Abstract
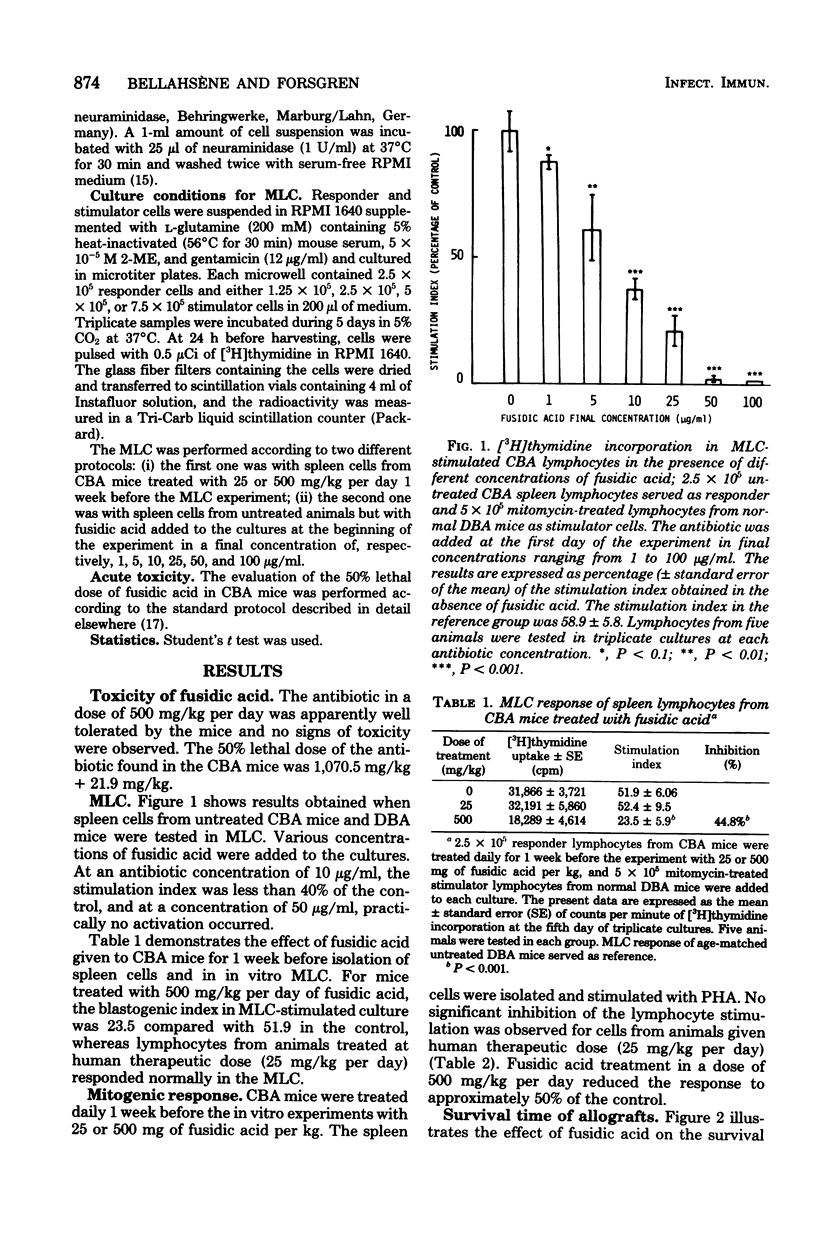
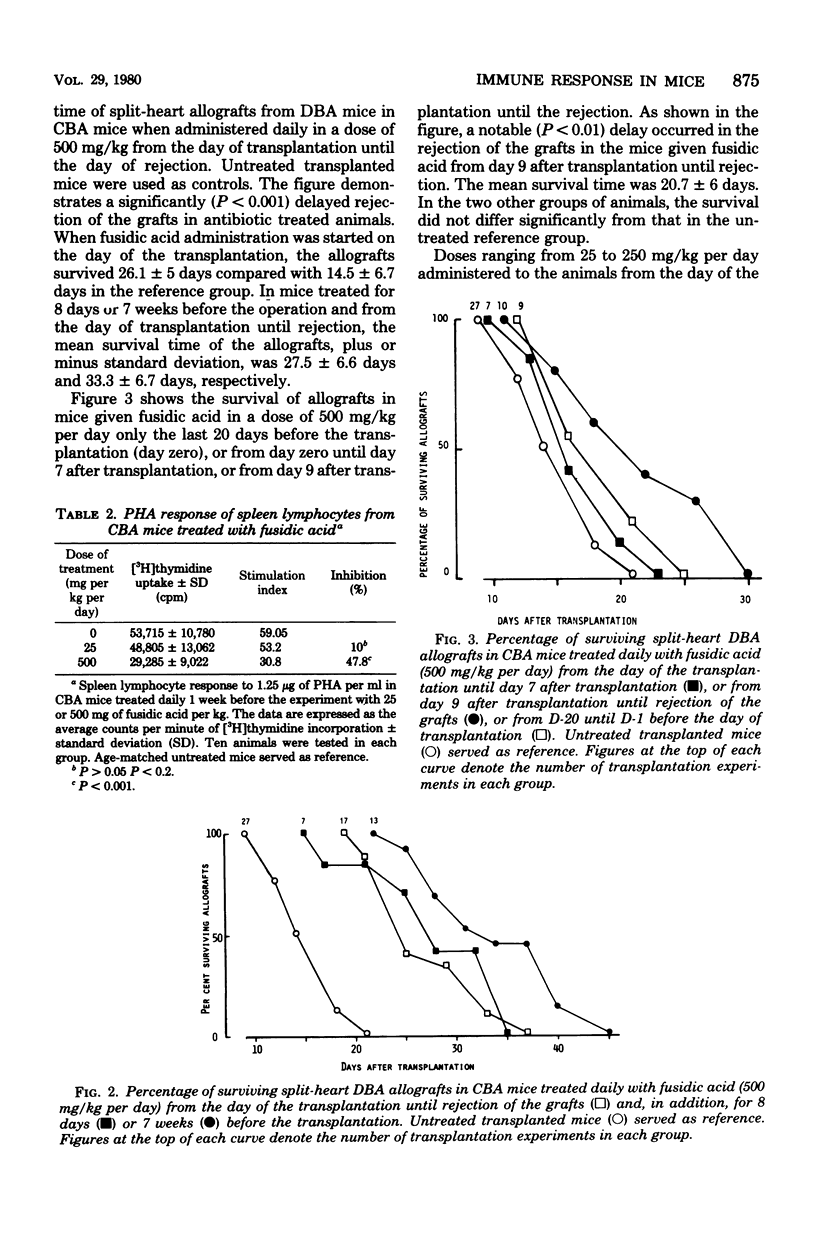
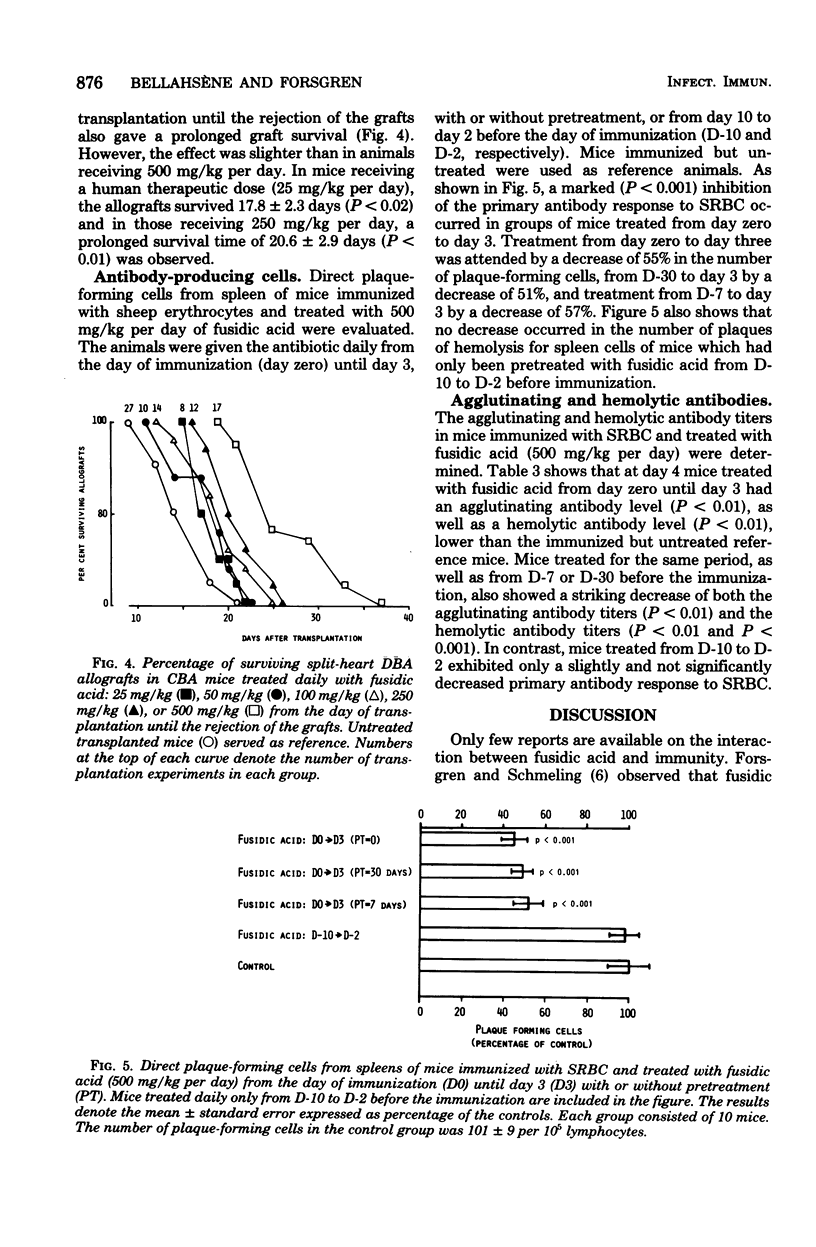
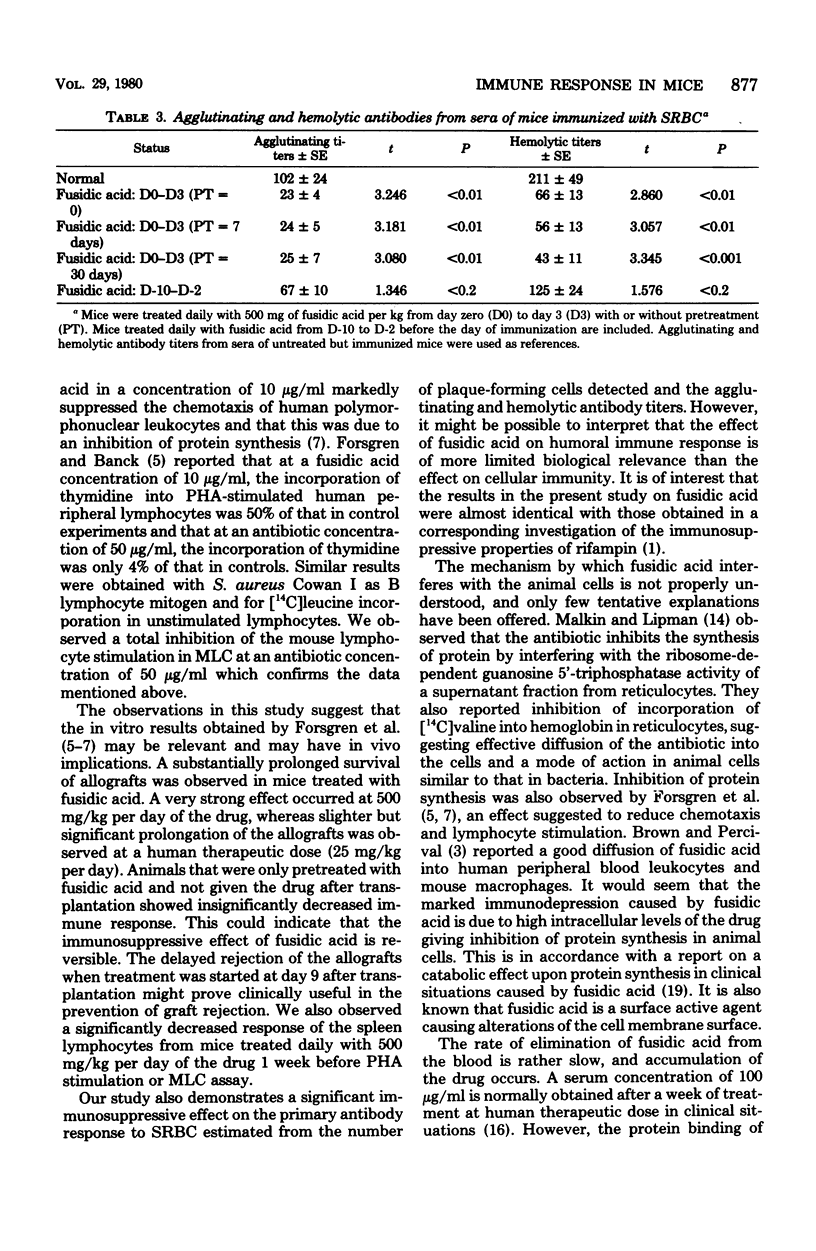
The effect of fusidic acid on the immune response in mice was studied. At the nontoxic dose of 500 mg/kg per day, the cell-mediated immunity was strongly inhibited. A marked and significant prolonged survival of split-heart allografts in treated animals was detected. The survival time of allografts in mice receiving fusidic acid from the day of the transplantation until the grafts were rejected was 26.1 days compared with 14.5 days in untreated animals. In mice treated also before the transplantation, the mean survival of the allografts were even longer. The phytohemagglutinin response, as well as the mixed lymphocyte culture stimulation of spleen lymphocytes from mice given 500 mg of fusidic acid per kg daily for 1 week, were significantly inhibited. At the same dose there was also a significantly decreased primary antibody response to sheep erythrocytes, but it was of limited biological significance. The immunosuppressive effect in animals treated with a human therapeutic dose of fusidic acid (25 mg/kg per day) was less pronounced but significant. The relevance of these results is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellahsène A., Forsgren A. Effect of rifampin on the immune response in mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):15–20. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.15-20.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. N., Percival A. Penetration of antimicrobials into tissue culture cells and leucocytes. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(14):251–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Pratt K. R. Polyclonal activation of bone-marrow-derived lymphocytes from human peripheral blood measured by a direct plaque-forming cell assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3676–3679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Schmeling D. Effect of antibiotics of chemotaxis of human leukocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):580–584. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Svedjelund A., Wigzell H. Lymphocyte stimulation by protein A of Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Mar;6(3):207–213. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güttler F., Tybring L., Engberg-Pedersen H. Interaction of albumin and fusidic acid. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Sep;43(1):151–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb07164.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K., Nordin A. A. Plaque Formation in Agar by Single Antibody-Producing Cells. Science. 1963 Apr 26;140(3565):405–405. doi: 10.1126/science.140.3565.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerrells T. R., Dean J. H., Richardson G. L., Herberman R. B. Depletion of monocytes from human peripheral blood mononuclear leukocytes: comparison of the sephadex G-10 column method with other commonly used techniques. J Immunol Methods. 1980;32(1):11–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judd K. P., Trentin J. J. Cardiac transplantation in mice. I. Factors influencing the take and survival of heterotopic grafts. Transplantation. 1971 Mar;11(3):298–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin M., Lipmann F. Fusidic acid: inhibition of factor T2 in reticulocyte protein synthesis. Science. 1969 Apr 4;164(3875):71–72. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3875.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemlander A., Andersson L. C., Häyry P. Rat mixed lymphocyte culture: optimization of culture conditions. Scand J Immunol. 1979;10(5):437–446. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb01373.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYNN V. METABOLIC EFFECTS OF THE STEROID ANTIBIOTIC FUSIDIC ACID. Br Med J. 1965 May 29;1(5447):1400–1404. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5447.1400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


