Abstract
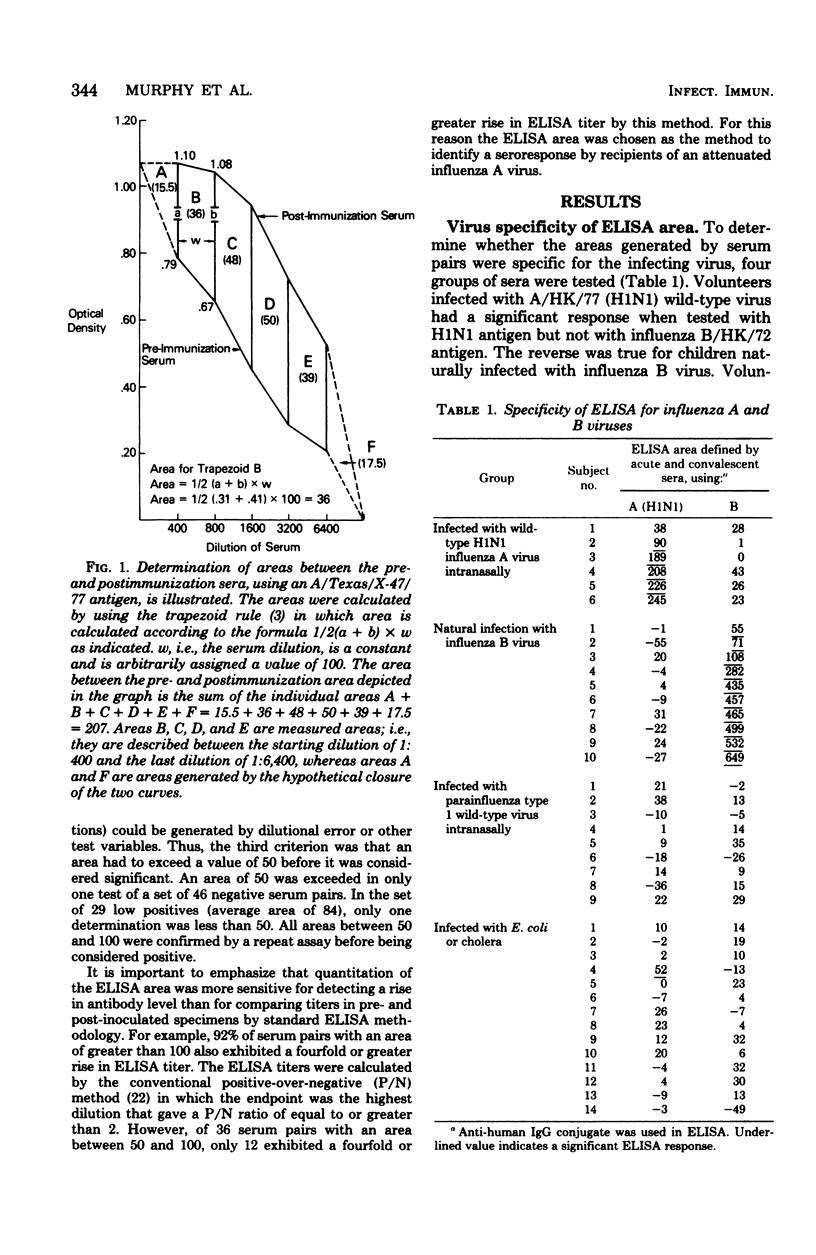
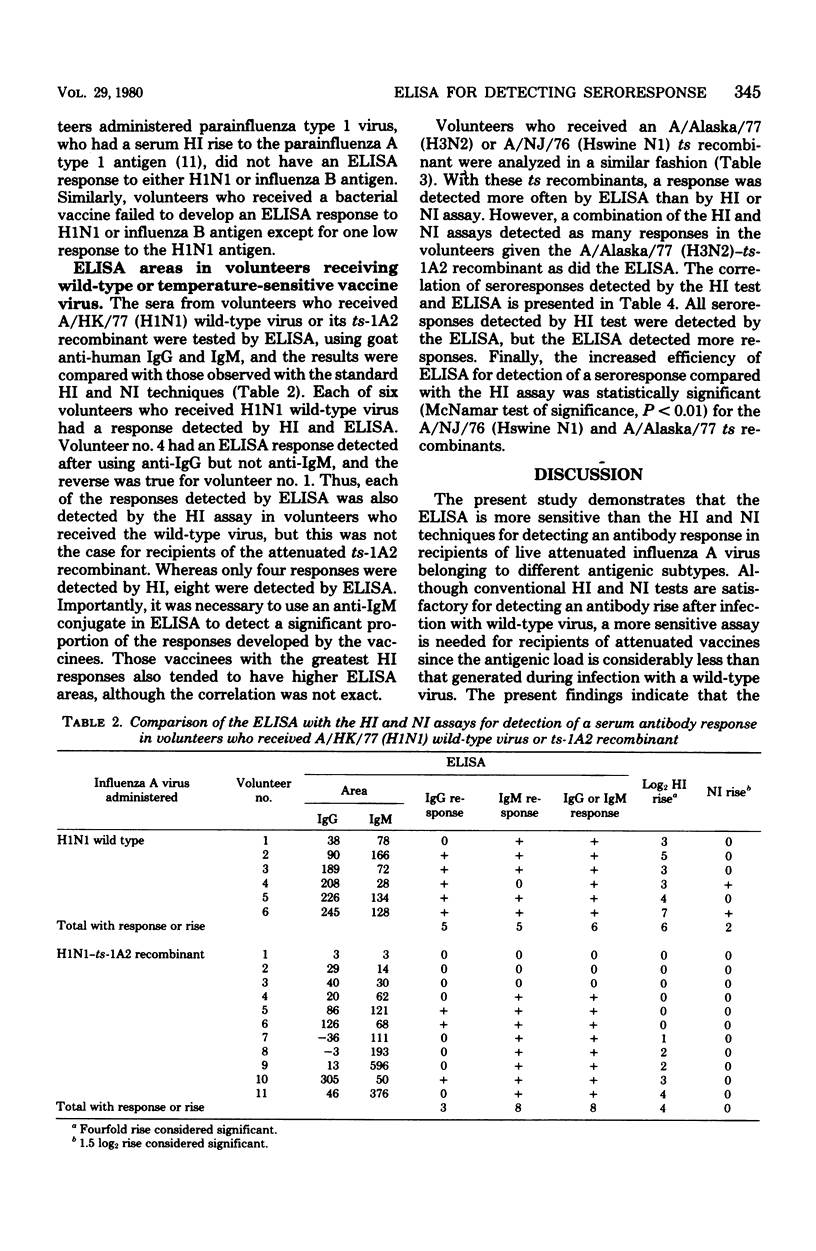
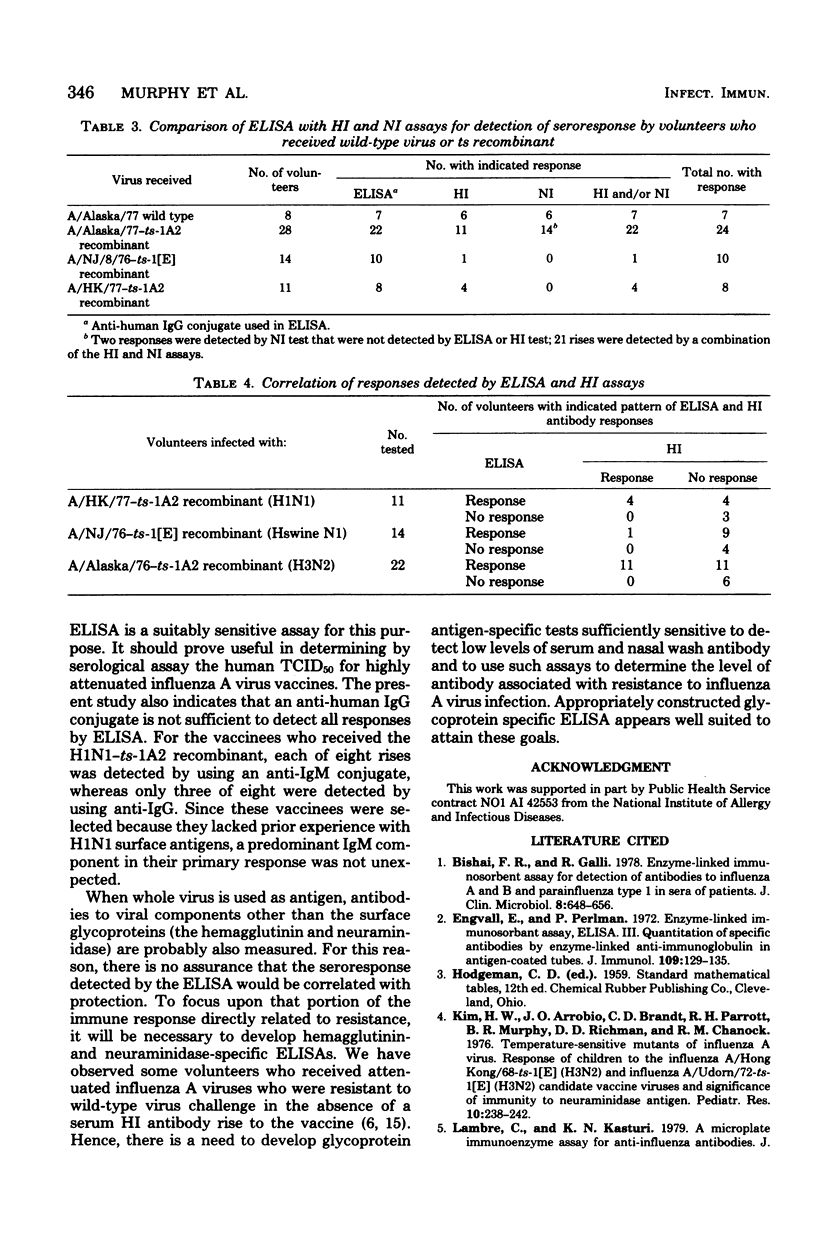
Sera from volunteers who received live influenza A wild-type or ts recombinant virus were tested by hemagglutination inhibition (HI) assay, neuraminidase inhibition (NI) assay, and the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to determine which assay system was the most sensitive in detecting an immunological response to infection. The ELISA was performed with inactivated whole virus antigen, and the optical density at each of five serial twofold dilutions of pre- and postimmunization sera was measured. The difference in the amount of ELISA antibody in pre- and postinoculation serum specimens was taken to be proportional to the area between the respective titration curves. The ELISA was more sensitive than the HI or NI test in detecting a seroresponse in volunteers infected with A/Hong Kong/123/77 (H1N1), A/New Jersey/8/76 (Hswine N1), or A/Alaska/6/77 (H3N2) ts recombinant virus. These results suggest that the ELISA should be used to determine the frequency of infection with attenuated viruses as well as the 50% human infectious dose of candidate live influenza A vaccine viruses.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishai F. R., Galli R. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibodies to influenza A and B and parainfluenza type 1 in sera of patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Dec;8(6):648–656. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.6.648-656.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. W., Arrobio J. O., Brandt C. D., Parrott R. H., Murphy B. R., Richman D. D., Chanock R. M. Temperature-sensitive mutants of influenza A virus: response of children to the influenza A/Hong Kong/68-ts-1(E) (H3N2) and influenza A/Udorn/72-ts-1(E) (H3N2) candidate vaccine viruses and significance of immunity to neuraminidase antigen. Pediatr Res. 1976 Apr;10(4):238–242. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197604000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambre C., Kasturi K. N. A microplate immunoenzyme assay for anti-influenza antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1979;26(1):61–67. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. R., Chalhub E. G., Nusinoff S. R., Chanock R. M. Temperature-sensitive mutants of influenza virus. II. Attenuation of ts recombinants for man. J Infect Dis. 1972 Aug;126(2):170–178. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.2.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. R., Chanock R. M., Levine M. M., van Blerk G. A., Berquist E. J., Douglas R. G., Betts R. F., Couch R. B., Cate T. R., Jr Temperature-sensitive mutants of influenza A virus: evaluation of the A/Victoria/75-ts-1A2 temperature-sensitive recombinant virus in seronegative adult volunteers. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):249–252. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.249-252.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. R., Markoff L. J., Hosier N. T., Rusten H. M., Chanock R. M., Kendal A. P., Douglas R. G., Betts R. F., Cate T. R., Jr, Couch R. B. Temperature-sensitive mutants of influenza A virus: evaluation of A/Victoria/3/75-ts-1[E] recombinant viruses in volunteers. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):671–677. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.671-677.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. R., Rennels M. B., Douglas R. G., Jr, Betts R. F., Couch R. B., Cate T. R., Jr, Chanock R. M., Kendal A. P., Maassab H. F., Suwanagool S. Evaluation of influenza A/Hong Kong/123/77 (H1N1) ts-1A2 and cold-adapted recombinant viruses in seronegative adult volunteers. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):348–355. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.348-355.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. R., Richman D. D., Chalhub E. G., Uhlendorf C. P., Baron S., Chanock R. M. Failure of attenuated temperature-sensitive influenza A (H3N2) virus to induce heterologous interference in humans to parainfluenza type 1 virus. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):62–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.62-68.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. R., Richman D. D., Spring S. B., Chanock R. M. Use of temperature-sensitive mutants of influenza A virus as live virus vaccine strains. Evaluation in laboratory animals, adults and children. Postgrad Med J. 1976 Jun;52(608):381–388. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.52.608.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford J. S., Schild G. C. Immunological and physicochemical studies of influenza matrix (M) polypeptides. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):394–402. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90345-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Murphy B. R., Chanock R. M., Gwaltney J. M., Jr, Douglas R. G., Betts R. F., Blacklow N. R., Rose F. B., Parrino T. A., Levine M. M. Temperature-sensitive mutants of influenza A virus. XII. Safety, antigenicity, transmissibility, and efficacy of influenza A/Udorn/72-ts-1[E] recombinant viruses in human adults. J Infect Dis. 1976 Dec;134(6):585–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Murphy B. R., Spring S. B., Coleman M. T., Chanock R. M. Temperature sensitive mutants of influenza virus. IX. Genetic and biological characterization of TS-1[E] lesions when transferred to a 1972 (H3N2) influenza A virus. Virology. 1975 Aug;66(2):551–562. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90227-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Six H. R., Kasel J. A. Radioimmunoprecipitation assay for quantitation of serum antibody to the hemagglutinin of type A influenza virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Feb;7(2):165–171. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.2.165-171.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spring S. B., Nusinoff S. R., Mills J., Richman D. D., Tierney E. L., Murphy B. R., Chanock R. M. Temperature-sensitive mutants of influenza virus. VI. Transfer of TS lesions from the Asian subtype of influenza A virus (H2N2) to the Hong Kong subtype (H3N2). Virology. 1975 Aug;66(2):522–532. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90224-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A. Enzyme immunoassays in diagnostic medicine. Theory and practice. Bull World Health Organ. 1976;53(1):55–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright P. F., Sell S. H., Shinozaki T., Thompson J., Karzon D. T. Safety and antigenicity of influenza A/Hong Kong/68-ts-1 (E) (H3N2). J Pediatr. 1975 Dec;87(6 Pt 2):1109–1116. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80123-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Kim H. W., Clem T., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for detection of human reovirus-like agent of infantile gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1977 Aug 6;2(8032):263–267. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90951-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Wyatt R. G., Kim H. W., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Immunological response to infection with human reovirus-like agent: measurement of anti-human reovirus-like agent immunoglobulin G and M levels by the method of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):540–546. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.540-546.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


