Abstract
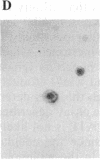
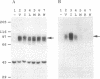
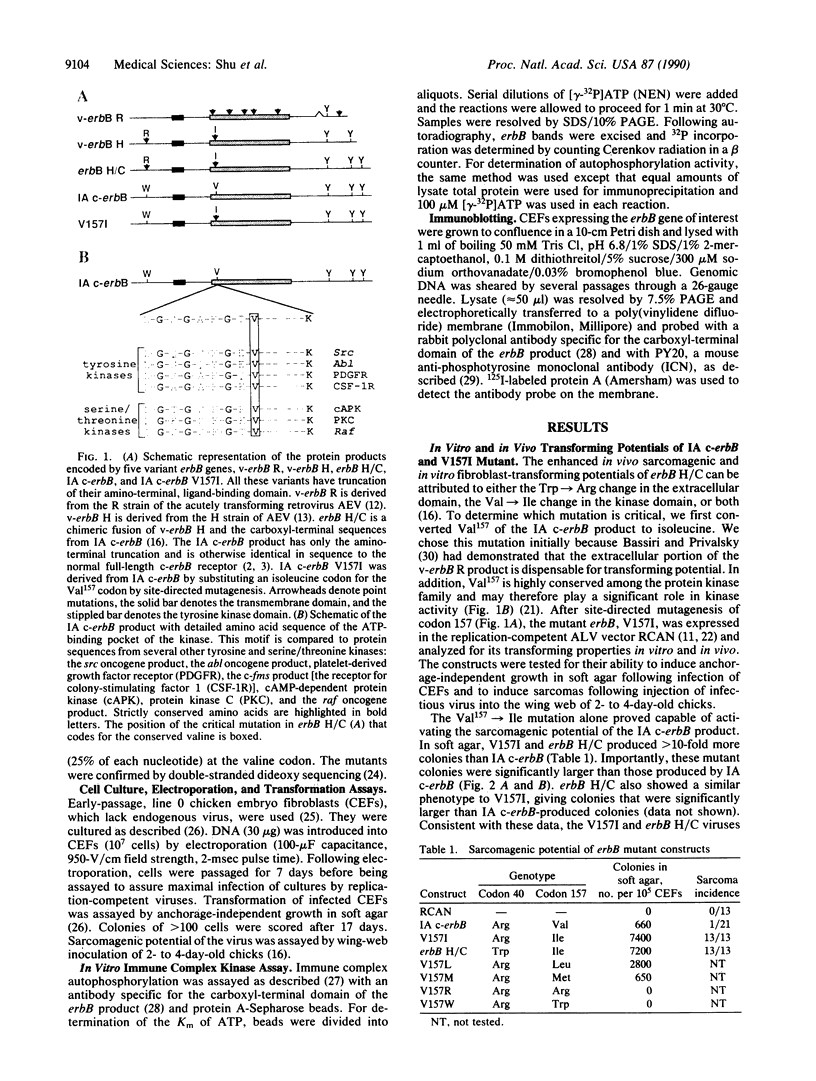
Avian c-erbB is activated to a leukemia oncogene following truncation of its amino-terminal, ligand-binding domain by retroviral insertion. The insertionally activated transcripts encode protein products that have constitutive tyrosine kinase activity and that can induce erythro-leukemia but not sarcomas. We have found that a single point mutation within the ATP-binding pocket of the tyrosine kinase domain in this truncated molecule can increase the ability of this oncogene to induce anchorage-independent growth of fibroblasts in vitro and fibrosarcoma formation in vivo. Associated with this increased transforming potential is a corresponding increase in the kinase activity of the mutant erbB protein product. The mutation, which converts a valine to isoleucine at position 157 of the insertionally activated c-erbB product, is at a residue that is highly conserved within the protein kinase family. To our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of a point mutation in the ATP-binding pocket that activates a tyrosine kinase.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antczak M., Kung H. J. Transformation of chicken embryo fibroblasts by direct DNA transfection of single oncogenes: comparative analyses of src, erbB, myc, and ras. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1451–1458. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1451-1458.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astrin S. M., Buss E. G., Haywards W. S. Endogenous viral genes are non-essential in the chicken. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):339–341. doi: 10.1038/282339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassiri M., Privalsky M. L. Transmembrane domain of the AEV erb B oncogene protein is not required for partial manifestation of the transformed phenotype. Virology. 1987 Jul;159(1):20–30. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90343-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertics P. J., Chen W. S., Hubler L., Lazar C. S., Rosenfeld M. G., Gill G. N. Alteration of epidermal growth factor receptor activity by mutation of its primary carboxyl-terminal site of tyrosine self-phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3610–3617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertics P. J., Weber W., Cochet C., Gill G. N. Regulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor by phosphorylation. J Cell Biochem. 1985;29(3):195–208. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240290304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorge J. D., Chan T. O., Antczak M., Kung H. J., Fujita D. J. Activated type I phosphatidylinositol kinase is associated with the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor following EGF stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3816–3820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. S., Lazar C. S., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Requirement for intrinsic protein tyrosine kinase in the immediate and late actions of the EGF receptor. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):820–823. doi: 10.1038/328820a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi O. R., Trainor C., Graf T., Beug H., Engel J. D. A single amino acid substitution in v-erbB confers a thermolabile phenotype to ts167 avian erythroblastosis virus-transformed erythroid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1751–1759. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Carpenter G., King L., Jr Epidermal growth factor-receptor-protein kinase interactions. Co-purification of receptor and epidermal growth factor-enhanced phosphorylation activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4834–4842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Yarden Y., Mayes E., Scrace G., Totty N., Stockwell P., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):521–527. doi: 10.1038/307521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. K., Lewis W. G., Crittenden L. B., Kung H. J. Activation of the cellular oncogene c-erbB by LTR insertion: molecular basis for induction of erythroblastosis by avian leukosis virus. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):357–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90417-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T., DeClue J. E., Martin G. S. Protein phosphorylation at tyrosine is induced by the v-erbB gene product in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):609–618. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90209-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin R. G., Rottman F. M., Callaghan T., Kung H. J., Maroney P. A., Nilsen T. W. c-erbB activation in avian leukosis virus-induced erythroblastosis: multiple epidermal growth factor receptor mRNAs are generated by alternative RNA processing. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3128–3133. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hihara H., Yamamoto H., Shimohira H., Arai K., Shimizu T. Avian erythroblastosis virus isolated from chick erythroblastosis induced by lymphatic leukemia virus subgroup A. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 May;70(5):891–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Dull T. J., Felder S., Van Obberghen E., Bellot F., Szapary D., Schmidt A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Point mutation at the ATP binding site of EGF receptor abolishes protein-tyrosine kinase activity and alters cellular routing. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90147-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Greenhouse J. J., Petropoulos C. J., Sutrave P. Adaptor plasmids simplify the insertion of foreign DNA into helper-independent retroviral vectors. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3004–3012. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3004-3012.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Most of the substrates of oncogenic viral tyrosine protein kinases can be phosphorylated by cellular tyrosine protein kinases in normal cells. Oncogene Res. 1988 Sep;3(2):105–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kris R. M., Lax I., Gullick W., Waterfield M. D., Ullrich A., Fridkin M., Schlessinger J. Antibodies against a synthetic peptide as a probe for the kinase activity of the avian EGF receptor and v-erbB protein. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):619–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90210-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax I., Johnson A., Howk R., Sap J., Bellot F., Winkler M., Ullrich A., Vennstrom B., Schlessinger J., Givol D. Chicken epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor: cDNA cloning, expression in mouse cells, and differential binding of EGF and transforming growth factor alpha. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1970–1978. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maihle N. J., Raines M. A., Flickinger T. W., Kung H. J. Proviral insertional activation of c-erbB: differential processing of the protein products arising from two alternate transcripts. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4868–4876. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Rapp U., Roberts T. M. Signal transduction from membrane to cytoplasm: growth factors and membrane-bound oncogene products increase Raf-1 phosphorylation and associated protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8855–8859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W., Maroney P. A., Goodwin R. G., Rottman F. M., Crittenden L. B., Raines M. A., Kung H. J. c-erbB activation in ALV-induced erythroblastosis: novel RNA processing and promoter insertion result in expression of an amino-truncated EGF receptor. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):719–726. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80052-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelley R. J., Maihle N. J., Boerkoel C., Shu H. K., Carter T. H., Moscovici C., Kung H. J. Disease tropism of c-erbB: effects of carboxyl-terminal tyrosine and internal mutations on tissue-specific transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7164–7168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelley R. J., Moscovici C., Hughes S., Kung H. J. Proviral-activated c-erbB is leukemogenic but not sarcomagenic: characterization of a replication-competent retrovirus containing the activated c-erbB. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1840–1844. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1840-1844.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Livneh E., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Mutations in the cytoplasmic domain of EGF receptor affect EGF binding and receptor internalization. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2179–2190. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04482.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines M. A., Lewis W. G., Crittenden L. B., Kung H. J. c-erbB activation in avian leukosis virus-induced erythroblastosis: clustered integration sites and the arrangement of provirus in the c-erbB alleles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2287–2291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines M. A., Maihle N. J., Moscovici C., Crittenden L., Kung H. J. Mechanism of c-erbB transduction: newly released transducing viruses retain poly(A) tracts of erbB transcripts and encode C-terminally intact erbB proteins. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2437–2443. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2437-2443.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines M. A., Maihle N. J., Moscovici C., Moscovici M. G., Kung H. J. Molecular characterization of three erbB transducing viruses generated during avian leukosis virus-induced erythroleukemia: extensive internal deletion near the kinase domain activates the fibrosarcoma- and hemangioma-inducing potentials of erbB. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2444–2452. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2444-2452.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M. F., Dull T. J., Rettenmier C. W., Ralph P., Ullrich A., Sherr C. J. Transforming potential of the c-fms proto-oncogene (CSF-1 receptor). Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):549–552. doi: 10.1038/325549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M. A., Bishop J. M., McGrath J. P., Levinson A. D. A mutation at the ATP-binding site of pp60v-src abolishes kinase activity, transformation, and tumorigenicity. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1772–1779. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Hanafusa H. Structure and sequence of the cellular gene homologous to the RSV src gene and the mechanism for generating the transforming virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):881–890. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Ott J., Eckstein F. The rapid generation of oligonucleotide-directed mutations at high frequency using phosphorothioate-modified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8765–8785. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy S. E., Woda B. A., Robinson H. L. Induction of angiosarcoma by a c-erbB transducing virus. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):304–310. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.304-310.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugurbil K., Guernsey D. L., Brown T. R., Glynn P., Tobkes N., Edelman I. S. 31P NMR studies of intact anchorage-dependent mouse embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4843–4847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Bishop J. M. Isolation and characterization of chicken DNA homologous to the two putative oncogenes of avian erythroblastosis virus. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Daniel T. O., Carpenter G. Antiphosphotyrosine recovery of phospholipase C activity after EGF treatment of A-431 cells. Science. 1988 Aug 19;241(4868):968–970. doi: 10.1126/science.2457254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Nishibe S., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Epidermal growth factor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II independently of receptor internalization and extracellular calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1568–1572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Hihara H., Nishida T., Kawai S., Toyoshima K. A new avian erythroblastosis virus, AEV-H, carries erbB gene responsible for the induction of both erythroblastosis and sarcomas. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Nishida T., Miyajima N., Kawai S., Ooi T., Toyoshima K. The erbB gene of avian erythroblastosis virus is a member of the src gene family. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90209-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]