Abstract
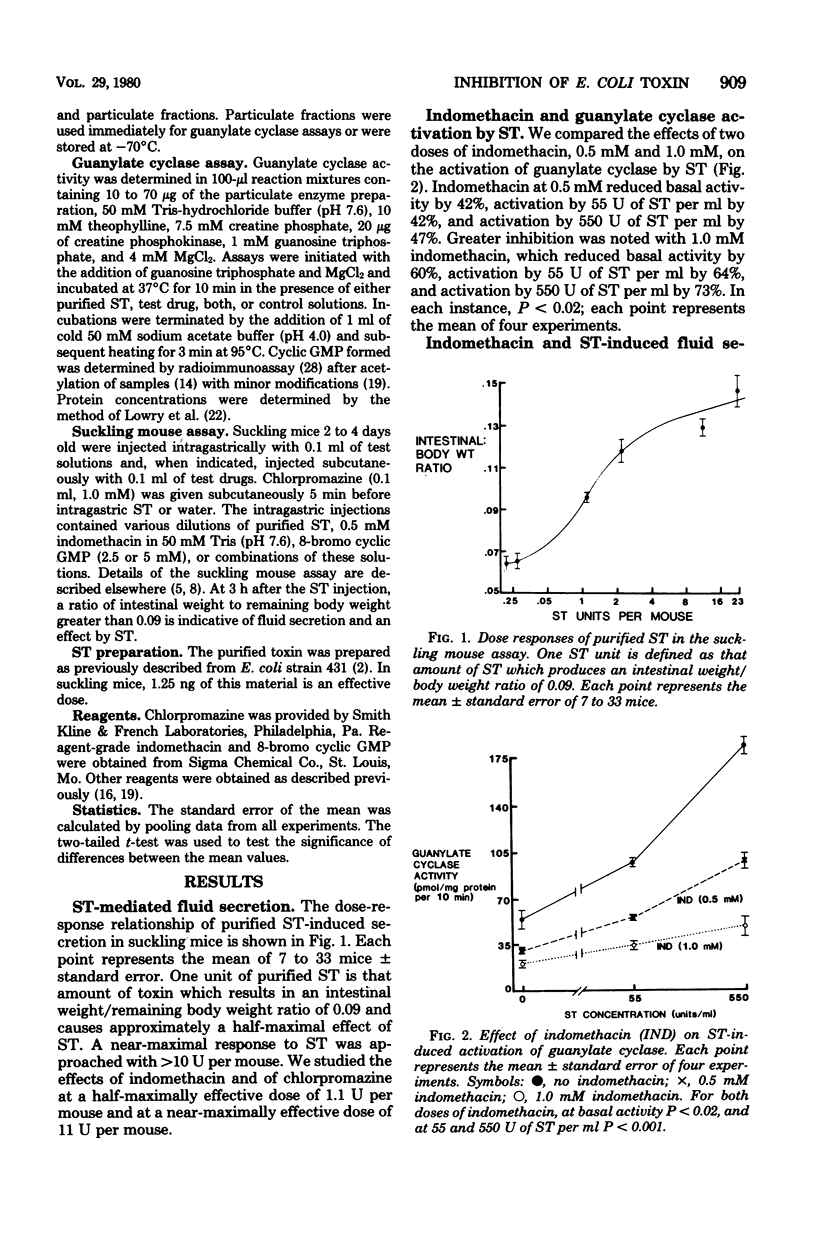
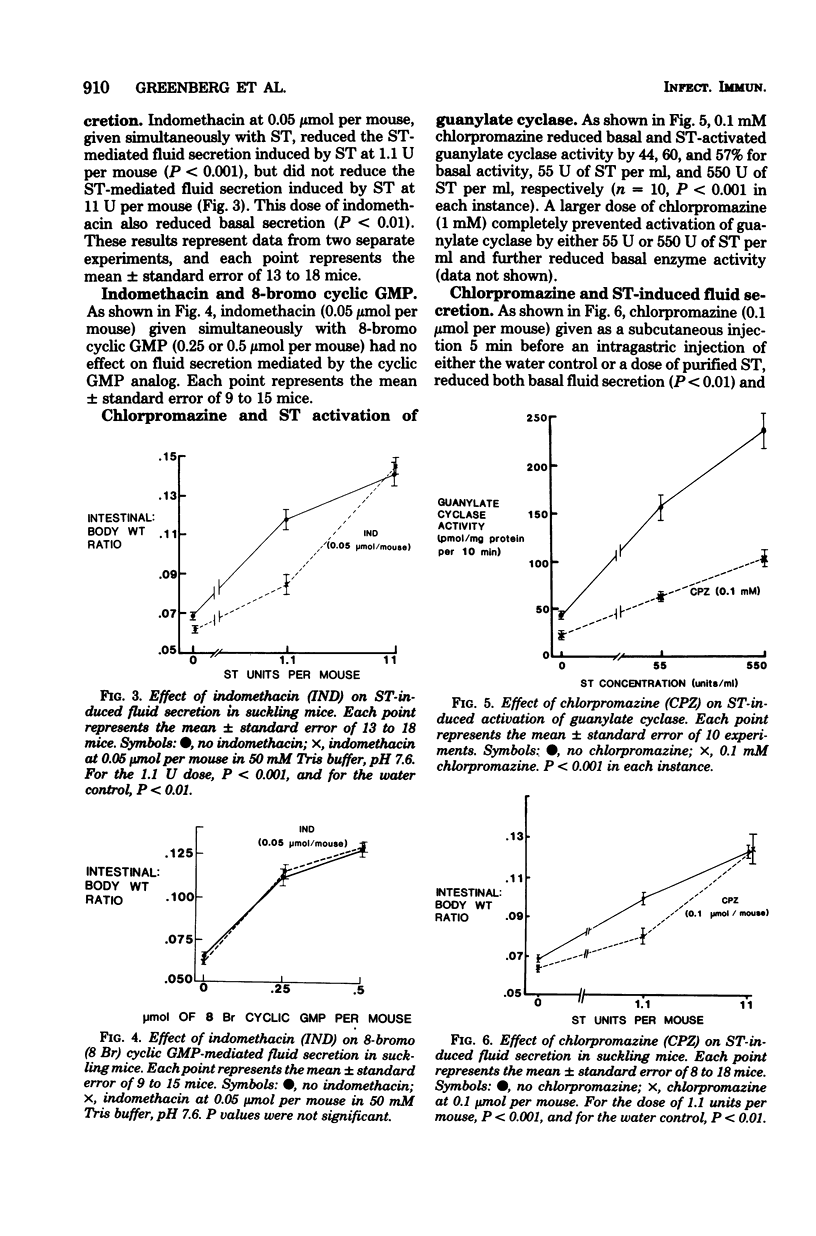
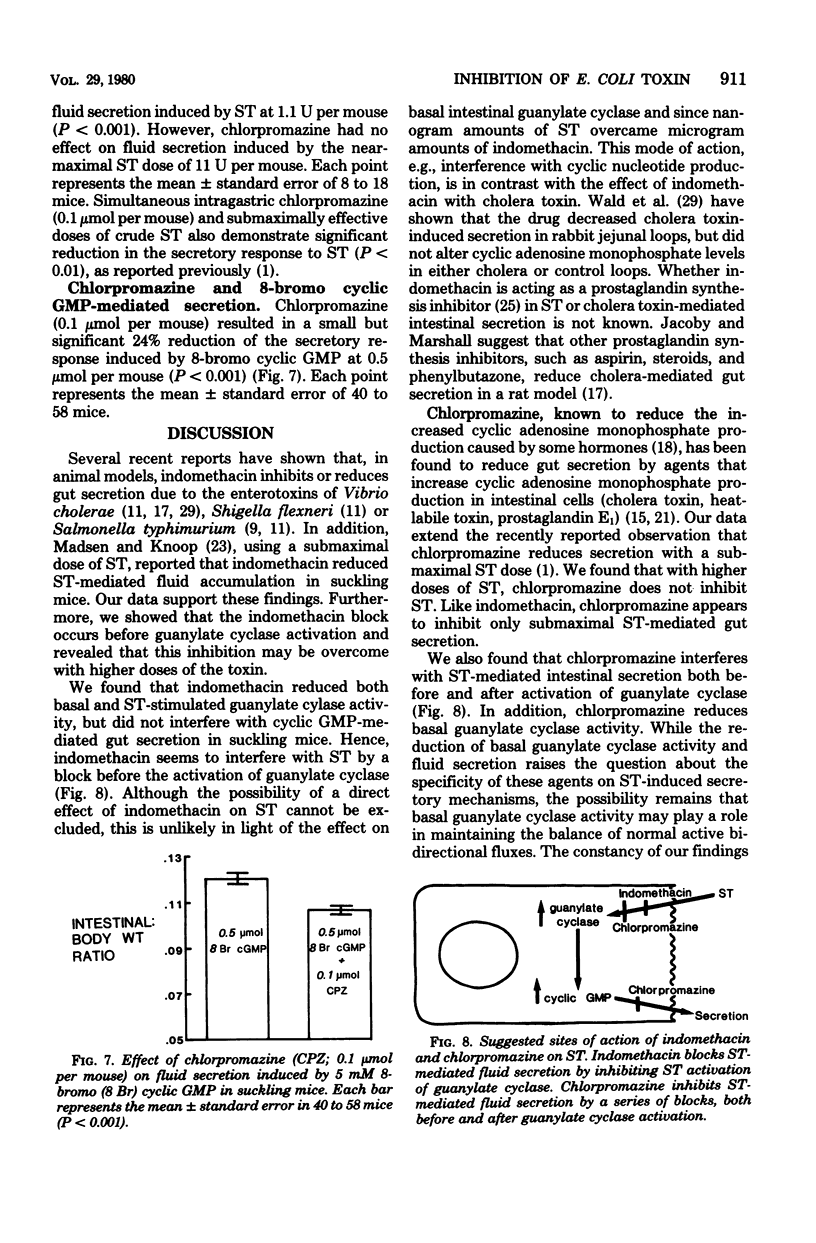
Purified heat-stable enterotoxin (ST) from a procine strain of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli activates quanylate cyclase in particulate fractions of rat intestinal tissue and induces fluid accumulation in suckling mice. These effects of ST were examined in the presence of either indomethacin or chlorpromazine. We also examined the effects of these two drugs on fluid accumulation in suckling mice induced by the 8-bromo analog of cyclic guanosine monophosphate. Either indomethacin or chlorpromazine reduced ST activation of guanylate cyclase. Both drugs also reduced intestinal fluid accumulation in suckling mice that resulted from submaximal doses of ST (both P < 0.001). However, there was no reduction in fluid secretion by either drug when a maximally effective dose of ST was used, suggesting that inhibition of fluid secretion by both drugs can be overcome by increasing the ST dose and that a threshold level of guanylate cyclase activity results in maximal secretory response. Both drugs also reduced basal guanylate cylase activity in rat intestinal tissue and fluid secreton in suckling mice. Chlorpromazine also reduced intestinal secretion mediated by 8-bromo cyclic guanosine monophosphate (P < 0.001). These findings indicate that chlorpromazine interferes with the effects of ST both before and after its activation of guanylate cyclase, whereas indomethacin interfers with ST only before its activation of guanylate cyclase.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbey D. M., Knoop F. C. Effect of chlorpromazine on the secretory activity of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1000–1003. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1000-1003.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Robertson D. C. Purification and chemical characterization of the heat-stable enterotoxin produced by porcine strains of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1021–1030. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1021-1030.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. C., Rohde J. E., Sharp G. W. Intestinal adenyl-cyclase activity in human cholera. Lancet. 1971 May 8;1(7706):939–941. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91443-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G., Heikkila R. E. The generation of hydrogen peroxide, superoxide radical, and hydroxyl radical by 6-hydroxydopamine, dialuric acid, and related cytotoxic agents. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 25;249(8):2447–2452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Chen L. C., Curlin G. T., Evans D. G. Stimulation of adenyl cyclase by Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Nat New Biol. 1972 Apr 5;236(66):137–138. doi: 10.1038/newbio236137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Graf L. H., Jr, Laird W. J., Smith P. L. Heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: in vitro effects on guanylate cyclase activity, cyclic GMP concentration, and ion transport in small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2800–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Rout W. R., Formal S. B. Effect of indomethacin on intestinal water transport in salmonella-infected rhesus monkeys. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):136–139. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.136-139.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A. Suckling mouse model for detection of heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin: characteristics of the model. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):95–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.95-99.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gots R. E., Formal S. B., Giannella R. A. Indomethacin inhibition of Salmonella typhimurium, Shigella flexneri, and cholera-mediated rabbit ileal secretion. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):280–284. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Chen L. C., Sharp G. W. Intestinal adenyl-cyclase activity in canine cholera: correlation with fluid accumulation. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):377–381. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Ganguly U., Casper A. G., Moore E. J., Pierce N. F., Carpenter C. C. Effect of Escherichia coli on fluid transport across canine small bowel. Mechanism and time-course with enterotoxin and whole bacterial cells. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jul;52(7):1707–1714. doi: 10.1172/JCI107352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. F., Brooker G. Femtomole sensitive radioimmunoassay for cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP after 2'0 acetylation by acetic anhydride in aqueous solution. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;1(4):207–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lange S., Lönnroth I. Reversal of cyclic AMP-mediated intestinal secretion in mice by chlorpromazine. Gastroenterology. 1978 Dec;75(6):1103–1108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. M., Murad F., Chang B., Guerrant R. L. Role of cyclic GMP in the action of heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1978 Feb 23;271(5647):755–756. doi: 10.1038/271755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby H. I., Marshall C. H. Antagonism of cholera enterotoxin by anti-inflammatory agents in the rat. Nature. 1972 Jan 21;235(5334):163–165. doi: 10.1038/235163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsuki S., Murad F. Regulation of adenosine cyclic 3',5'-monophosphate and guanosine cyclic 3',5'-monophosphate levels and contractility in bovine tracheal smooth muscle. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;13(2):330–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnroth I., Andrén B., Lange S., Martinsson K., Holmgren J. Chlorpromazine reverses diarrhea in piglets caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):900–905. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.900-905.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnroth I., Holmgren J., Lange S. Chlorpromazine inhibits cholera toxin-induced intestinal hypersecretion. Med Biol. 1977 Jun;55(3):126–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsome P. M., Burgess M. N., Mullan N. A. Effect of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin on cyclic GMP levels in mouse intestine. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):290–291. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.290-291.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickander R., McMahon F. G., Ridolfo A. S. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1979;19:469–490. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.19.040179.002345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbani G. H., Greenough W. B., 3rd, Holmgren J., Lönnroth I. Chlorpromazine reduces fluid-loss in cholera. Lancet. 1979 Feb 24;1(8113):410–412. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90885-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. The membrane actions of anesthetics and tranquilizers. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Dec;24(4):583–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner A. L., Parker C. W., Kipnis D. M. Radioimmunoassay for cyclic nucleotides. I. Preparation of antibodies and iodinated cyclic nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1106–1113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald A., Gotterer G. S., Rajendra G. R., Turjman N. A., Hendrix T. R. Effect of indomethacin on cholera-induced fluid movement, unidirectional sodium fluxes, and intestinal cAMP. Gastroenterology. 1977 Jan;72(1):106–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff D. J., Brostrom C. O. Properties and functions of the calcium-dependent regulator protein. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;11:27–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


