Abstract
Peanut is one of the calciphilous plants. Calcium serves as a ubiquitous central hub in a large number of signaling pathways. In the field, free calcium ion (Ca2+)-deficient soil can result in unfilled pods. Four pod stages were analyzed to determine the relationship between Ca2+ excretion and pod development. Peanut shells showed Ca2+ excretion at all four stages; however, both the embryo of Stage 4 (S4) and the red skin of Stage 3 (S3) showed Ca2+ absorbance. These results showed that embryo and red skin of peanut need Ca2+ during development. In order to survey the relationship among calcium, hormone and seed development from gene perspective, we further analyzed the seed transcriptome at Stage 2 (S2), S3, and S4. About 70 million high quality clean reads were generated, which were assembled into 58,147 unigenes. By comparing these three stages, total 4,457 differentially expressed genes were identified. In these genes, 53 Ca2+ related genes, 40 auxin related genes, 15 gibberellin genes, 20 ethylene related genes, 2 abscisic acid related genes, and 7 cytokinin related genes were identified. Additionally, a part of them were validated by qRT-PCR. Most of their expressions changed during the pod development. Since some reports showed that Ca2+ signal transduction pathway is involved in hormone regulation pathway, these results implied that peanut seed development might be regulated by the collaboration of Ca2+ signal transduction pathway and hormone regulation pathway.
Keywords: peanut, calcium, hormone, pod development, transcriptome
Introduction
Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) is an important crop member of the legume family and a major source of plant oil, proteins, essential vitamins and minerals that can be used for human consumption, animal feed, bioenergy, and health products (Higgs, 2002; Li et al., 2010, 2011). Seed formation of peanut is a central stage of pod development. Some reports illustrated that seed development depends on the highly coordination between endogenous signal and environment stimuli (Sun, 2008). For instance, several plant hormones have long been known to play a significant role in peanut gynophore elongation and embryo differentiation, such as auxin (Jacobs, 1951; Moctezuma and Feldman, 1996), the ration of NAA and kinetin (Ziv and Zamski, 1975), ABA (Ziv and Kahana, 1988), ethylene (Shlamovitz et al., 1995), and so on. In addition, peanut needs more calcium relative to other plants. Free Ca2+ concentration in soil serious affects peanut fruiting and yield (Cox et al., 1982). During pod development, more than 90% calcium was directly absorbed from the soil by pod (Beringer and Taha, 1976). For plants, Ca2+ not only play roles as a nutrient element, but also as a second messenger in the regulation of diverse metabolic processes (Poovaih and Ready, 1993). As to the possible relationship between calcium signal transduction and plant hormones, Yang et al. (2015) reported that the expressions of most calmodulin-binding transcription activators of M. Truncatula (MtCAMTAs) were responsive to the four hormones, including IAA, salicylic acid (SA), jasmonic acid (JA), and ABA, which play critical roles in the regulation of nodule organogenesis in legumes. Additionally, it seems that the ripening of strawberry fruit are co-regulated by phytohormone and calcium signal transduction (Chen et al., 2016). Recent years, although there is a comprehensive understanding of calcium physiology related to peanut abiotic stress resistance, it is of vitally important to isolate and characterize more candidate genes for understanding some mechanisms regulating peanut pod development, especially Ca2+ and hormone regulating pathway.
With the development of molecular biological techniques, the genomic research has been conducted and made a considerable progress in model legume, e.g., soybean (Severin et al., 2010; Wilson and Grant, 2010; Woody et al., 2011) and Medicago (Cannon et al., 2005), but relatively less progress in peanut (Pandey et al., 2012; Zhang et al., 2012). The advent of rapid and high-throughput technology for quantification of the transcriptome (Malone and Oliver, 2011) benefited the peanut genomics research, and was used in the seed development and tissue expression of peanut (Zhang et al., 2012; Chen et al., 2013; Wang et al., 2013; Zhu et al., 2014). These researches make it probability to study the relationship of between calcium and peanut pod development by transcriptome method, and explore valuably candidate genes. In the present study, to better understand the roles of Ca2+ in pod development, we compared the transcriptome profile of peanut pod at different developmental stages, through which some potential candidate genes was identified to be related to calcium and hormone.
Materials and Methods
Plant Materials and Treatments
Peanut cultivar, ‘Huayu 22,’ was provided by Biotechnology Research Center, Shandong Academy of Agricultural Science (SAAS, China). Free Ca2+ content in soil is 14 g (free Ca2+) kg-1 (dry soil). The pods were collected at the 1st (Stage 1, abbr. S1), 5th (Stage 2, abbr. S2), 10th (Stage 3, abbr. S3), 20th (Stage 4, abbr. S4) day after the peg elongation into the soil. Four stage materials were used for Ca2+ excretion determination. The materials of S2, S3, and S4 were collected and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen, and then stored in a freezer at -80°C for comparative transcriptome analysis.
Calcium oxide (CaO) Application in Soil
Field experiments was conducted to observe effects of free Ca2+ in soil on pod development in Sanzhuang, Rizhao, Shandong Province in spring 2014 and 2015. Free Ca2+ content in soil is 4 g (free Ca2+) kg-1 (dry soil). The 120 kg CaO ha-1 was applied in soil as Ca2+ treatment, and non-CaO treatment was as control. Each treatment had three replicates. CaO was applied before sowing.
Ca2+ Excretion Measured by Non-invasive Micro-test Technology (NMT)
Ca2+ excretion in pods of peanut were measured with NMT system (NMT100 Series, YoungerUSA LLC, Amherst, MA, United States; Xuyue (Beijing) Science and Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) and iFluxes/imFluxes 1.0 (YoungerUSA, LLC, Amherst, MA, United States) Software. Steady-state ion fluxes were measured for 5–20 min. After that, the test treatment was applied and the ion flux in the meristematic zone (120 μm from the root/pod tip) was measured for further 10 min and recorded the data (Yue et al., 2012). And the roots and pods were treated with 40 μm Ca2+ solution. Each treatment was repeated at least three times and all tests were repeated at least six times.
Total RNA Isolation and mRNAs Purification
Total RNA was isolated and integrity confirmed using a 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies). Beads with oligo(dT) were used to isolate poly(A) mRNA from total RNA (Qiagen GmbH, Hilden, Germany).
Synthesis of cDNA and Sequencing
Following purification, the mRNA was fragmented using divalent cations under elevated temperature. Taking these short fragments as templates, the first-strand cDNA was synthesized using random hexamer primers and SuperscriptTM III (InvitrogenTM, Carlsbad, CA, United States). The second strand cDNA was synthesized using buffer, dNTPs, RNaseH, and DNA polymerase I. Short fragments were purified with a QiaQuick PCR extraction kit (Qiagen) and resolved with EB buffer for end reparation and poly(A) addition. The short fragments were then connected using sequencing adapters. After agarose gel electrophoresis, suitable fragments were used as templates for PCR amplification. Finally, the library was sequenced from both directions on HiSeq 2000 System (illumina, San Diego, CA, United States) with 100 bp of data collected per run by applying TruSeq PE Cluster and TruSeq SBS Kits (illumina, San Diego, CA, United States). Data analysis and base calling were achieved by applying the illumina instrument software.
Transcriptome De Novo Assembly
The reference transcripts of a progenitor of cultivated peanut (Arachis ipaensis) were used to generate an integrated reference library. The processing and assembly of transcriptome data were performed with the application of modified Velvet to construct unique consensus sequences (Zerbino and Birney, 2008). The gene expression profile was developed by mapping trimmed transcriptome reads onto the unique consensus sequences by using SOAP2 (Li et al., 2009).
Annotation and Classification of Unigenes
Comparative transcriptomics analysis was conducted among the three different developmental stages. The intensity values of each sample were further transformed on log2-scale and used for differential expression analysis. The probe sets with a P-value < 0.01 and > two-fold changes in at least one of the comparisons were considered as differentially expressed genes (DEGs) for further analysis. Unigenes were used for BLAST searches and annotation against an NCBI Nr protein database (NCBI non-redundant sequence database) by using an E-value cut-off of 10-5 (E-value < 0.00001). Unigenes sequences were further aligned by BLASTX to protein databases such as Swiss-Prot, KEGG, and COG, retrieving proteins with the highest sequence similarity with the given unigenes along with their protein functional annotations. If results of different databases conflicted, a priority order of Nr, Swiss-Prot, KEGG, and COG was followed. For unigenes that did not align to any of the above databases, EST Scan software (Iseli et al., 1999) was used to predict their coding regions and determine sequence direction. Unigenes aligned to databases with higher priority did not enter the next circle. The alignments were considered complete when all circles were finished. The coding region sequences were then determined for proteins with the highest ranks using BLAST. Unigenes that could not be aligned to any database were scanned by EST Scan (Iseli et al., 1999) to determine the nucleotide (50–30) and amino acid sequences of the coding regions. The Blast2 GO was used to obtain Gene Ontology (GO) annotations for the unigenes, as well as for KEGG and COG analysis (Conesa et al., 2005). The WEGO software was then used to perform GO functional classification of all unigenes to view the distribution of gene functions of the species at the macro level (Ye et al., 2006). It was mapped all of the annotated unigenes to GO terms in the database and calculated the number of unigenes associated with every term.
Real-Time Fluorescent Quantitative PCR Analysis
Total RNA was isolated and purified using TRIzol Reagent (Tiangen, China) according to the manufacture’s instruction. The first-strand cDNA was synthesized by using Reverse Transcriptase M-MLV (Takara, Japan) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The PCR was amplified following the instruction of SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM (Takara, Japan) with the fluorescent quantitative PCR amplification instrument (ABI 7500, United States). The target gene primers were used to detect the sample mRNA. Control reactions were carried out by using primers Tua5-F and Tua5-R to detect the transcript encoding ubiquitously expressed tua5 (Chi et al., 2012). All assays for a target gene were performed in triplicate synchronously under identical conditions.
Results
Effects of Calcium on Peanut Pod Development and Ca2+ Excretion of Different Pod Tissues
Peanut is one of the important oil crops for China, and its yield is often affected by all kinds of environmental factors, including free Ca2+ content in soil. When free Ca2+ is deficient in soil, it will cause unfilling of pods. Figure 1 showed that pods were unfilled under 4 g (free Ca2+) kg-1 (dry soil), and CaO application can benefit pod filling.
FIGURE 1.
Effects of soil free Ca2+ on peanut pod development. The experiments were conducted on a farmland with 4 g (free Ca2+) kg-1 (dry soil). (A) Applied 120 kg CaO ha-1. (B) Without CaO application.
To assess the role of Ca2+ on pod development, hair root and four stages of pods were analyzed to determine Ca2+ excretion where: the peg just entered the soil (S1), tip of the peg initiated expansion (S2), beginning of pod reticulation (S3), and when the pod was clearly reticulated (S4), respectively, used to analyze (Figure 2A). The non-invasive microtest technique was used to detect net fluxes of Ca2+ at different seed tissues of different stages. Besides hair roots, peanut shells showed Ca2+ excretion at all four stages; however, both the embryo of S4 and the red skin of S3 and S4 showed Ca2+ absorbance. These results showed that embryo alone and embryo with red skin of peanut need Ca2+ during development (Figure 2B).
FIGURE 2.
Effects of calcium on peanut pod development and the Ca2+ excretion of different pod tissues. (A) Hair roots and four different pod developing stages were selected as detecting materials. (B) Ca2+ excretion was further detected on different tissues of these stages. Each value was averaged from more than three replicates (mean ± SD).
Assembly and Functional Annotations of Peanut Seed Transcriptomes
To further detect some mechanisms relate to the roles of Ca2+ in pod development. About 70 million high quality reads were obtained from the library. The average read size, Q30 percentage (sequencing error rate, 0.1%), and GC percentage for each library was 90 bp, >95%, and >40%, respectively. Clean reads from each library were used for assembly separately. And 263,110 unigenes were generated from library. The de novo assembly of all sequencing data using the modified Velvet was followed by the application of the SOAP2 program for unigene identification. The average sequence length of the unigenes was 1,235 bp and its range was 201–4,000 bp (Figure 3A).
FIGURE 3.
Assembly and functional annotations of peanut seed transcriptomes. (A) Sequence lengths of 263,110 assembled peanut unigenes. (B) A histogram of unigene ontology classification.
The GO assignments were used to categorize the functions of the predicted peanut Unigenes. Based on the sequence homologies, the sequences were categorized into 45 functional groups (Figure 3B), contained three main categories of the GO classification (biological processes, cellular components, and molecular functions). The genes involved in cellular process and metabolic process were dominant in the “Biological Process” category. “Cell,” “Cell part,” and the “Organelle” are the top three abundant categories in “Cellular component,” While “Binding,” and “catalytic activity” are dominant in the “Molecular function” category (Figure 3B).
Comparative Analysis of Three Pod Developmental Stages
To investigate expression levels of stage-specific genes during pods development, we conducted comparative analysis of the transcriptome profiles among three pod development stages at 5th (S2), 10th (S3), 20th (S4) day after the peg elongation into the soil. As shown in Figure 4A, totally 1,169 DEGs were obtained between S2 and S3, including 50 up-regulated and 1,119 down-regulated genes. Similarly, 1,172 DEGs (including 53 up-regulated and 1,119 down-regulated genes), 7 DEGs (including two up-regulated and five down-regulated genes) were identified between S3 and S4, S2 and S4, respectively. In addition, some other stage-specific expression genes were also analyzed. Approximately 39, 2157, and 1 stage-specific expression genes were identified between S2 and S3, S3 and S4, S2 and S4, respectively (Figure 4B).
FIGURE 4.
Comparative analysis of three pod developmental stages. (A) Comparative analysis of different expressed genes between three pod developmental stages. (B) The number of differentially expressed genes between three pods development stages. The numbers of up-regulated and down-regulated genes are indicated at the 5th (S2), 10th (S3), 20th (S4) day after the peg elongation into the soil.
Calcium and Ca2+ Signal Related Unigenes and Their Functional Categories
Since deficient free Ca2+ in soil can cause unfilling of pods, some DEGs involved in biological process of Ca2+ binding and Ca2+ signaling were identified based on GO analysis. These potential candidate genes contained 53 Ca2+ or Ca2+ signal pathway related genes (Table 1). These genes were significant differentially expressed during seed and pod development, suggesting that Ca2+ and calcium related protein might be involved in seed development.
Table 1.
The annotation of candidate genes related to calcium during pods development.
| Gene ID | Uniprot No. | Gene description | Species | E-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| comp33933 | Q8RYJ8 | Putative calcium-binding protein CML19 | Oryza | 4.00e - 23 |
| comp43665 | Q9LE22 | Probable calcium-binding protein CML27 | Arabidopsis | 5.00e - 55 |
| comp36255 | Q8L3R2 | Probable calcium-binding protein CML41 | Arabidopsis | 9.00e - 37 |
| comp50658 | Q9ZQH1 | Probable calcium-binding protein CML48 | Arabidopsis | 1.00e - 13 |
| comp53390 | Q9LF79 | Calcium-transporting ATPase 8 | Arabidopsis | 0 |
| comp51237 | Q9FKP1 | Cation/calcium exchanger 1 | Arabidopsis | 3.00e - 174 |
| comp45295 | Q9FKP2 | Cation/calcium exchanger 2 | Arabidopsis | 1.00e - 50 |
| comp14601 | Q8LEM7 | Calcineurin B-like protein 3 | Arabidopsis | 1.00e - 63 |
| comp47042 | O81223 | Calcineurin B-like protein 4 | Arabidopsis | 8.00e - 100 |
| comp47926 | O65718 | Cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel 2 | Arabidopsis | 0 |
| comp42319 | P51074 | Annexin-like protein RJ4 | Fragaria | 2.00e - 158 |
| comp45239 | Q940H6 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase SRK2E | Arabidopsis | 0 |
| comp36540 | Q96262 | Plasma membrane-associated cation-binding protein 1 | Arabidopsis | 1.00e - 47 |
| comp48463 | Q93ZH2 | Nuclear transcription factor Y subunit A-3 | Arabidopsis | 3.00e - 36 |
| comp40687 | P34913 | Bifunctional epoxide hydrolase 2 | Homo | 2.00e - 19 |
| comp49372 | Q8LFG1 | Probable alpha-amylase 2 | Arabidopsis | 1.00e - 149 |
| comp52512 | P14226 | Oxygen-evolving enhancer protein 1 | Pisum | 0 |
| comp38946 | P16059 | Oxygen-evolving enhancer protein 2 | Pisum | 2.00e - 151 |
| comp46793 | Q41932 | Oxygen-evolving enhancer protein 3-2 | Arabidopsis | 3.00e - 81 |
| comp48726 | Q39254 | Vacuolar cation/proton exchanger 2 | Arabidopsis | 8.00e - 6 |
| comp45043 | Q93Z81 | Vacuolar cation/proton exchanger 3 | Arabidopsis | 2.00e - 151 |
| comp47437 | Q2HXL0 | Respiratory burst oxidase homolog protein C | Solanum | 0 |
| comp51314 | O48538 | Respiratory burst oxidase homolog protein F | Arabidopsis | 0 |
| comp31869 | Q39033 | Phosphoinositide phospholipase C 2 | Arabidopsis | 8.00e - 50 |
| comp50062 | P17859 | Phosphoinositide phospholipase C 2 | Arabidopsis | 8.00e - 50 |
| comp41809 | O82598 | Aquaporin TIP1-3 | Arabidopsis | 2.00e - 129 |
| comp33153 | A5A7I7 | Calcium-dependent protein kinase 4 | Solanum | 0 |
| comp45958 | Q9SSF8 | Calcium-dependent protein kinase 30 | Arabidopsis | 0 |
| comp44027 | P28583 | Calcium-dependent protein kinase SK5 | Glycine | 0 |
| comp52882 | Q6DN14 | Multiple C2 and transmembrane domain-containing protein 1 | Homo | 2.00e - 10 |
| comp50090 | Q6DN12 | Multiple C2 and transmembrane domain-containing protein 2 | Homo | 4.00e - 23 |
| comp41514 | O81270 | Peroxygenase 1 | Arabidopsis | 1.00e - 107 |
| comp51310 | Q641Z6 | EH domain-containing protein 1 | Rattus | 2.00e - 146 |
| comp53583 | Q8L493 | Branched-chain-amino-acid aminotransferase-like protein 3 | Arabidopsis | 6.00e - 134 |
| comp46176 | O81916 | Uncharacterized calcium-binding protein At1g02270 | Arabidopsis | 1.00e - 150 |
| comp43596 | Q8LBL1 | Two-pore potassium channel 1 | Arabidopsis | 2.00e - 131 |
| comp40656 | Q9LDQ3 | Putative cysteine-rich receptor-like protein kinase 35 | Arabidopsis | 6.00e - 78 |
| comp52241 | Q8L7E9 | Protein MID1-COMPLEMENTING ACTIVITY 1 | Arabidopsis | 0 |
| comp52082 | Q94A4 | Alpha-amylase 3, chloroplastic | Arabidopsis | 0 |
| comp52718 | Q9C8E7 | Glutamate receptor 3.3 | Arabidopsis | 0 |
| comp43681 | Q9LSQ6 | Calcium-binding protein PBP1 | Arabidopsis | 4.00e - 37 |
| comp34785 | Q9LSQ6 | Calcium-binding protein PBP1 | Arabidopsis | 3.00e - 43 |
| comp49728 | Q41142 | Phospholipase D alpha 1 | Ricinus | 2.00e - 43 |
| comp50171 | Q9FYH7 | Vacuolar-sorting receptor 6 | Arabidopsis | 4.00e - 13 |
| comp50757 | Q9FYH7 | Vacuolar-sorting receptor 6 | Arabidopsis | 0 |
| comp44749 | Q93Z81 | Vacuolar cation/proton exchanger 3 | Arabidopsis | 5.00e - 171 |
| comp46345 | P42055 | Mitochondrial outer membrane protein porin of 34 kDa | Solanum | 1.00e - 35 |
| comp51265 | Q9C9L5 | Wall-associated receptor kinase-like 9 | Arabidopsis | 5.00e - 8 |
| comp25145 | F4JJJ3 | NAD(P)H dehydrogenase B3, mitochondrial | Arabidopsis | 0 |
| comp48262 | Q9BVG8 | Kinesin-like protein KIFC3 | Homo | 4.00e - 60 |
| comp49233 | Q9FKI0 | Fimbrin-like protein 2 | Arabidopsis | 0 |
| comp45947 | Q298L5 | Mitochondrial Rho GTPase | Sophophora | 5.00e - 87 |
| comp42934 | Q9S7C9 | Putative DNA-binding protein ESCAROLA | Arabidopsis | 5.00e - 6 |
Hormone Related Unigenes and Their Functional Categories
Genes related to hormone response were screened out by GO analysis. There were 40 auxin related genes, 15 gibberellin related genes, 20 ethylene related genes, 2 abscisic acid related genes, and 7 cytokinin related genes (Table 2) showed significant differentially expression during seed and pod development.
Table 2.
The annotation of candidate genes related to hormone during pods development.
| Gene ID | Uniprot No. | Gene description | Species | E-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auxin-related | ||||
| comp43478 | Q6J163 | Auxin-induced protein 5NG4 | Pinus | 4.00e - 8 |
| comp47743 | Q6J163 | Auxin-induced protein 5NG4 | Pinus | 1.00e - 49 |
| comp39204 | Q6J163 | Auxin-induced protein 5NG4 | Pinus | 3.00e - 15 |
| comp51971 | Q6J163 | Auxin-induced protein 5NG4 | Pinus | 2.00e - 46 |
| comp48589 | Q6J163 | Auxin-induced protein 5NG4 | Pinus | 6.00e - 77 |
| comp44220 | Q6J163 | Auxin-induced protein 5NG4 | Pinus | 1.00e - 39 |
| comp40373 | Q6J163 | Auxin-induced protein 5NG4 | Pinus | 5.00e - 29 |
| comp48904 | Q6J163 | Auxin-induced protein 5NG4 | Pinus | 2.00e - 11 |
| comp39544 | Q6J163 | Auxin-induced protein 5NG4 | Pinus | 1.00e - 42 |
| comp44395 | Q6J163 | Auxin-induced protein 5NG4 | Pinus | 1.00e - 29 |
| comp45206 | Q6J163 | Auxin-induced protein 5NG4 | Pinus | 2.00e - 56 |
| comp49555 | Q6J163 | Auxin-induced protein 5NG4 | Pinus | 3.00e - 29 |
| comp41016 | Q6J163 | Auxin-induced protein 5NG4 | Pinus | 2.00e - 64 |
| comp43783 | Q6J163 | Auxin-induced protein 5NG4 | Pinus | 8.00e - 6 |
| comp41488 | Q6J163 | Auxin-induced protein 5NG4 | Pinus | 5.00e - 47 |
| comp46020 | Q6J163 | Auxin-induced protein 5NG4 | Pinus | 3.00e - 20 |
| comp47084 | Q6J163 | Auxin-induced protein 5NG4 | Pinus | 1.00e - 28 |
| comp34759 | Q6J163 | Auxin-induced protein 5NG4 | Pinus | 2.00e - 62 |
| comp35338 | Q6J163 | Auxin-induced protein 5NG4 | Pinus | 5.00e - 7 |
| comp45159 | Q6J163 | Auxin-induced protein 5NG4 | Pinus | 3.00e - 81 |
| comp36946 | Q6J163 | Auxin-induced protein 5NG4 | Pinus | 1.00e - 129 |
| comp43310 | Q6J163 | Auxin-induced protein 5NG4 | Pinus | 3.00e - 146 |
| comp43748 | Q8LAL2 | Auxin-responsive protein IAA26 | Arabidopsis | 1.00e - 70 |
| comp36524 | Q9ZSY8 | Auxin-responsive protein IAA27 | Arabidopsis | 8.00e - 91 |
| comp35718 | Q8H174 | Auxin-responsive protein IAA31 | Arabidopsis | 3.00e - 31 |
| comp50484 | Q94BT2 | Auxin-induced in root cultures protein 12 | Arabidopsis | 3.00e - 6 |
| comp46184 | Q94BT2 | Auxin-induced in root cultures protein 12 | Arabidopsis | 8.00e - 15 |
| comp44924 | Q94BT2 | Auxin-induced in root cultures protein 12 | Arabidopsis | 2.00e - 15 |
| comp35357 | Q9LF79 | Auxin-induced protein 15A | Glycine | 2.00e - 19 |
| comp30777 | P33081 | Auxin-induced protein 15A | Glycine | 1.00e - 20 |
| comp36019 | P33079 | Auxin-induced protein 10A5 | Glycine | 8.00e - 13 |
| comp36785 | Q9FEL6 | Auxin transporter-like protein 3 | Medicago | 0 |
| comp45084 | O24543 | Auxin-induced protein 22E | Vigna | 1.00e - 63 |
| comp52994 | Q9FGV1 | Auxin response factor 8 | Arabidopsis | 7.00e - 133 |
| comp46658 | Q9XED8 | Auxin response factor 9 | Arabidopsis | 0 |
| comp28367 | Q653H7 | Auxin response factor 18 | Oryza | 7.00e - 63 |
| comp45289 | Q653H7 | Auxin response factor 18 | Oryza | 1.00e - 162 |
| comp33145 | Q653H7 | Auxin response factor 18 | Oryza | 7.00e - 47 |
| comp32944 | Q96247 | Auxin transporter protein 1 | Arabidopsis | 9.00e - 163 |
| comp41401 | O04012 | Auxin-binding protein ABP19 | Prunus | 5.00e - 74 |
| Gibberellin-related | ||||
| comp53643 | O04706 | Gibberellin 20 oxidase 1-B | Triticum | 1.00e - 121 |
| comp46516 | Q39111 | Gibberellin 20 oxidase 2 | Arabidopsis | 2.00e - 129 |
| comp44953 | Q39111 | Gibberellin 20 oxidase 2 | Arabidopsis | 8.00e - 80 |
| comp45036 | Q9SQ80 | Gibberellin 2-beta-dioxygenase 1 | Pisum | 4.00e - 160 |
| comp48090 | Q9SQ80 | Gibberellin 2-beta-dioxygenase 1 | Pisum | 6.00e - 162 |
| comp43715 | Q9XFR9 | Gibberellin 2-beta-dioxygenase 2 | Arabidopsis | 6.00e - 17 |
| comp47582 | O49561 | Gibberellin 2-beta-dioxygenase 8 | Arabidopsis | 4.00e - 46 |
| comp40312 | O49561 | Gibberellin 2-beta-dioxygenase 8 | Arabidopsis | 3.00e - 51 |
| comp44039 | Q39103 | Gibberellin 3-beta-dioxygenase 1 | Arabidopsis | 1.00e - 88 |
| comp45509 | Q9SVS8 | Gibberellin 3-beta-dioxygenase 3 | Arabidopsis | 3.00e - 20 |
| comp37867 | P46690 | Gibberellin-regulated protein 4 | Arabidopsis | 6.00e - 38 |
| comp41469 | P46690 | Gibberellin-regulated protein 4 | Arabidopsis | 7.00e - 33 |
| comp13386 | Q9LFR3 | Gibberellin-regulated protein 14 | Arabidopsis | 1.00e - 19 |
| comp27867 | F4IQJ4 | Gibberellin-regulated protein 11 | Arabidopsis | 1.00e - 23 |
| comp40799 | Q9FDW1 | Transcription factor MYB44 | Arabidopsis | 3.00e - 32 |
| Ethylene-related | ||||
| comp35300 | Q84QC2 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF017 | Arabidopsis | 7.00e - 33 |
| comp11865 | Q8LBQ7 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF034 | Arabidopsis | 9.00e - 23 |
| comp45116 | Q9SKT1 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF053 | Arabidopsis | 5.00e - 43 |
| comp34495 | Q9LY05 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF106 | Arabidopsis | 5.00e - 35 |
| comp37722 | Q9CA27 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF118 | Arabidopsis | 5.00e - 20 |
| comp53691 | Q8LC30 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor RAP2-1 | Arabidopsis | 9.00e - 41 |
| comp42029 | P42736 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor RAP2-3 | Arabidopsis | 2.00e - 37 |
| comp48452 | Q6X5Y6 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor WRI1 | Arabidopsis | 3.00e - 37 |
| comp44242 | O80340 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor 4 | Arabidopsis | 9.00e - 9 |
| comp42489 | Q40477 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor 4 | Nicotiana | 2.00e - 22 |
| comp37530 | Q8L9K1 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor 13 | Arabidopsis | 2.00e - 34 |
| comp47316 | Q9SUQ2 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor CRF2 | Arabidopsis | 1.00e - 33 |
| comp43675 | Q9SUE3 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor CRF4 | Arabidopsis | 4.00e - 50 |
| comp47833 | Q9LVG2 | AP2-like ethylene-responsive transcription factor TOE2 | Arabidopsis | 1.00e - 6 |
| comp43442 | Q38914 | AP2-like ethylene-responsive transcription factor ANT | Arabidopsis | 1.00e - 132 |
| comp51344 | Q38914 | AP2-like ethylene-responsive transcription factor ANT | Arabidopsis | 2.00e - 19 |
| comp48832 | Q1PFE1 | AP2-like ethylene-responsive transcription factor AIL1 | Arabidopsis | 4.00e - 129 |
| comp47962 | Q52QU2 | AP2-like ethylene-responsive transcription factor AIL6 | Arabidopsis | 5.00e - 14 |
| comp50155 | Q0WPQ2 | Ethylene receptor 2 | Arabidopsis | 0 |
| comp42987 | Q8GWK2 | AP2-like ethylene-responsive transcription factor At2g41710 | Arabidopsis | 2.00e - 148 |
| Cytokinin-related | ||||
| comp44683 | Q9ZW95 | Cytokinin hydroxylase | Arabidopsis | 6.00e - 72 |
| comp14370 | Q9FF18 | Cytokinin hydroxylase | Arabidopsis | 22.00e - 516 |
| comp42133 | Q9FF18 | Cytokinin hydroxylase | Arabidopsis | 2.00e - 175 |
| comp42347 | Q9FUJ1 | Cytokinin dehydrogenase 7 | Arabidopsis | 3.00e - 41 |
| comp40332 | Q9FUJ1 | Cytokinin dehydrogenase 7 | Arabidopsis | 1.00e - 166 |
| comp53620 | Q8L8B8 | Cytokinin riboside 5’-monophosphate phosphoribohydrolase LOG3 | Arabidopsis | 4.00e - 130 |
| comp38806 | Q84MC2 | Cytokinin riboside 5’-monophosphate phosphoribohydrolase LOG8 | Arabidopsis | 2.00e - 127 |
| Abscisic acid-related | ||||
| comp38442 | Q8RYD6 | Abscisic acid insensitive 5-like protein 1 | Arabidopsis | 3.00e - 28 |
| comp29840 | Q9FH76 | Abscisic acid 8’-hydroxylase 3 | Arabidopsis | 5.00e - 160 |
Real-Time Fluorescent Quantitative PCR Analysis
In order to confirm the transcriptome sequencing results, Ca2+ and hormone related genes were selected from DEGs based on the GO analysis and used to real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR analysis. As shown in Figure 5, the expression pattern of 8 selected DEGs, which are related to Ca2+ signal pathway, were consistent with their respective microarrays data. Among these genes, two genes, which includes one CDPK gene (comp33153) and one uncharacterized calcium-binding protein At1g02270 (comp46176), were up-regulated at S4. The Serine/threonine-protein kinase SRK2E (comp45239) was up-regulated at S2, down-regulated at S3, and then up-regulated at S4. Three probable calmodulin like protein CMLs (comp33933, comp43665, and comp50658), one calcineurin B-like protein (comp47042) and one calcium-binding protein PBP1 (comp43681) were up-regulated at S2 and then down-regulated during the later stages.
FIGURE 5.
Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR analysis on mRNA transcription of the selected differentially expressed calcium related genes. These were the 5th (S2), 10th (S3), 20th (S4) day after the peg elongation into the soil. The ordinate axis greater than one means up-regulated, less than one was down-regulated.
Among the 12 selected auxin related genes, six genes, i.e., auxin-induced protein 5NG4 (comp43478), auxin-responsive protein IAA31 (comp35718), auxin-induced in root cultures protein 12 (comp50484), auxin-induced protein 15A (comp35357), auxin-induced protein 10A5 (comp36019), and auxin transporter-like protein 3 (comp36785), were down-regulated in S2 and then up-regulated during the later stages. Three auxin response factor 8 (comp52994, comp45289, and comp46658), one auxin-responsive protein IAA26 (comp36524) were down-regulated at S4. One auxin-induced protein 22E (comp45084) was down-regulated at S2, up-regulated at S3, and then down-regulated at S4 (Figure 6).
FIGURE 6.
Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR analysis on mRNA transcription of the selected differentially expressed auxin related genes. These were the 5th (S2), 10th (S3), 20th (S4) day after the peg elongation into the soil. The ordinate axis greater than one means up-regulated, less than one was down-regulated.
Among 11 selected gibberellin related genes, four genes, i.e., two gibberellin-regulated protein (comp41469, comp27867), two gibberellin 2-beta-dioxygenase (comp45036, comp43715), were down-regulated at S2 and then up-regulated at S4. One transcription factor MYB44 (comp40799), one gibberellin 20 oxidase (comp44953) and one gibberellin 3-beta-dioxygenase (comp44039) were up-regulated at S4. One gibberellin 20 oxidases (comp53643), one gibberellin 2-beta-dioxygenase (comp47582), one gibberellin 3-beta-dioxygenase (comp45509) and one gibberellin-regulated protein (comp13386) were up-regulated at S2, down-regulated at S3 and then up-regulated at S4 (Figure 7).
FIGURE 7.
Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR analysis on mRNA transcription of the selected differentially expressed gibberellin related genes. These were the 5th (S2), 10th (S3), 20th (S4) day after the peg elongation into the soil. The ordinate axis greater than one means up-regulated, less than one was down-regulated.
Seventeen selected ethylene related genes were analyzed. Two ethylene-responsive transcription factor RAP2 (comp53691 and comp42029), one ethylene-responsive transcription factor WRI1 (comp48452), three ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF (comp34495, comp37722, and comp11865) and one AP2-like ethylene-responsive transcription factor AIL (comp47962) were down-regulated at S2 then up-regulated at S4. One ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF (comp35300), one ethylene-responsive transcription factor (comp44242), two ethylene-responsive transcription factor CRF (comp47316 and comp43675) and one AP2-like ethylene-responsive transcription factor ANT (comp43442) were only down-regulated at S4. The AP2-like ethylene-responsive transcription factor TOE (comp47833) and ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF (comp45116) were up-regulated at S4. AP2-like ethylene-responsive transcription factor At2g41710 (comp42987) and AP2-like ethylene-responsive transcription factor AIL1 (comp48832) were down-regulated at S2, up-regulated at S3, and then down-regulated at S4. The ethylene-responsive transcription factor 13 (comp37530) was up-regulated at S2 and S3, then down-regulated at S4 (Figure 8).
FIGURE 8.
Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR analysis on mRNA transcription of the selected differentially expressed ethylene related genes. These were the 5th (S2), 10th (S3), 20th (S4) day after the peg elongation into the soil. The ordinate axis greater than one means up-regulated, less than one was down-regulated.
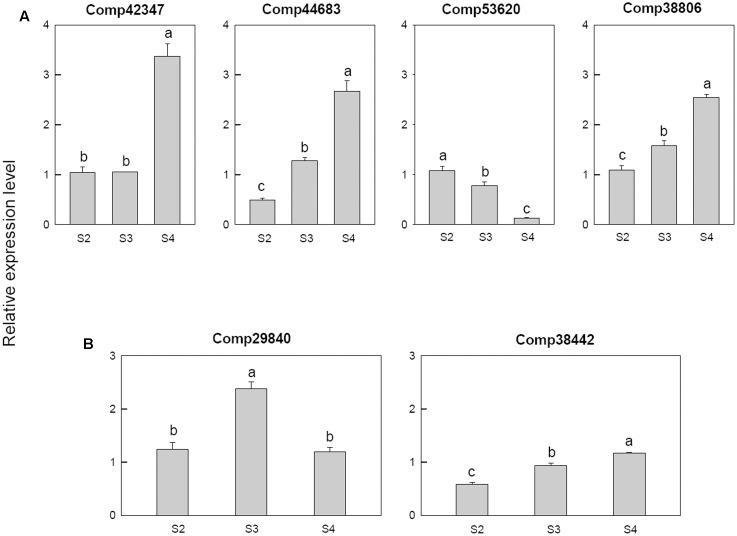
Among the four cytokinin related genes, cytokinin dehydrogenase (comp42347) was only up regulated at S4, cytokinin hydroxylase (comp44683) was down-regulated at S2 then up-regulated in later stage, cytokinin riboside 5′-monophosphate phosphoribohydrolase LOG3 (comp53620) was down-regulated from S3 and the Cytokinin riboside 5′-monophosphate phosphoribohydrolase LOG8 (comp38806) up-regulated from S3 (Figure 9A).
FIGURE 9.
Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR analysis on mRNA transcription of the selected differentially expressed genes. (A) Cytokinin related genes, (B) abscisic acid related genes. These were the 5th (S2), 10th (S3), 20th (S4) day after the peg elongation into the soil. The ordinate axis greater than one means up-regulated, less than one was down-regulated.
For the two abscisic acid related genes, the abscisic acid 8′-hydroxylase 3 (comp29840) was up-regulated at S3 and then down-regulated, however, the abscisic acid insensitive 5-like protein 1 (comp38442) was down-regulated at S2 (Figure 9B).
Discussion
Calcium is not only an essential macroelement for plant growth, but also a second messenger involved in regulating diverse physiological processes (Poovaih and Ready, 1993). Peanut remains one of the most important oil-crops in the world, and Calcium is by far the most critical nutrient for this crop to achieve high yields. Calcium deficiency in soil can results in a decrease in yield, e.g., unfilled pods (Cox et al., 1982). Unfilled pods were also found in free Ca2+-insufficient soil in the present work (Figure 1), and the pod yield would decreased by 20% or more. For pods, it seems that embryo alone or embryo with red skin are the main tissues need more Ca2+ (Figure 2B). It attracts us to pay more attention to investigate the mechanisms of how Ca2+ is involved in pod development.
As a powerful technique, transcriptome sequencing was used to observe global gene expression profiles and the physiological processes involved in various plants (Clarke and Zhu, 2006). As to fruit development, it has been applied to strawberry (Aharoni and O’Connell, 2002), tomato (Alba et al., 2005), pear (Fonseca et al., 2004), apple (Lee et al., 2007), and peanut seed development (Zhang et al., 2012; Zhu et al., 2014). But the relationship between calcium and peanut seed at different pods developmental stages was seldom mentioned. In the present work, 263,110 unigenes were obtained from library. We identified 4,457 DEGs via sequencing analysis, and got 2,197 stage-specific expressed genes at different pod developmental stages (Figure 4B). It has been reported that free Ca2+ concentration in soil seriously affected peanut fruiting and yield, ovary handle and pods could absorb Ca2+ from soil, and transport it to both the developing seed and the vegetative organs, such as stem, leaves, etc. (Beringer and Taha, 1976). In this study, through Gene Ontology analysis, many DEGs involved in the Ca2+ responding and Ca2+ signal transduction, which were identified as potential candidate genes responsible for development of pods (Table 1). That is to say, calcium was related to pod development at the genetic levels.
Besides an important essential element, Ca2+ also acts as a secondary messenger in various biological processes. It has been shown that various Ca2+ transporters in plants (Dayod et al., 2010) and Ca2+ signal transduction protein were involved in gametogenesis, fertilization and early pollen tube growth (Tirlapur and Cresti, 1992). Interestingly, in the present study, we found some calcium-related unigenes at different pod developmental stages, and eight Ca2+ signaling-related genes were analyzed. These genes were calcium-dependent protein kinase (CDPK), calcineurin B-like protein (CBL), calmodulin like protein (CML), and some other Ca2+ signaling related genes. CDPKs were thought be involved in embryogenesis, seed development and germination of sandalwood (Anil et al., 2000) and in rice seed development (Morello et al., 2000). OsCDPK2 protein had a low level during early seed development, but had a high level which maintained in 20 days after fertilization (Frattini et al., 1999). Overexpression of the CDPK OsCDPK2 in transgenic rice disrupted seed development (Laura et al., 2000). In peanut, CDPK genes might be involved in pod development since they were up-regulated at 20th day after the peg elongation into the soil (Figure 5). However, some other calcium signal related genes, such as CBL, CML, and PBP1 were all down-regulated. These results implied that Ca2+-signaling transduction pathway might be involved in pod development.
Auxin, gibberellin, abscisic acid, cytokinin, and ethylene have been implicated in regulating the peanut seed development and pod maturation (Jacobs, 1951; Ziv and Kahana, 1988; Shlamovitz et al., 1995; Moctezuma and Feldman, 1996; Ozga and Reinecke, 2003). Meanwhile, genes encoding key enzymes related to hormone metabolism showed significant changes in transcriptional level during peanut early pod development (Xia et al., 2013). In this study, a number of DEGs related to hormone response were identified at different pods developmental stages, e.g., auxin response factor, auxin-induced protein, auxin response factor, gibberellin-regulated protein, gibberellin 2-beta-dioxygenase, gibberellin 3-beta-dioxygenase, ethylene-responsive transcription factor, AP2-like ethylene-responsive transcription factor, cytokinin hydroxylase, cytokinin dehydrogenase, abscisic acid insensitive 5-like protein, and abscisic acid 8′-hydroxylase (Table 2). All these revealed that hormone response genes potentially played a crucial role in peanut seed development.
Seed development is a complex process, many physiological processes occurred during seed development (Figure 3), calcium and hormone seems to play important roles in this progress, respectively. It has been known that hormonal controls on cell division and expansion are active in the development of fruit. Many of phytohormonal pathways utilize changes in cytoplasmic calcium concentration ([Ca2C]cyt) as a secondary signal messenger (e.g., ABA, JA, auxin, GA, ethylene, brassinosteroids, and cytokinins) (Fortes et al., 2015). Recently, more and more reports showed that Ca2+ signal transduction pathway is involved in phytohormonal pathways. In Arabidopsis, a CPK4 is involved in modulating ABA signaling (Wang et al., 2017), meanwhile, CPK28 plays a role in balancing the phytohormones JA and GA in development (Matschi et al., 2015), and affects ethylene biosynthesis (Jin et al., 2017). Additionally, the calmodulin-like protein CML20, a functional Ca2+ sensor, negatively regulates ABA-induced stomatal movement in Arabidopsis (Wu et al., 2017), StCDPK3 in involved in the cross-talk between ABA and GA signaling at the onset of potato tuber development (Grandellis et al., 2016).
The present study provided basis for finding and screening calcium related gene and hormone response genes during peanut seed development. We speculated that besides being components of cell, such as membrane or something else, peanut seed development might be regulated by the collaboration of Ca2+ signal transduction pathway and hormone regulation pathway, or Ca2+ regulates pod development through modulating hormone since Ca2+ signal transduction pathway can modulate plant hormone (Yang and Komatsu, 2000; Ullanat and Jayabaskaran, 2002; Mori et al., 2006), and it also might be related to the utilization calcium of auxin and ABA pathways as both a protein binding secondary messenger and in membrane transport mechanisms that modify turgor and solute accumulation to drive cell expansion and ripening (Hocking et al., 2016).
Author Contributions
SW and XL planned and designed the research. YL, JM, FG, SY, JZ, YG, and LC performed experiments. YL collected data and conducted analysis. YL and XL wrote the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31571581, 31571605, 31601261, 31601261), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2015YL077 and BS2015SW020), the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (2016M592236), the Project of Significant Application of Agricultural Technology Innovation in Shandong Province, International Science and Technology Cooperation Program of China (2015DFA31190), the Supporting Plan of National Science and Technology of China (2014BAD11B04), the earmarked fund for Modern Agroindustry Technology Research System (CARS14).
References
- Aharoni A., O’Connell A. (2002). Gene expression analysis of strawberry achene and receptacle maturation using DNA microarrays. J. Exp. Bot. 53 2073–2087. 10.1093/jxb/erf06 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alba R., Payton P., Fei Z., McQuinn R., Debbie P., Martin G. B., et al. (2005). Transcriptome and selected metabolite analyses reveal multiple points of ethylene control during tomato fruit development. Plant Cell 17 2954–2965. 10.1105/tpc.105.036053 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anil V. S., Harmon A. C., Rao K. S. (2000). Spatio-temporal accumulation and activity of calcium-dependent protein kinases during embryogenesis, seed development, and germination in sandalwood. Plant Physiol. 122 1035–1043. 10.1104/pp.122.4.1035 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beringer H., Taha H. A. (1976). 45Calcium absorption by two cultivars of groundnut (Arachis hypogea). Exp. Agric. 12 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Cannon S. B., Crow J. A., Heuer M. L., Wang X., Cannon E. K. S., Dwan C., et al. (2005). Databases and information integration for the Medicago truncatula genome and transcriptome. Plant Physiol. 138 38–46. 10.1104/pp.104.059204 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Mao L., Mi H., Lu W., Ying T., Luo Z. (2016). Involvement of three annexin genes in the ripening of strawberry fruit regulated by phytohormone and calcium signal transduction. Plant Cell Rep. 35 733–743. 10.1007/s00299-015-1915-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X. P., Zhu W., Azam S., Li H., Zhu F., Li H., et al. (2013). Deep sequencing analysis of the transcriptomes of peanut aerial and subterranean young pods identifies candidate genes related to early embryo abortion. Plant Biotechnol. J. 11 115–127. 10.1111/pbi.12018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi X. Y., Hu R. B., Yang Q. L., Zhang X. W., Pan L. J., Chen N., et al. (2012). Validation of reference genes for gene expression studies in peanut by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Mol. Genet. Genomics 287 167–176. 10.1007/s00438-011-0665-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke J. D., Zhu T. (2006). Microarray analysis of the transcriptome as a stepping stone towards understanding biological systems: practical considerations and perspectives. Plant J. 45 630–650. 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02668.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conesa A., Gotz S., Garcia-Gomez J. M., Terol J., Talon M., Robles M. (2005). Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 21 3674–3676. 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti610 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox F. R., Adams F., Tucker B. B. (1982). “Liming, fertilization, and mineral nutrition,” in Peanut Science and Technology, eds Pattee H. E., Young C. T. (Yoakum, TX: American Peanut Research and Education Society, Inc.), 139–163. [Google Scholar]
- Dayod M., Tyerman S., Leigh R., Gilliham M. (2010). Calcium storage in plants and the implications for calcium biofortification. Protoplasma 247 215–231. 10.1007/s00709-010-0182-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca S., Hackler L., Zvara A., Ferreira S., Baldé A., Dudits D., et al. (2004). Monitoring gene expression along pear fruit development, ripening and senescence using cDNA microarrays. Plant Sci. 167 457–469. 10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.0.3.33 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Fortes A. M., Teixeira R. T., Agudelo-Romero P. (2015). Complex interplay of hormonal signals during grape berry ripening. Molecules 20 9326–9343. 10.3390/molecules20059326 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frattini M., Morello L., Breviario D. (1999). Rice calcium-dependent protein kinase isoforms OsCDPK2 and OsCDPK11 show different responses to light and different expression patterns during seed development. Plant Mol. Biol. 41 753–764. 10.1023/A:1006316422400 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandellis C., Fantino E., Muñiz García M. N., Bialer M. G., Santin F., Capiati D. A., et al. (2016). StCDPK3 phosphorylates in vitro two transcription factors involved in GA and ABA signaling in potato: StRSG1 and StABF1. PLoS ONE 11:e0167389 10.1371/journal.pone.0167389 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs J. (2002). The beneficial role of peanuts in the diet-an update and rethink! Peanuts and their role in CHD. Mol. Nutr. Food Sci. 32 214–218. 10.1108/00346650210454190 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hocking B., Tyerman S. D., Burton R. A., Gilliham M. (2016). Fruit calcium: transport and physiology. Front. Plant Sci. 7:569 10.3389/fpls.2016.00569 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iseli C., Jongeneel C. V., Bucher P. (1999). “ESTScan: a program for detecting, evaluating, and reconstructing potential coding regions in EST sequences,” in Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology, ISMB, Heidelberg, 138–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs W. P. (1951). Auxin relationships in an intercalary meristem: further studies on the gynophore of Arachis hypogaea L. Am. J. Bot. 38 307–310. [Google Scholar]
- Jin Y., Ye N., Zhu F., Li H., Wang J., Jiang L., et al. (2017). Calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK28 targets the methionine adenosyltransferases for degradation by the 26S proteasome and affects ethylene biosynthesis and lignin deposition in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 90 304–318. 10.1111/tpj.13493 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laura M., Milo F., Silvia G., Paul C., Diego B. (2000). Overexpression of the calcium-dependent protein kinase OsCDPK2 in transgenic rice is repressed by light in leaves and disrupts seed development. Transgenic Res. 9 453–462. 10.1023/A:1026555021606 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. P., Yu G. H., Seo Y. S., Han S. E., Choi Y. O., Daeil K., et al. (2007). Microarray analysis of apple gene expression engaged in early fruit development. Plant Cell Rep. 26 917–926. 10.1007/s00299-007-0308-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Yu C., Li Y., Lam T. W., Yiu S. M., Kristiansen K., et al. (2009). SOAP2: an improved ultrafast tool for short read alignment. Bioinformatics 25 1966–1967. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp.336 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Hou S., Su M., Yang M., Shen S., Jiang G., et al. (2010). Major energy plants and their potential for bioenergy development in China. J. Environ Manage. 46 579–589. 10.1007/s00267-010-9443-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Rezaei R., Li P., Wu G. (2011). Composition of amino acids in feed ingredients for animal diets. Amino Acids 40 1159–1168. 10.1007/s00726-010-0740-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone J. H., Oliver B. (2011). Microarrays, deep sequencing and the true measure of the transcriptome. BMC Biol. 9:34 10.1186/1741-7007-9-34 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matschi S., Hake K., Herde M., Hause B., Romeis T. (2015). The calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK28 regulates development by inducing growth phase-specific, spatially restricted alterations in jasmonic acid levels independent of defense responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 27 591–606. 10.1105/tpc.15.00024 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moctezuma E., Feldman L. J. (1996). IAA redistributes to the upper side of gravistimulated peanut (Arachis hypogaea) gynophores. Plant Physiol. 111:S73. [Google Scholar]
- Morello L., Frattini M., Christou P., Breviario D. (2000). Overexpression of the calcium-dependent protein kinase OsCDPK2 in transgenic rice is repressed by light in leaves and disrupts seed development. Transgenic Res. 9 453–462. 10.1023/A:1026555021606 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori I. C., Murata Y., Yang Y., Munemasa S., Wang Y. F., Andreoli S., et al. (2006). CDPKs CPK6 and CPK3 function in ABA regulation of guard cell S-type anion- and Ca2+- permeable channels and stomatal closure. PLoS Biol. 4:e327 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040327 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozga J. A., Reinecke D. M. (2003). Hormonal interactions in fruit development. J. Plant Growth Regul. 22 73–81. 10.1007/s00344-003-0024-9 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey M. K., Monyo E., Ozias-Akins P., Liang X., Guimaraes P., Nigam S. N., et al. (2012). Advances in Arachis genomics for peanut improvement. Biotechnol. Adv. 30 639–651. 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.11.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poovaih B. W., Ready A. S. (1993). Calcium and signal transduction in plants. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 12 185–211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severin A. J., Woody J. L., Bolon Y. T., Joseph B., Diers B. W., Farmer A. D., et al. (2010). RNA-Seq Atlas of Glycine max: a guide to the soybean transcriptome. BMC Plant Biol. 10:160 10.1186/1471-2229-10-160 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlamovitz N., Ziv M., Zamski E. (1995). Light, dark and growth regulator involvement in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) pod development. Plant Growth Regul. 16 37–42. 10.1007/BF00040505 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D. (2008). Plant Breeding. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 424–443. [Google Scholar]
- Tirlapur U. K., Cresti M. (1992). Computer-assisted video image analysis of spatial variations in membrane-associated Ca2+ and calmodulin during pollen hydration, germination and tip growth in Nicotiana tabacum L. Ann. Rot. 69 503–508. [Google Scholar]
- Ullanat R., Jayabaskaran C. (2002). Distinct light-, cytokinin- and tissue-specific regulation of calcium dependent protein kinase gene expression in cucumber (Cucumis sativus). Plant Sci. 162 153–163. 10.1016/S0168-9452(01)00546-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang P., Yang Q., Sang S., Chen Y., Zhong Y., Wei Z. (2017). Arabidopsis inositol polyphosphate kinase AtIpk2β is phosphorylated by CPK4 and positively modulates ABA signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.06.060 [Epub ahead of print]. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T., Chen X. P., Li H. F., Liu H. Y., Hong Y. B., Yang Q. L., et al. (2013). Transcriptome identification of the resistance-associated genes (RAGs) to Aspergillus flavus infection in pre-harvested peanut (Arachis hypogaea). Funct. Plant Biol. 40 292–303. 10.1071/FP12143 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. F., Grant D. (2010). Soybean Genomics Research Program Accomplishments Report. Available at: https://soybase.org/SoyGenStrat2007/SoyGenStratPlan2008-2012-Accomplishments%20v1.6.pdf [Google Scholar]
- Woody J. L., Severin A. J., Bolon Y. T., Joseph B., Diers B. W., Farmer A. D., et al. (2011). Gene expression patterns are correlated with genomic and genic structure in soybean. Genome 54 10–18. 10.1139/G10-090 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu X., Qiao Z., Liu H., Acharya B. R., Li C., Zhang W. (2017). CML20, an Arabidopsis calmodulin-like protein, negatively regulates guard cell ABA signaling and drought stress tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 8:824 10.3389/fpls.2017.00824 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia H., Zhao C. Z., Hou L., Li A. Q., Zhao S. Z., Bi Y. P., et al. (2013). Transcriptome profiling of peanut gynophores revealed global reprogramming of gene expression during early pod development in darkness. BMC Genomics 14:517 10.1186/1471-2164-14-517 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang G., Komatsu S. (2000). Involvement of calcium-dependent protein kinase in rice (Oryza sativa L.) lamina inclination caused by brassinolide. Plant Cell Physiol. 41 1243–1250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y., Sun T., Xu L., Pi E., Wang S., Wang H., et al. (2015). Genome-wide identification of CAMTA gene family members in Medicago truncatula and their expression during root nodule symbiosis and hormone treatments. Front. Plant Sci. 6:457 10.3389/fpls.2015.00459 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye J., Fang L., Zheng H., Zhang Y., Chen J., Zhang Z., et al. (2006). WEGO: a web tool for plotting GO annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 34 W293–W297. 10.1371/journal.pone.0060881 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue Y., Zhang M., Zhang J., Duan L., Li Z. (2012). SOS1 gene overexpression increased salt tolerance in transgenic tobacco by maintaining a higher K+/Na+ ratio. J. Plant Physiol. 169 225–261. 10.1016/j.jplph.2011.10.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerbino D. R., Birney E. (2008). Velvet: algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res. 18 821–829. 10.1101/gr.074492.107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Liang S., Duan J., Wang J., Chen S., Cheng Z., et al. (2012). De novo assembly and characterisation of the transcriptome during seed development, and generation of genic-SSR markers in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). BMC Genomics 13:90 10.1186/1471-2164-13-90 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu W., Chen X. P., Li H. F., Zhu F. H., Hong Y. B., Varshney K. R., et al. (2014). Comparative transcriptome analysis of aerial and subterranean pods development provides insights into seed abortion in peanut. Plant Mol. Biol. 85 395–409. 10.1007/s11103-014-0193-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziv M., Kahana O. (1988). The role of the peanut (Araschis hypogaea) ovular tissue in the photo-morphogenetic response of the embryo. Plant Sci. 57 159–164. 10.1016/0168-9452(88)90082-9 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Ziv M., Zamski E. (1975). Geotropic responses and pod development in gynophore explants of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) cultured in vitro. Ann. Bot. Fenn. 39 579–583. 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aob.a084968 [DOI] [Google Scholar]