Abstract
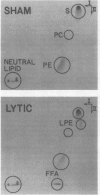
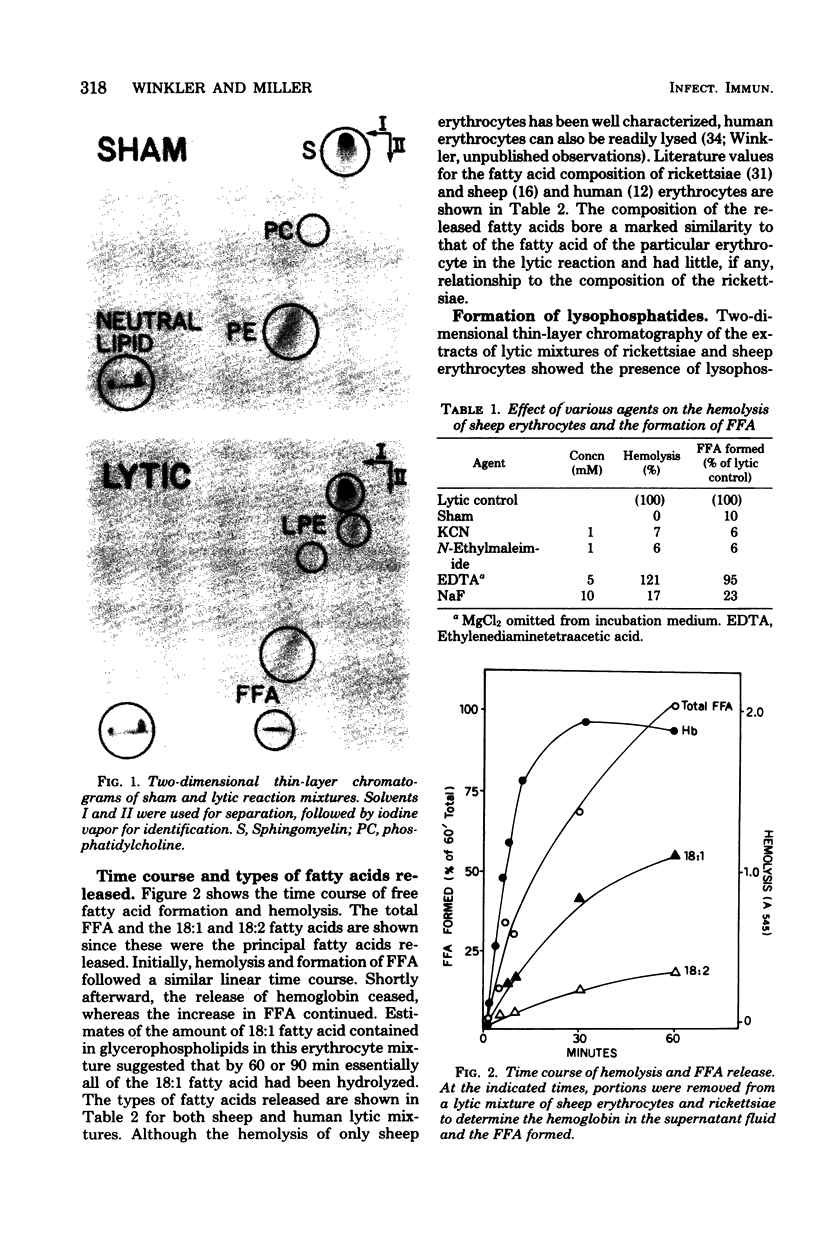
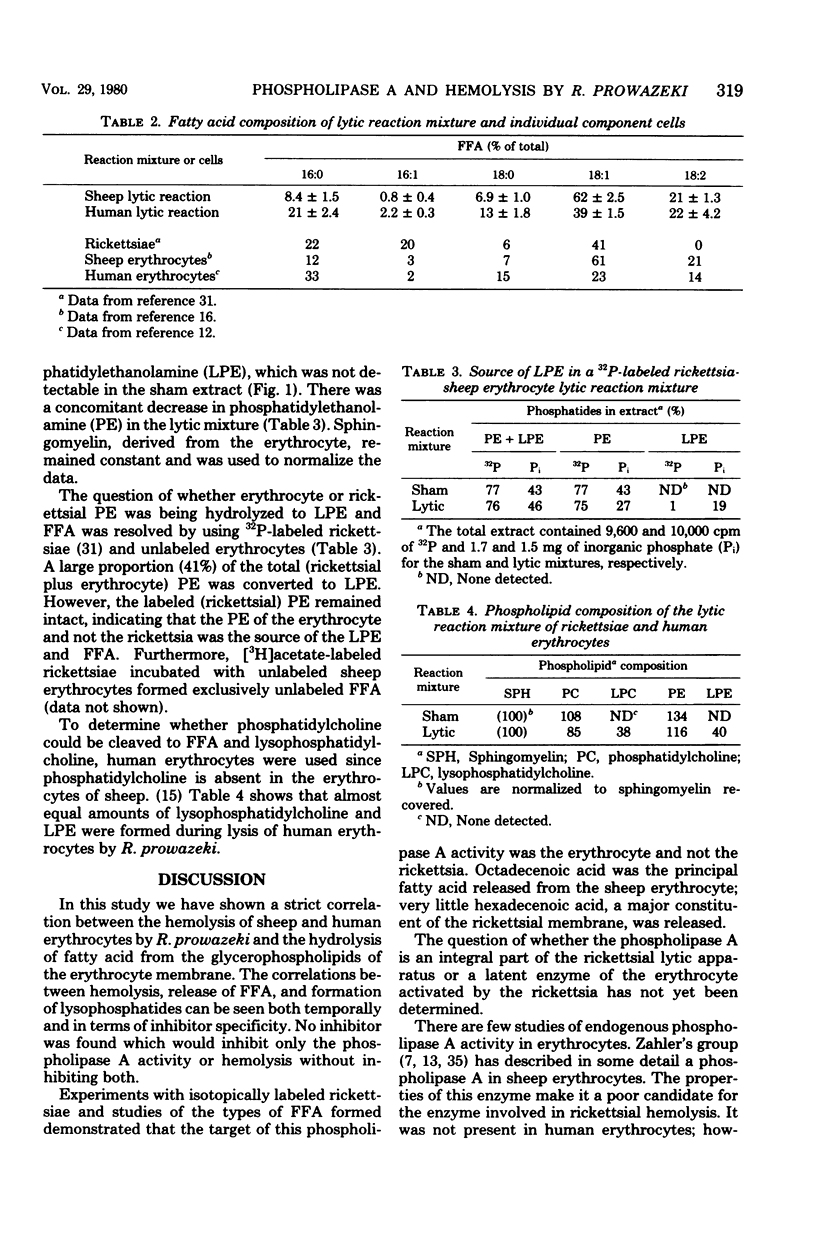
Incubation of Rickettsia prowazeki with sheep or human erythrocytes resulted in lysis of the erythrocytes and formation of free fatty acids and lysophosphatides. Inhibitors of lysis were also invariably inhibitors of this phospholipase A activity. The target for this activity was the glycerophospholipids of the erythrocyte and not those of the rickettsia. Rickettsial phosphatidylethanolamine labeled with 32PO4 or [3H]acetate remained intact during lysis, and the composition of the free fatty acids released resembled that of the erythrocyte species used and not the rickettsiae. The products of hydrolysis remained associated with the sedimentable material in the reaction mixture under the usual conditions but partitioned into the supernatant fluid when bovine serum albumin was present. Initially, the time course of phospholipase A activity and lysis was identical, but the release of free fatty acids continued for a short time after the release of hemoglobin was complete. Both the inner and outer leaflets of the erythrocyte membrane were accessible to this rickettsial phospholipase A activity since both phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine were substrates in human erythrocytes. The questions of whether rickettsiae possess their own phospholipase A or activate a latent erythrocyte enzyme and what the role of the energy requirement is in these processes remain unanswered.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOVARNICK M. R., MILLER J. C., SNYDER J. C. The influence of certain salts, amino acids, sugars, and proteins on the stability of rickettsiae. J Bacteriol. 1950 Apr;59(4):509–522. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.4.509-522.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., BOZEMAN F. M., CAMPBELL J. M., HUMPHRIES J. W., SAWYER T. K. Study on growth of Rickettsia. V. Penetration of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi into mammalian cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1959 Mar 1;109(3):271–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.3.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley C. M., Zwaal R. F., Roelofsen B., van Deenen L. L. Lytic and non-lytic degradation of phospholipids in mammalian erythrocytes by pure phospholipases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 25;307(1):74–82. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasch G. A., Weiss E. Characterization of the Madrid E strain of Rickettsia prowazekii purified by renografin density gradient centrifugation. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):280–286. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.280-286.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frei E., Zahler P. Phospholipase A2 from sheep erythrocyte membranes. Ca2+ dependence and localization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 2;550(3):450–463. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gambrill M. R., Wisseman C. L., Jr Mechanisms of immunity in typhus infections. I. Multiplication of typhus rickettsiae in human macrophage cell cultures in the nonimmune system: influence of virulence of rickettsial strains and of chloramphenicol. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):519–527. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.519-527.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb M. H. The reactivity of human erythrocyte membrane cholesterol with a cholesterol oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 2;466(3):422–428. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90335-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gul S., Smith A. D. Haemolysis of intact human erythrocytes by purified cobra venom phospholipase A2 in the presence of albumin and Ca2+. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 15;367(3):271–281. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90084-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOGL F., de GIER, MULDER I., van DEENEN L. Metabolism and functions of phosphatides. Specific fatty acid composition of the red blood cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Sep 9;43:95–103. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90411-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R., Jungi B., Zahler P. SomeSome characteristics of a phospholipase A2 from sheep red cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 24;373(3):404–415. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. K., Luthra M. G., Wells M. A., Watts R. P., Hanahan D. J. Phospholipase A2 as a probe of phospholipid distribution in erythrocyte membranes. Factors influencing the apparent specificity of the reaction. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 16;14(25):5400–5408. doi: 10.1021/bi00696a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson G. J. Lipid composition of erythrocytes in various mammalian species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 2;144(2):221–232. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson G. J. Studies on the lipids of sheep red blood cells. 3. The fayy acid composition of phospholipids in HK and LK cells. Lipids. 1969 Sep;4(5):350–355. doi: 10.1007/BF02531005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramm L. E., Winkler H. H. Identification of cholesterol in the receptor site for rickettsiae on sheep erythrocyte membranes. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):120–126. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.120-126.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramm L. E., Winkler H. H. Rickettsial hemolysis: adsorption of rickettsiae to erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1973 Jan;7(1):93–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.1.93-99.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramm L. E., Winkler H. H. Rickettsial hemolysis: effect of metabolic inhibitors upon hemolysis and adsorption. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):550–555. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.550-555.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rikihisa Y., Ito S. Intracellular localization of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):703–708. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelofsen B., Zwaal R. F., Comfurius P., Woodward C. B., van Deenen L. L. Action of pure phospholipase A 2 and phospholipase C on human erythrocytes and ghosts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 14;241(3):925–929. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouser G., Fkeischer S., Yamamoto A. Two dimensional then layer chromatographic separation of polar lipids and determination of phospholipids by phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids. 1970 May;5(5):494–496. doi: 10.1007/BF02531316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNYDER J. C., BOVARNICK M. R., MILLER J. C., CHANG R. S. M. Observations on the hemolytic properties of typhus rickettsiae. J Bacteriol. 1954 Jun;67(6):724–730. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.6.724-730.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISSEMAN C. L., Jr, JACKSON E. B., HAHN F. E., LEY A. C., SMADEL J. E. Metabolic studies of rickettsiae. I. The effects of antimicrobial substances and enzyme inhibitors on the oxidation of glutamate by purified rickettsiae. J Immunol. 1951 Aug;67(2):123–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. S., Winkler H. H. Penetration of cultured mouse fibroblasts (L cells) by Rickettsia prowazeki. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):200–208. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.200-208.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. S., Winkler H. H. Rickettsial hemolysis: rapid method for enumeration of metabolically active typhus rickettsiae. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 May;9(5):645–647. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.5.645-647.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Coolbaugh J. C., Williams J. C. Separation of viable Rickettsia typhi from yolk sac and L cell host components by renografin density gradient centrifugation. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Sep;30(3):456–463. doi: 10.1128/am.30.3.456-463.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H. Inhibitory and restorative effects of adenine nucleotides on rickettsial adsorption and hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):119–126. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.119-126.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Miller E. T. Phospholipid composition of Rickettsia prowazeki grown in chicken embryo yolk sacs. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):175–178. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.175-178.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Ramm L. E. Adsorption of typhus rickettsiae to ghosts of sheep erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1244–1251. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1244-1251.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H. Rickettsial hemolysis: adsorption, desorption, readsorption, and hemagglutination. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):607–612. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.607-612.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H. Rickettsial permeability. An ADP-ATP transport system. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):389–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaal R. F., Flückiger R., Moser S., Zahler P. Lecithinase activities at the external surface of ruminant erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 24;373(3):416–424. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaal R. F., Roelofsen B., Colley C. M. Localization of red cell membrane constituents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 10;300(2):159–182. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(73)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]