Abstract
Virulent Shigella sonnei synthesize a surface antigen (form I) which appears to be one of several requirements needed for this host to invade epithelial cells. Upon restreaking on agar media, form I cells readily and irreversibly generate form II cells that lack the form I antigen. All form II cells are avirulent. Plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid of form I and II cells of four different S. sonnei isolates, obtained from different areas of the world, was analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. A large plasmid (approximately 120 megadaltons in three of the strains) that is present in form I cells was always absent from form II derivatives. Attempts to transfer conjugally only this large plasmid from form I to genetically marked form II cells were unsuccessful. However, a composite molecule, apparently formed by recombination between the large form I plasmid and a self-transmissible plasmid, was found to transfer the form I trait. Transconjugant S. sonnei strains acquiring the form I antigen could retransfer this trait to S. sonnei, Shigella flexneri, or Salmonella typhi. These preliminary findings demonstrate that S. sonnei form I antigen synthesis is mediated by a large plasmid which is lost spontaneously at a relatively high frequency from S. sonnei strains.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Jr, Takeuchi A., Washington O., Formal S. B. Shigellosis due to Shigella dysenteriae. 1. Relative importance of mucosal invasion versus toxin production in pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1972 Nov;126(5):523–530. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.5.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
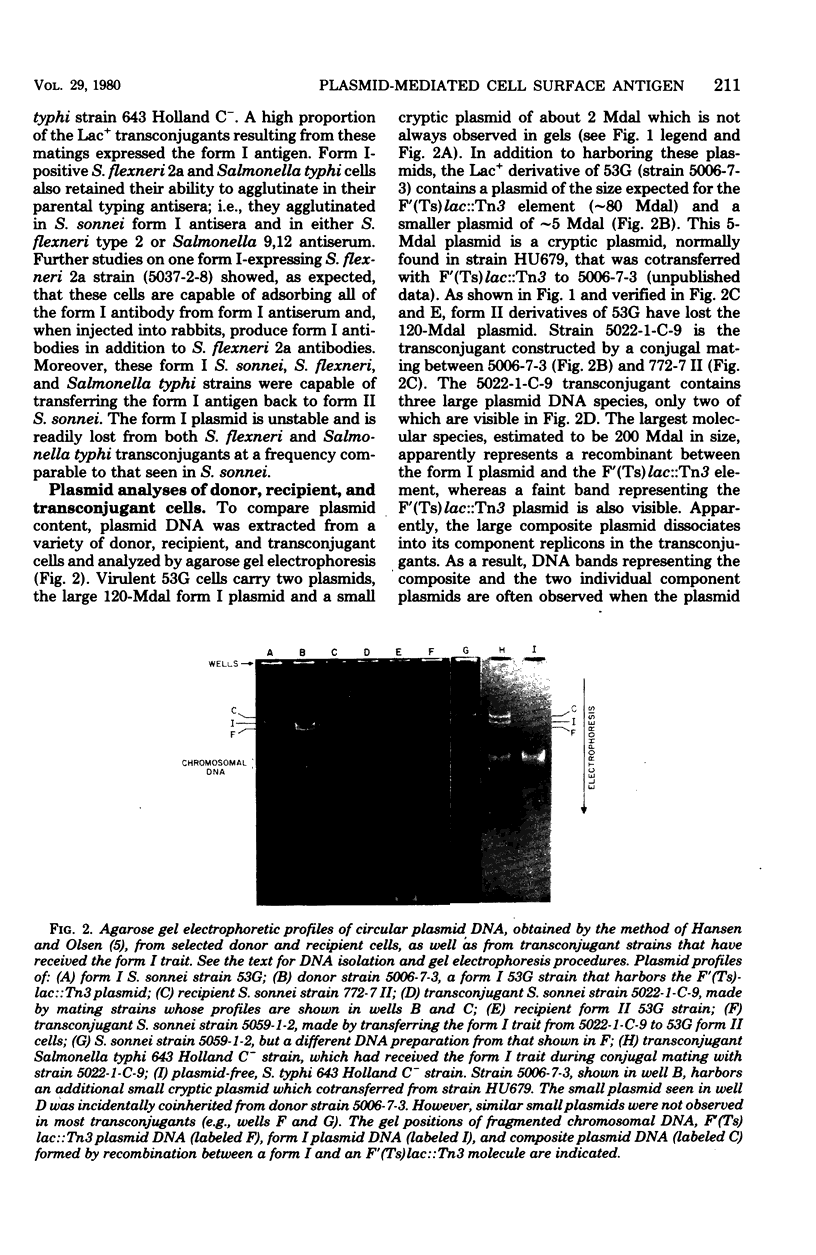
- Hansen J. B., Olsen R. H. Isolation of large bacterial plasmids and characterization of the P2 incompatibility group plasmids pMG1 and pMG5. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):227–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.227-238.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontrohr T. The identification of 2-amino-2-deoxy-L-altruronic acid as a constituent of Shigella sonnei phase I lipopolysaccharide. Carbohydr Res. 1977 Oct;58(2):498–500. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)84379-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopecko D. J., Holcombe J., Formal S. B. Molecular characterization of plasmids from virulent and spontaneously occurring avirulent colonial variants of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):580–582. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.580-582.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretschmer P. J., Cohen S. N. Selected translocation of plasmid genes: frequency and regional specificity of translocation of the Tn3 element. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):888–899. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.888-899.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrec E. H., Schneider H., Magnani T. J., Formal S. B. EPITHELIAL CELL PENETRATION AS AN ESSENTIAL STEP IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF BACILLARY DYSENTERY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88(5):1503–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1503-1518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Kopecko D. J., Jones K. R., Ayers D. J., McCowen S. M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERENY B. Experimental shigella keratoconjunctivitis; a preliminary report. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1955;2(3):293–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]