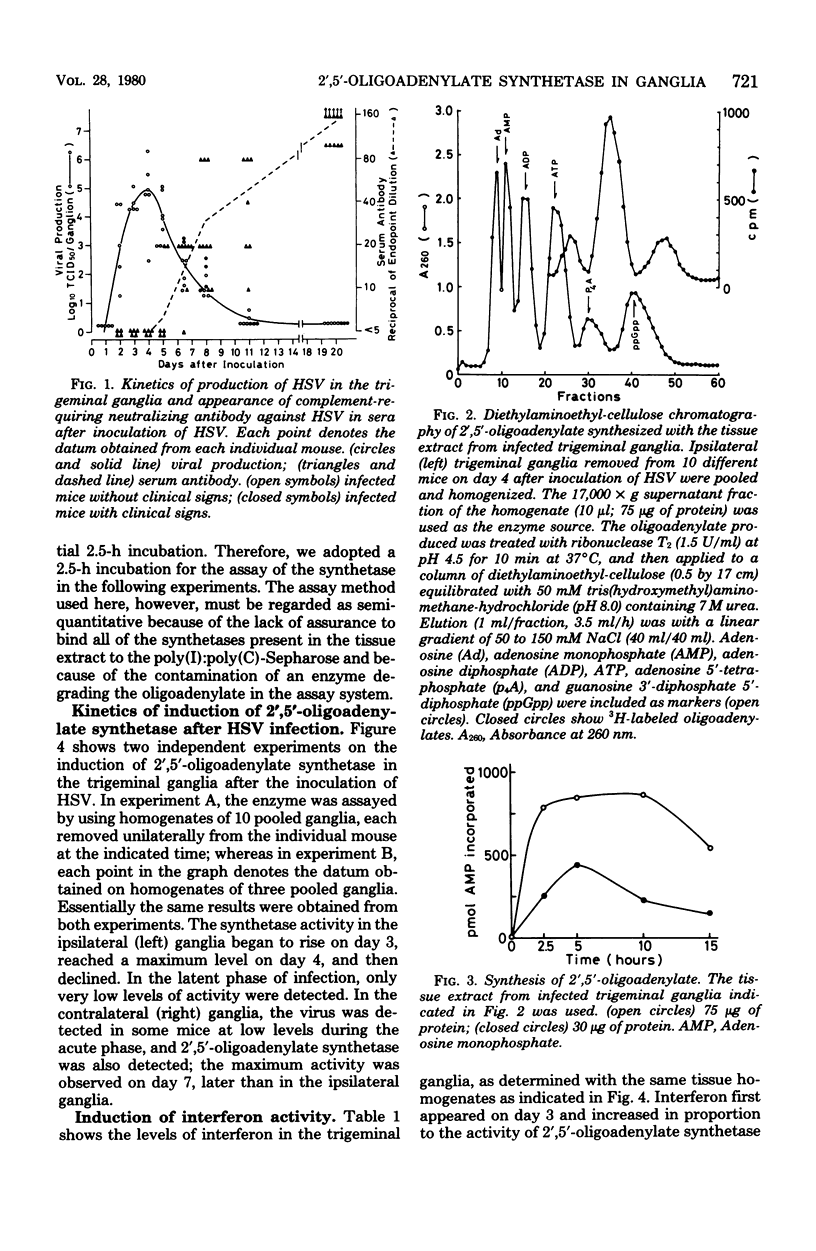
The activity of 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetase, which is induced by interferon action, was detected in mouse trigeminal ganglia infected with herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 1. When HSV was inoculated on the left cheek of mice, the virus began to appear in the ipsilateral trigeminal ganglia on day 2, reached its maximum accumulation on day 4, declined thereafter, and was no longer detected in the tissue homogenate after 11 days. After this short acute productive phase, the virus entered into the latent phase of infection. 2',5'-Oligoadenylate synthetase appeard in the trigeminal ganglia shortly after the beginning of virus multiplication; the synthetase activity began to rise on day 3, reached a maxium level on day 4, and then declined. Interferon activity (type I) also appeared in the infected ganglia, but diminished more rapidly than the synthetase. The antibody against HSV in the sera began to appear at the time when the virus and synthetase were declining. From these results it may be hypothesized, although not concluded, that in the acute productive phase of HSV infection in mouse trigeminal ganglia, virus multiplication is suppressed by interferon action, including 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetase induction.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baglioni C. Interferon-induced enzymatic activities and their role in the antriviral state. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):255–264. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90151-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. C., Graham C. F., Lehman J. M. Appearance of interferon inducibility and sensitivity during differentiation of murine teratocarcinoma cells in vitro. Cell. 1978 Feb;13(2):243–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90193-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook M. L., Stevens J. G. Pathogenesis of herpetic neuritis and ganglionitis in mice: evidence for intra-axonal transport of infection. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):272–288. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.272-288.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujibayashi T., Hooks J. J., Notkins A. L. Production of interferon by immune lymphocytes exposed to herpes simplex virus-antibody complexes. J Immunol. 1975 Nov;115(5):1191–1193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Tovey M. G., Maury C., Bandu M. T. Role of interferon in the pathogenesis of virus diseases in mice as demonstrated by the use of anti-interferon serum. II. Studies with herpes simplex, Moloney sarcoma, vesicular stomatitis, Newcastle disease, and influenza viruses. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1316–1323. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovanessian A. G., Brown R. E., Kerr I. M. Synthesis of low molecular weight inhibitor of protein synthesis with enzyme from interferon-treated cells. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):537–540. doi: 10.1038/268537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAACS A., HITCHCOCK G. Role of interferon in recovery from virus infections. Lancet. 1960 Jul 9;2(7141):69–71. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)91215-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKendall R. R., Klassen T., Baringer J. R. Host defenses in herpes simplex infections of the nervous system: effect of antibody on disease and viral spread. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):305–311. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.305-311.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakes J. E. Role for cell-mediated immunity in the resistance of mice to subcutaneous herpes simplex virus infection. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):166–172. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.166-172.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Katz B. J., Notkins A. L. Latent infection of the peripheral ANS with herpes simplex virus. Nature. 1975 Oct 23;257(5528):686–688. doi: 10.1038/257686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puga A., Rosenthal J. D., Openshaw H., Notkins A. L. Herpes simplex virus DNA and mRNA sequences in acutely and chronically infected trigeminal ganglia of mice. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):102–111. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu N., Sokawa Y. 2',5'-Oligoadenylate synthetase activity in lymphocytes from normal mouse. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):12034–12037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G., Cook M. L. Latent herpes simplex virus in spinal ganglia of mice. Science. 1971 Aug 27;173(3999):843–845. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3999.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G., Cook M. L. Latent infections induced by herpes simplex viruses. Cancer Res. 1973 Jun;33(6):1399–1401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada A., Yoshino K. A new microplate neutralization test for typing of herpes simplex virus. Microbiol Immunol. 1978;22(7):415–426. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1978.tb00387.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz M. A., Price R. W., Notkins A. L. Latent ganglionic infection with herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2: viral reactivation in vivo after neurectomy. Science. 1974 Jun 14;184(4142):1185–1187. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4142.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. N., Hovanessian A. G. Interferon enhances 2-5A synthetase in embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1979 Nov 1;282(5734):74–76. doi: 10.1038/282074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S. Properties of interferon induced by specific antigens. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1977;35:17–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



