Abstract
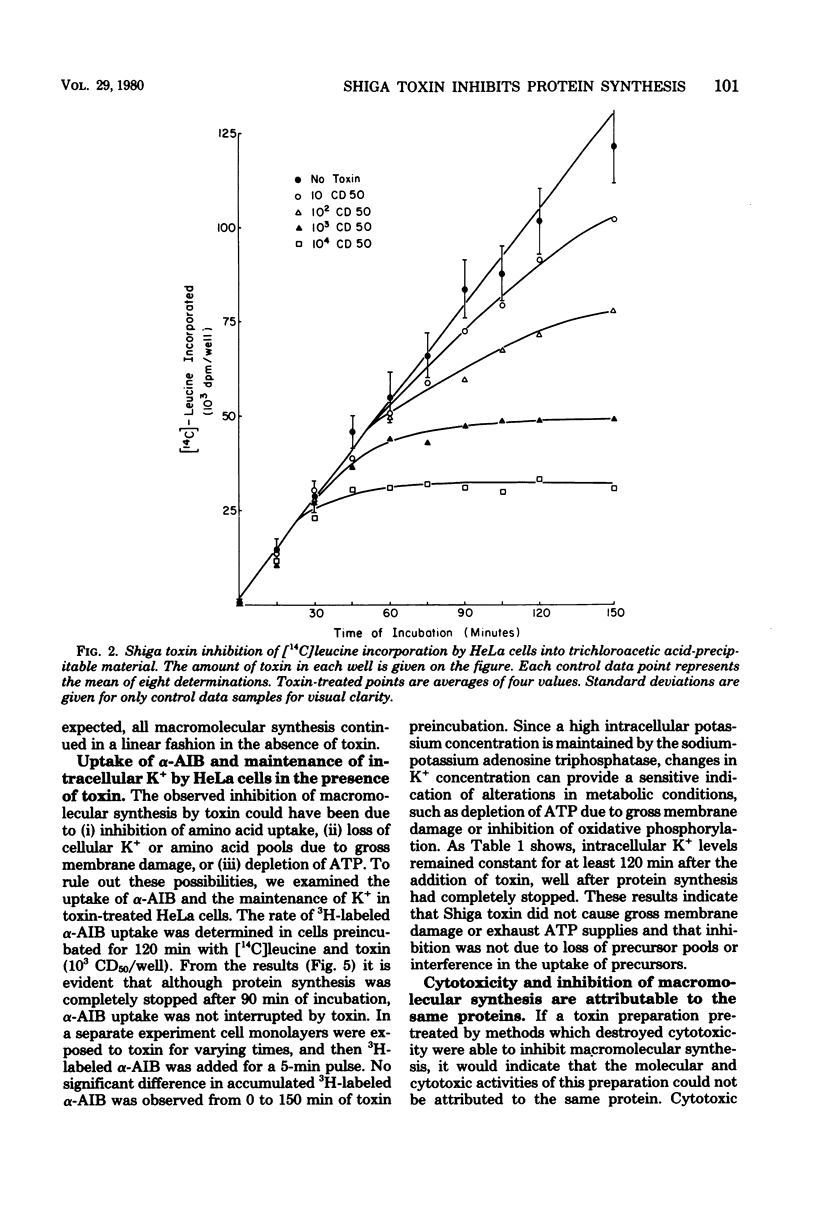
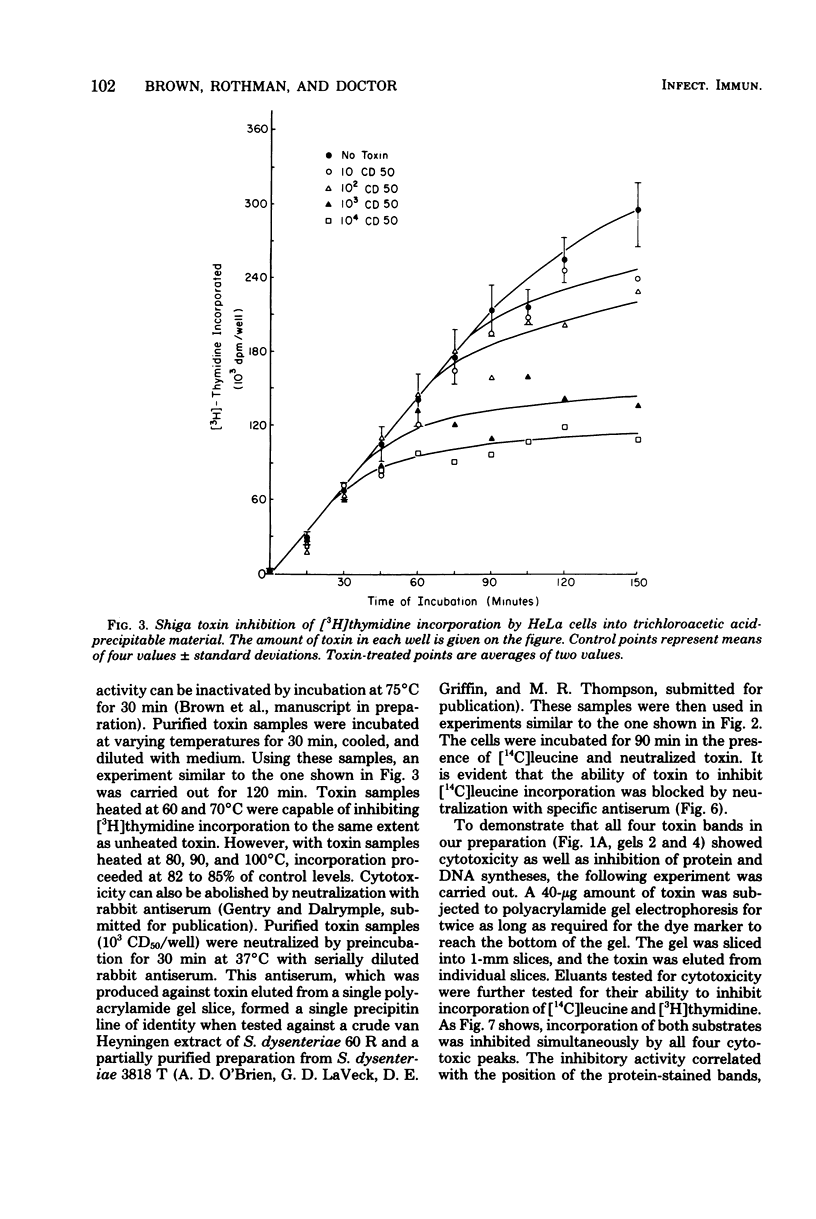
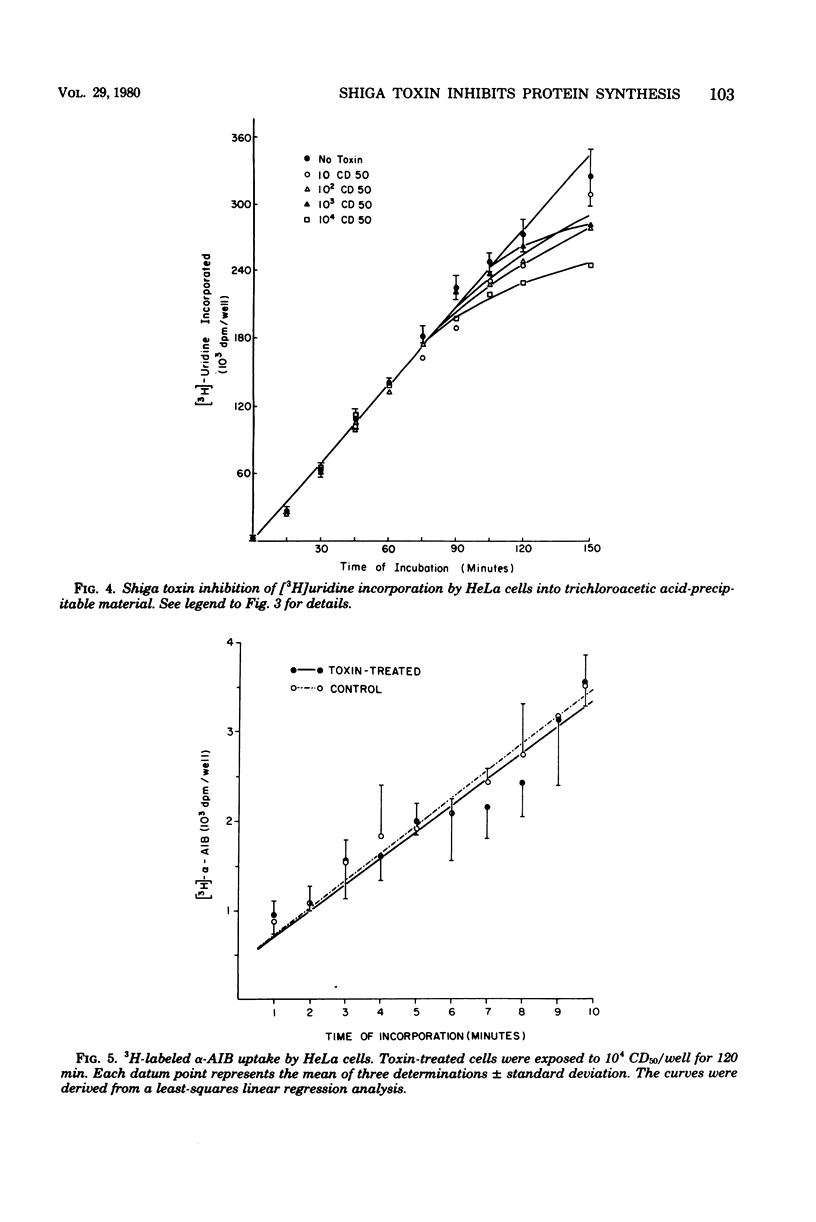
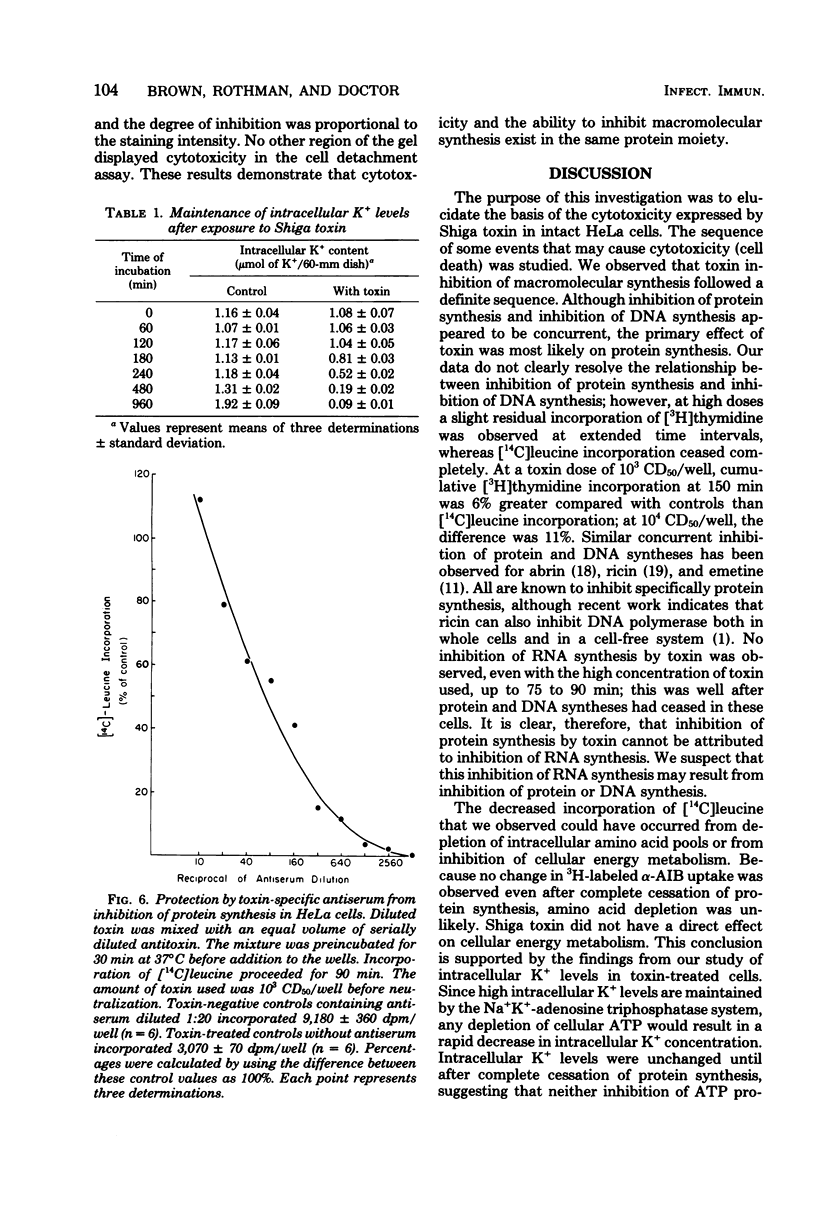
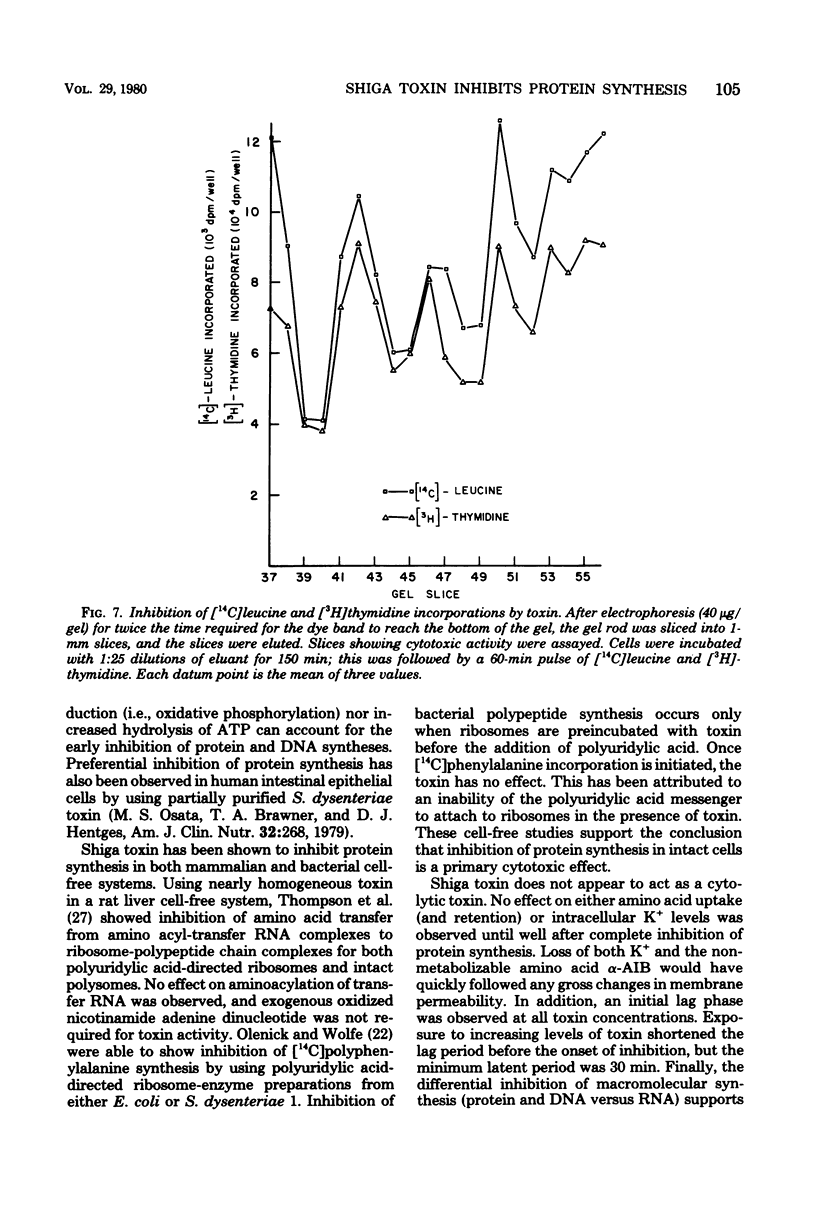
Shiga toxin purified to near homogeneity from cell lysates of Shigella dysenteriae 1 inhibited protein and deoxyribonucle acid syntheses in intact HeLa cells. Inhibition was dependent on toxin concentration and time of incubation. A minimal latent period of 30 min was observed with saturating doses of toxin. Ribonucleic acid synthesis, uptake of alpha-aminoisobutyric acid, and maintenance of intracellular K+ concentrations were not affected until well after maximal inhibition of protein and deoxyribonucleic acid syntheses. The inhibitory effect of toxin was sensitive to heat inactivation and was prevented by antibody neutralization. Several cytotoxic components were separated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the purified toxin preparations; all inhibited protein and deoxyribonucleic acid syntheses equally.
Full text
PDF




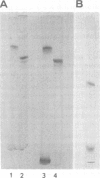
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhattacharya P., Simet I., Basu S. Inhibition of human neuroblastoma DNA polymerase activities by plant lectins and toxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2218–2221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder H. J., Whiting D. S. Inhibition of small-intestinal sugar and amino acid transport by the enterotoxin of Shigella dysenteriae I. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):510–512. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.510-512.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAVANAGH J. B., HOWARD J. G., WHITBY J. L. The neurotoxin of Shigella shigae; a comparative study of the effects produced in various laboratory animals. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Jun;37(3):272–278. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charney A. N., Gots R. E., Formal S. B., Giannella R. A. Activation of intestinal mucosal adenylate cyclase by Shigella dysenteriae I enterotoxin. Gastroenterology. 1976 Jun;70(6):1085–1090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donowitz M., Keusch G. T., Binder H. J. Effect of Shigella enterotoxin on electrolyte transport in rabbit ileum. Gastroenterology. 1975 Dec;69(6):1230–1237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Grady G. F., McIver J., Witkum P., Beckman B., Sharp G. W. Comparison of the effects of enterotoxins of Shigella dysenteriae and Vibrio cholerae on the adenylate cyclase system of the rabbit intestine. J Infect Dis. 1974 Oct;130(4):374–379. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.4.374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Jr, Takeuchi A., Washington O., Formal S. B. Shigellosis due to Shigella dysenteriae. 1. Relative importance of mucosal invasion versus toxin production in pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1972 Nov;126(5):523–530. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.5.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A., Carlson K., Rosenbaum J. L. Simple method for quantitive densitometry of polyacrylamide gels using fast green. Anal Biochem. 1970 Jun;35(2):359–370. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90196-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grollman A. P. Inhibitors of protein biosynthesis. V. Effects of emetine on protein and nucleic acid biosynthesis in HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1968 Aug 10;243(15):4089–4094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keusch G. T., Grady G. F., Mata L. J., McIver J. The pathogenesis of Shigella diarrhea. I. Enterotoxin production by Shigella dysenteriae I. J Clin Invest. 1972 May;51(5):1212–1218. doi: 10.1172/JCI106915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keusch G. T., Grady G. F., Takeuchi A., Sprinz H. The pathogenesis of shigella diarrhea. II. Enterotoxin-induced acute enteritis in the rabbit ileum. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jul;126(1):92–95. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.1.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keusch G. T., Jacewicz M., Hirschman S. Z. Quantitative microassay in cell culture for enterotoxin of Shigella dysenteriae. J Infect Dis. 1972 May;125(5):539–541. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.5.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keusch G. T., Jacewicz M. The pathogenesis of Shigella diarrhea. VI. Toxin and antitoxin in Shigella flexneri and Shigella sonnei infections in humans. J Infect Dis. 1977 Apr;135(4):552–556. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.4.552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrec E. H., Schneider H., Magnani T. J., Formal S. B. EPITHELIAL CELL PENETRATION AS AN ESSENTIAL STEP IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF BACILLARY DYSENTERY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88(5):1503–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1503-1518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. Y., Kao W. Y., Tserng K. Y., Chen C. C., Tung T. C. Effect of crystalline abrin on the biosynthesis of protein, RNA, and DNA in experimental tumors. Cancer Res. 1970 Sep;30(9):2431–2433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. Y., Liu K., Chen C. C., Tung T. C. Effect of crystalline ricin on the biosynthesis of protein, RNA, and DNA in experimental tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1971 Jul;31(7):921–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Thompson M. R., Gemski P., Doctor B. P., Formal S. B. Biological properties of Shigella flexneri 2A toxin and its serological relationship to Shigella dysenteriae 1 toxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):796–798. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.796-798.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olenick J. G., Wolfe A. D. Shigella toxin inhibition of binding and translation of polyuridylic acid by Escherichia coli ribosomes. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1246–1250. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1246-1250.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Eiklid K. Isolation and characterization of Shigella shigae cytotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):284–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Sandvig K., Eiklid K., Pihl A. Properties and action mechanism of the toxic lectin modeccin: interaction with cell lines resistant to modeccin, abrin, and ricin. J Supramol Struct. 1978;9(1):15–25. doi: 10.1002/jss.400090103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg S. E., Banwell J. G., Yardley J. H., Keusch G. T., Hendrix T. R. Comparison of secretory and histological effects of shigella and cholera enterotoxins in rabbit jejunum. Gastroenterology. 1975 Feb;68(2):309–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson M. R., Steinberg M. S., Gemski P., Formal S. B., Doctor B. P. Inhibition of in vitro protein synthesis by Shigella dysenteriae 1 toxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 9;71(3):783–788. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90899-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN HEYNINGEN W. E., GLADSTONE G. P. The neurotoxin of Shigella shigae. I. Production, purification and properties of the toxin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1953 Apr;34(2):202–216. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VICARI G., OLITZKI A. L., OLITZKI Z. The action of the thermolabile toxin of Shigella dysenteriae on cells cultivated in vitro. Br J Exp Pathol. 1960 Apr;41:179–189. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]